备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
scikit-learn 1.3的发布亮点#
我们很高兴宣布scikit-learn 1.3的发布!添加了许多错误修复和改进,以及一些新的关键功能。我们在下面详细介绍了该版本的一些主要功能。 For an exhaustive list of all the changes ,请参阅 release notes .
安装最新版本(使用pip):
pip install --upgrade scikit-learn
或带有conda::
conda install -c conda-forge scikit-learn
元数据路由#
我们正在引入一种新的方式来路由元数据,例如 sample_weight 整个代码库,这将影响元估计器(例如 pipeline.Pipeline 和 model_selection.GridSearchCV 路由元数据。虽然此功能的基础架构已经包含在此版本中,但工作仍在进行中,并非所有元估计器都支持此新功能。您可以在 Metadata Routing User Guide .请注意,此功能仍在开发中,尚未为大多数元估计器实现。
第三方开发人员已经可以开始将其纳入他们的元估计器中。详情见 metadata routing developer guide .
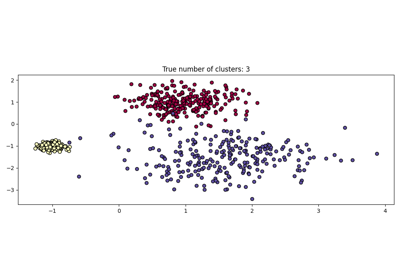
HDSCAN:基于密度的分层集群#
最初托管在scikit-learn-contrib存储库中, cluster.HDBSCAN 已经被引入scikit-learn。它缺少了原始实现中的一些功能,这些功能将在未来的版本中添加。通过执行修改后的 cluster.DBSCAN 同时超过多个预设值, cluster.HDBSCAN 发现不同密度的集群,使其对参数选择比 cluster.DBSCAN .更多详情请参阅 User Guide .
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import HDBSCAN
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import v_measure_score
X, true_labels = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
print(f"number of digits: {len(np.unique(true_labels))}")
hdbscan = HDBSCAN(min_cluster_size=15).fit(X)
non_noisy_labels = hdbscan.labels_[hdbscan.labels_ != -1]
print(f"number of clusters found: {len(np.unique(non_noisy_labels))}")
print(v_measure_score(true_labels[hdbscan.labels_ != -1], non_noisy_labels))
number of digits: 10
number of clusters found: 11
0.9694898472080092
Target Encoder:一种新的类别编码策略#
非常适合具有高基数的类别特征, preprocessing.TargetEncoder 基于属于该类别的观察的平均目标值的缩小估计对类别进行编码。更多详情请参阅 User Guide .
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import TargetEncoder
X = np.array([["cat"] * 30 + ["dog"] * 20 + ["snake"] * 38], dtype=object).T
y = [90.3] * 30 + [20.4] * 20 + [21.2] * 38
enc = TargetEncoder(random_state=0)
X_trans = enc.fit_transform(X, y)
enc.encodings_
[array([90.3, 20.4, 21.2])]
决策树中缺失的值支持#
的类 tree.DecisionTreeClassifier 和 tree.DecisionTreeRegressor 现在支持缺失的值。对于非缺失数据上的每个潜在阈值,拆分器将评估将所有缺失值转移到左节点或右节点的拆分。请参阅更多详细信息 User Guide 或看到 梯度增强树的梯度中的功能 有关此功能的用例示例 HistGradientBoostingRegressor .
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
X = np.array([0, 1, 6, np.nan]).reshape(-1, 1)
y = [0, 0, 1, 1]
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0).fit(X, y)
tree.predict(X)
array([0, 0, 1, 1])
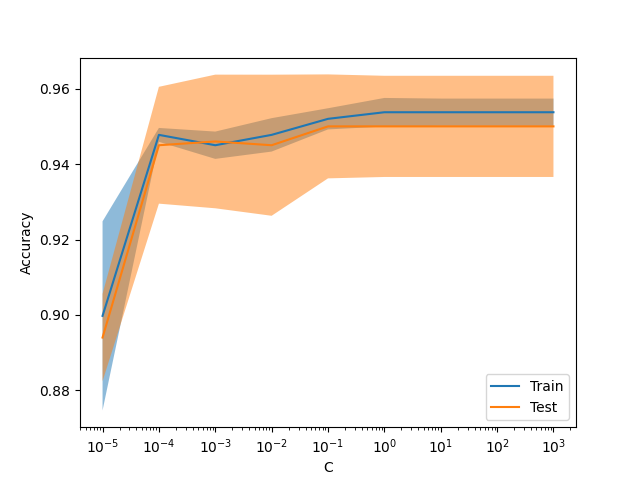
新型显示 ValidationCurveDisplay#
model_selection.ValidationCurveDisplay is now available to plot results
from model_selection.validation_curve.
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import ValidationCurveDisplay
X, y = make_classification(1000, 10, random_state=0)
_ = ValidationCurveDisplay.from_estimator(
LogisticRegression(),
X,
y,
param_name="C",
param_range=np.geomspace(1e-5, 1e3, num=9),
score_type="both",
score_name="Accuracy",
)
梯度增强的伽玛损失#
类 ensemble.HistGradientBoostingRegressor 通过支持Gamma偏差损失功能 loss="gamma" .此损失函数对于对具有右偏分布的严格正目标建模非常有用。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_low_rank_matrix
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
n_samples, n_features = 500, 10
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X = make_low_rank_matrix(n_samples, n_features, random_state=rng)
coef = rng.uniform(low=-10, high=20, size=n_features)
y = rng.gamma(shape=2, scale=np.exp(X @ coef) / 2)
gbdt = HistGradientBoostingRegressor(loss="gamma")
cross_val_score(gbdt, X, y).mean()
np.float64(0.46858513287221654)
删除不常见的类别 OrdinalEncoder#
类似于 preprocessing.OneHotEncoder ,班级 preprocessing.OrdinalEncoder 现在支持将不常见的类别聚合到每个功能的单个输出中。支持收集不常见类别的参数包括 min_frequency 和 max_categories .看到 User Guide 了解更多详细信息。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder
X = np.array(
[["dog"] * 5 + ["cat"] * 20 + ["rabbit"] * 10 + ["snake"] * 3], dtype=object
).T
enc = OrdinalEncoder(min_frequency=6).fit(X)
enc.infrequent_categories_
[array(['dog', 'snake'], dtype=object)]
Total running time of the script: (0分1.098秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _