备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
目标编码器的内部交叉拟合#
的 TargetEncoder 用该类别目标变量的缩小平均值替换分类特征的每个类别。这种方法在类别特征和目标之间存在强关系的情况下很有用。为了防止过度贴合, TargetEncoder.fit_transform 使用内部 cross fitting 对下游模型使用的训练数据进行编码的方案。该计划涉及将数据拆分为 k 折叠并使用另一个折叠学习的编码对每个折叠进行编码 k-1 折叠。在这个例子中,我们展示了交叉配合程序对于防止过度配合的重要性。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
创建合成数据集#
对于本示例,我们构建一个具有三个类别特征的数据集:
具有中等基数的信息特征(“信息”)
具有中等基数的无信息特征(“洗牌”)
具有高基数的无信息特征(“near_unique”)
首先,我们生成信息功能:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
n_samples = 50_000
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
y = rng.randn(n_samples)
noise = 0.5 * rng.randn(n_samples)
n_categories = 100
kbins = KBinsDiscretizer(
n_bins=n_categories,
encode="ordinal",
strategy="uniform",
random_state=rng,
subsample=None,
)
X_informative = kbins.fit_transform((y + noise).reshape(-1, 1))
# Remove the linear relationship between y and the bin index by permuting the
# values of X_informative:
permuted_categories = rng.permutation(n_categories)
X_informative = permuted_categories[X_informative.astype(np.int32)]
具有中等基数的无信息特征通过置换信息特征并移除与目标的关系来生成:
X_shuffled = rng.permutation(X_informative)
生成具有高基数的无信息特征,使其独立于目标变量。我们将表明,没有 cross fitting 将导致下游回归源灾难性的过度装配。这些高基数特征基本上是样本的唯一标识符,通常应该从机器学习数据集中删除这些样本。在这个例子中,我们生成它们来展示如何 TargetEncoder 的默认 cross fitting 行为会自动缓解过度匹配问题。
X_near_unique_categories = rng.choice(
int(0.9 * n_samples), size=n_samples, replace=True
).reshape(-1, 1)
最后,我们组装数据集并执行火车测试拆分:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = pd.DataFrame(
np.concatenate(
[X_informative, X_shuffled, X_near_unique_categories],
axis=1,
),
columns=["informative", "shuffled", "near_unique"],
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
训练山脊回归者#
在本节中,我们在有和没有编码的数据集上训练岭回归器,并探索有和没有内部编码的目标编码器的影响。 cross fitting .首先,我们看到在原始特征上训练的Ridge模型的性能很低。这是因为我们排列了信息性特征含义的顺序 X_informative 原始时不提供信息:
import sklearn
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
# Configure transformers to always output DataFrames
sklearn.set_config(transform_output="pandas")
ridge = Ridge(alpha=1e-6, solver="lsqr", fit_intercept=False)
raw_model = ridge.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Raw Model score on training set: ", raw_model.score(X_train, y_train))
print("Raw Model score on test set: ", raw_model.score(X_test, y_test))
Raw Model score on training set: 0.0049896314219659565
Raw Model score on test set: 0.004577621581492997
接下来,我们使用目标编码器和山脊模型创建一个管道。管道使用 TargetEncoder.fit_transform 它使用 cross fitting .我们看到该模型很好地适合数据并推广到测试集:
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import TargetEncoder
model_with_cf = make_pipeline(TargetEncoder(random_state=0), ridge)
model_with_cf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Model with CF on train set: ", model_with_cf.score(X_train, y_train))
print("Model with CF on test set: ", model_with_cf.score(X_test, y_test))
Model with CF on train set: 0.8000184677460305
Model with CF on test set: 0.7927845601690917
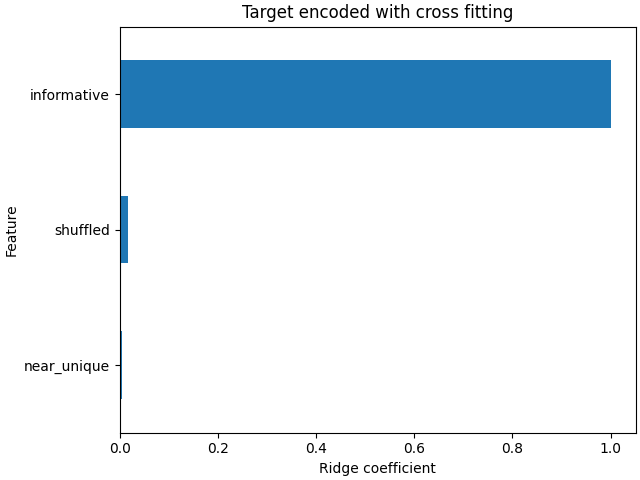
线性模型的系数表明,大部分权重位于列索引0处的特征上,该特征是信息性特征
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
plt.rcParams["figure.constrained_layout.use"] = True
coefs_cf = pd.Series(
model_with_cf[-1].coef_, index=model_with_cf[-1].feature_names_in_
).sort_values()
ax = coefs_cf.plot(kind="barh")
_ = ax.set(
title="Target encoded with cross fitting",
xlabel="Ridge coefficient",
ylabel="Feature",
)
而 TargetEncoder.fit_transform 使用内部 cross fitting 学习训练集编码的方案, TargetEncoder.transform 本身并不。它使用完整的训练集来学习编码并转换类别特征。因此,我们可以使用 TargetEncoder.fit 其次是 TargetEncoder.transform 禁用 cross fitting .然后将此编码传递到脊模型。
target_encoder = TargetEncoder(random_state=0)
target_encoder.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_train_no_cf_encoding = target_encoder.transform(X_train)
X_test_no_cf_encoding = target_encoder.transform(X_test)
model_no_cf = ridge.fit(X_train_no_cf_encoding, y_train)
我们评估没有使用的模型 cross fitting 当编码并看到它过度适合:
print(
"Model without CF on training set: ",
model_no_cf.score(X_train_no_cf_encoding, y_train),
)
print(
"Model without CF on test set: ",
model_no_cf.score(
X_test_no_cf_encoding,
y_test,
),
)
Model without CF on training set: 0.858486250088675
Model without CF on test set: 0.6338211367102258
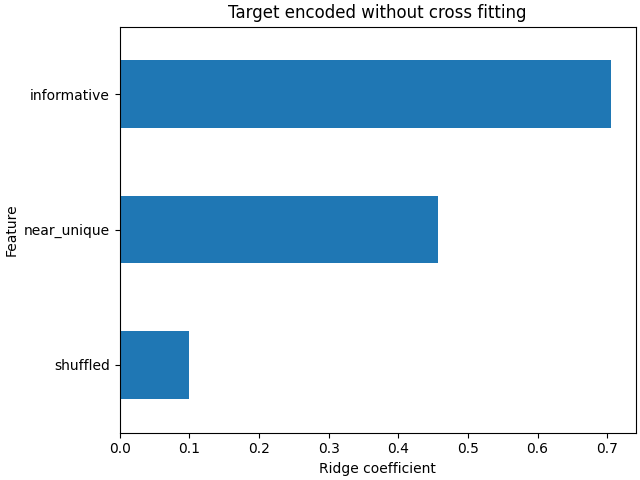
岭模型过度适合,因为它为无信息的极高基数(“near_unique”)和中等基数(“shuffled”)特征赋予了比使用模型时更多的权重 cross fitting 对特征进行编码。
coefs_no_cf = pd.Series(
model_no_cf.coef_, index=model_no_cf.feature_names_in_
).sort_values()
ax = coefs_no_cf.plot(kind="barh")
_ = ax.set(
title="Target encoded without cross fitting",
xlabel="Ridge coefficient",
ylabel="Feature",
)
结论#
This example demonstrates the importance of TargetEncoder's internal
cross fitting. It is important to use
TargetEncoder.fit_transform to encode training data before passing it
to a machine learning model. When a TargetEncoder is a part of a
Pipeline and the pipeline is fitted, the pipeline
will correctly call TargetEncoder.fit_transform and use
cross fitting when encoding the training data.
Total running time of the script: (0分0.281秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _