备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
具有多重共线或相关特征的排列重要性#
在这个例子中,我们计算 permutation_importance 训练过的特征 RandomForestClassifier 使用 威斯康星州乳腺癌(诊断)数据集 .该模型可以轻松获得测试数据集约97%的准确率。由于该数据集包含多共线特征,因此排列重要性表明没有一个特征是重要的,这与高测试准确性相矛盾。
我们演示了一种处理多重共线性的可能方法,其中包括对特征的Spearman等级顺序相关性进行分层集群、选择阈值以及从每个集群中保留单个特征。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
随机森林特征对乳腺癌数据的重要性#
首先,我们定义一个函数来简化绘制:
import matplotlib
from sklearn.inspection import permutation_importance
from sklearn.utils.fixes import parse_version
def plot_permutation_importance(clf, X, y, ax):
result = permutation_importance(clf, X, y, n_repeats=10, random_state=42, n_jobs=2)
perm_sorted_idx = result.importances_mean.argsort()
# `labels` argument in boxplot is deprecated in matplotlib 3.9 and has been
# renamed to `tick_labels`. The following code handles this, but as a
# scikit-learn user you probably can write simpler code by using `labels=...`
# (matplotlib < 3.9) or `tick_labels=...` (matplotlib >= 3.9).
tick_labels_parameter_name = (
"tick_labels"
if parse_version(matplotlib.__version__) >= parse_version("3.9")
else "labels"
)
tick_labels_dict = {tick_labels_parameter_name: X.columns[perm_sorted_idx]}
ax.boxplot(result.importances[perm_sorted_idx].T, vert=False, **tick_labels_dict)
ax.axvline(x=0, color="k", linestyle="--")
return ax
然后我们训练 RandomForestClassifier 上 威斯康星州乳腺癌(诊断)数据集 并在测试集上评估其准确性:
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True, as_frame=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(f"Baseline accuracy on test data: {clf.score(X_test, y_test):.2}")
Baseline accuracy on test data: 0.97
接下来,我们绘制基于树的特征重要性和排列重要性。排列重要性是在训练集中计算的,以显示模型在训练期间对每个特征的依赖程度。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
mdi_importances = pd.Series(clf.feature_importances_, index=X_train.columns)
tree_importance_sorted_idx = np.argsort(clf.feature_importances_)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 8))
mdi_importances.sort_values().plot.barh(ax=ax1)
ax1.set_xlabel("Gini importance")
plot_permutation_importance(clf, X_train, y_train, ax2)
ax2.set_xlabel("Decrease in accuracy score")
fig.suptitle(
"Impurity-based vs. permutation importances on multicollinear features (train set)"
)
_ = fig.tight_layout()

左侧的图显示了该模型的基尼重要性。作为scikit-learn的实现 RandomForestClassifier 使用一个随机子集, \(\sqrt{n_\text{features}}\) 每次分裂时的特征,它能够稀释任何单个相关特征的主导地位。因此,个体特征重要性可以在相关特征之间更均匀地分布。由于特征具有很大的基数并且分类器是非过适应的,因此我们可以相对信任这些值。
右侧图中的置换重要性表明,置换要素最多会降低准确度 0.012 ,这表明这些功能都不重要。这与作为基线计算的高测试准确性相矛盾:某些特征必须很重要。
同样,在测试集中计算的准确性分数的变化似乎是偶然驱动的:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 6))
plot_permutation_importance(clf, X_test, y_test, ax)
ax.set_title("Permutation Importances on multicollinear features\n(test set)")
ax.set_xlabel("Decrease in accuracy score")
_ = ax.figure.tight_layout()
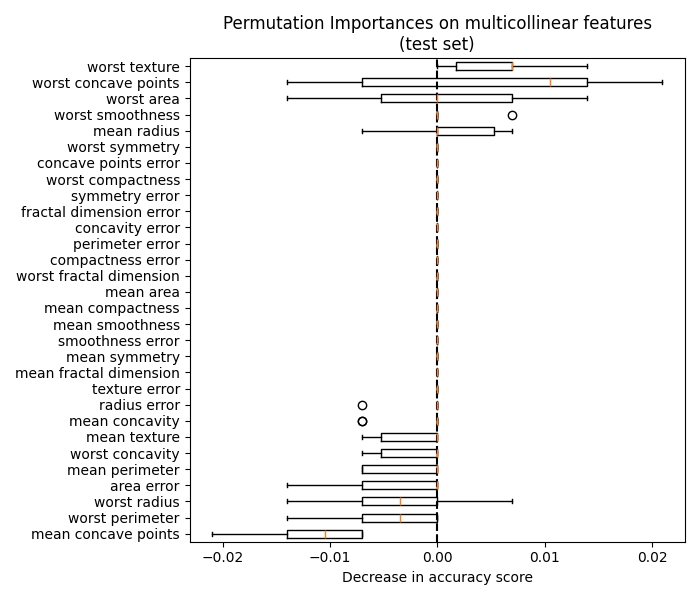
然而,在存在相关特征的情况下,仍然可以计算有意义的排列重要性,如以下部分所示。
处理多共线特征#
当特征共线时,置换一个特征对模型性能影响很小,因为它可以从相关特征获得相同的信息。请注意,并非所有预测模型都属于这种情况,而是取决于其底层实现。
处理多共线特征的一种方法是对Spearman等级顺序相关性执行分层集群,选择阈值,并从每个集群中保留单个特征。首先,我们绘制相关特征的热图:
from scipy.cluster import hierarchy
from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform
from scipy.stats import spearmanr
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 8))
corr = spearmanr(X).correlation
# Ensure the correlation matrix is symmetric
corr = (corr + corr.T) / 2
np.fill_diagonal(corr, 1)
# We convert the correlation matrix to a distance matrix before performing
# hierarchical clustering using Ward's linkage.
distance_matrix = 1 - np.abs(corr)
dist_linkage = hierarchy.ward(squareform(distance_matrix))
dendro = hierarchy.dendrogram(
dist_linkage, labels=X.columns.to_list(), ax=ax1, leaf_rotation=90
)
dendro_idx = np.arange(0, len(dendro["ivl"]))
ax2.imshow(corr[dendro["leaves"], :][:, dendro["leaves"]])
ax2.set_xticks(dendro_idx)
ax2.set_yticks(dendro_idx)
ax2.set_xticklabels(dendro["ivl"], rotation="vertical")
ax2.set_yticklabels(dendro["ivl"])
_ = fig.tight_layout()
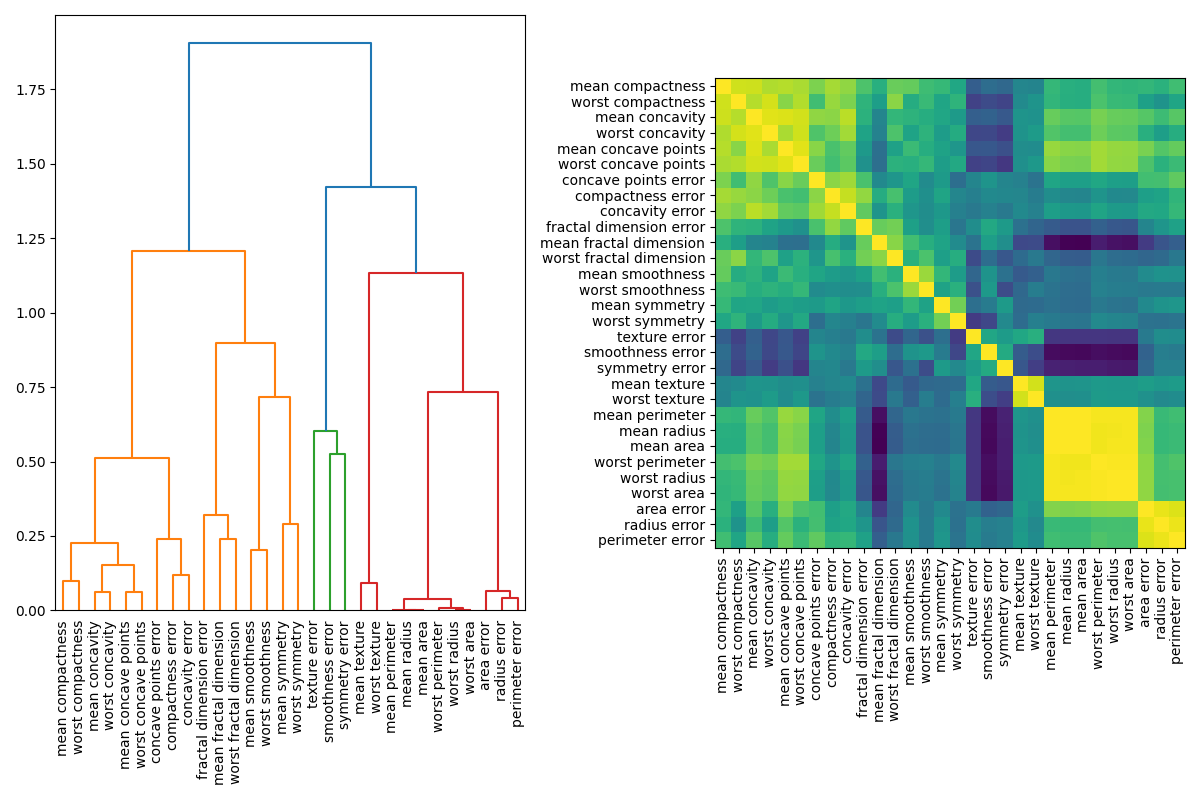
接下来,我们通过视觉检查树图来手动选择一个阈值,将我们的特征分组到集群中,并从每个集群中选择一个要保留的特征,从我们的数据集中选择这些特征,并训练新的随机森林。与在完整数据集上训练的随机森林相比,新随机森林的测试准确性没有太大变化。
from collections import defaultdict
cluster_ids = hierarchy.fcluster(dist_linkage, 1, criterion="distance")
cluster_id_to_feature_ids = defaultdict(list)
for idx, cluster_id in enumerate(cluster_ids):
cluster_id_to_feature_ids[cluster_id].append(idx)
selected_features = [v[0] for v in cluster_id_to_feature_ids.values()]
selected_features_names = X.columns[selected_features]
X_train_sel = X_train[selected_features_names]
X_test_sel = X_test[selected_features_names]
clf_sel = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
clf_sel.fit(X_train_sel, y_train)
print(
"Baseline accuracy on test data with features removed:"
f" {clf_sel.score(X_test_sel, y_test):.2}"
)
Baseline accuracy on test data with features removed: 0.97
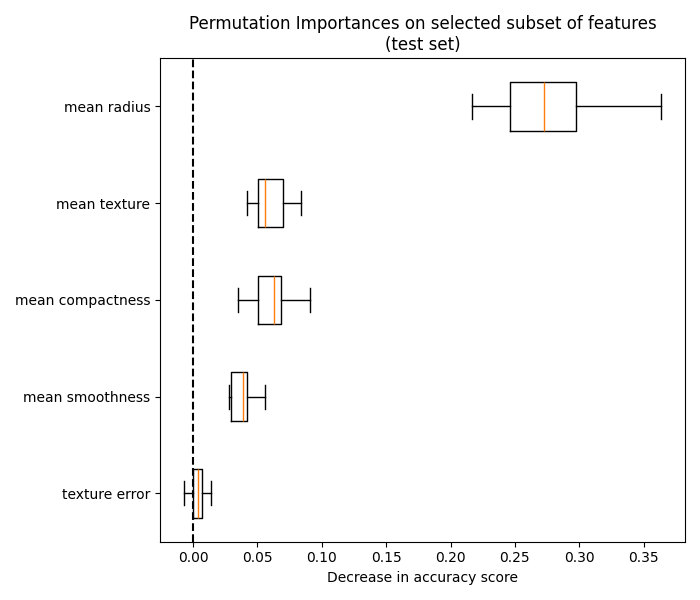
我们最终可以探索所选特征子集的排列重要性:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 6))
plot_permutation_importance(clf_sel, X_test_sel, y_test, ax)
ax.set_title("Permutation Importances on selected subset of features\n(test set)")
ax.set_xlabel("Decrease in accuracy score")
ax.figure.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0分5.377秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _