备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
收缩协方差估计:LedoitWolf vs OAS和最大似然#
当使用协方差估计时,通常的方法是使用最大似然估计器,例如 EmpiricalCovariance .它是无偏的,即当给出许多观察时,它收敛于真实(总体)协方差。然而,为了减少其方差,对其进行规则化也可能是有益的;这反过来又会引入一些偏见。这个例子说明了在 收缩协方差 估计器。特别是,它重点关注如何设置正规化量,即如何选择偏差方差权衡。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成示例数据#
import numpy as np
n_features, n_samples = 40, 20
np.random.seed(42)
base_X_train = np.random.normal(size=(n_samples, n_features))
base_X_test = np.random.normal(size=(n_samples, n_features))
# Color samples
coloring_matrix = np.random.normal(size=(n_features, n_features))
X_train = np.dot(base_X_train, coloring_matrix)
X_test = np.dot(base_X_test, coloring_matrix)
计算测试数据的可能性#
from scipy import linalg
from sklearn.covariance import ShrunkCovariance, empirical_covariance, log_likelihood
# spanning a range of possible shrinkage coefficient values
shrinkages = np.logspace(-2, 0, 30)
negative_logliks = [
-ShrunkCovariance(shrinkage=s).fit(X_train).score(X_test) for s in shrinkages
]
# under the ground-truth model, which we would not have access to in real
# settings
real_cov = np.dot(coloring_matrix.T, coloring_matrix)
emp_cov = empirical_covariance(X_train)
loglik_real = -log_likelihood(emp_cov, linalg.inv(real_cov))
比较设置正规化参数的不同方法#
在这里我们比较了3种方法:
根据潜在收缩参数网格,通过三倍交叉验证可能性来设置参数。
Ledoit和Wolf提出了一个计算渐进最优正规化参数(最小化SSE准则)的封闭公式,得到
LedoitWolf协方差估计。对Ledoit-Wolf收缩率的改进,
OAS,由Chen等人提出。在假设数据是高斯的情况下,其收敛性明显更好,特别是对于小样本。
from sklearn.covariance import OAS, LedoitWolf
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# GridSearch for an optimal shrinkage coefficient
tuned_parameters = [{"shrinkage": shrinkages}]
cv = GridSearchCV(ShrunkCovariance(), tuned_parameters)
cv.fit(X_train)
# Ledoit-Wolf optimal shrinkage coefficient estimate
lw = LedoitWolf()
loglik_lw = lw.fit(X_train).score(X_test)
# OAS coefficient estimate
oa = OAS()
loglik_oa = oa.fit(X_train).score(X_test)
图结果#
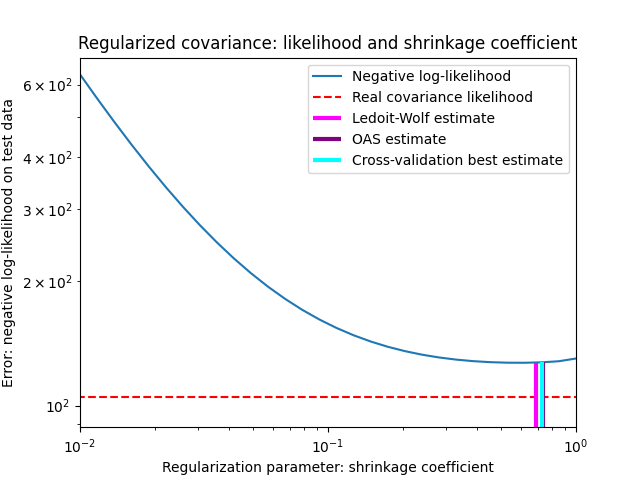
为了量化估计误差,我们绘制了不同收缩参数值的未见数据的可能性。我们还通过交叉验证或LedoitWolf和OAS估计来显示选择。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Regularized covariance: likelihood and shrinkage coefficient")
plt.xlabel("Regularization parameter: shrinkage coefficient")
plt.ylabel("Error: negative log-likelihood on test data")
# range shrinkage curve
plt.loglog(shrinkages, negative_logliks, label="Negative log-likelihood")
plt.plot(plt.xlim(), 2 * [loglik_real], "--r", label="Real covariance likelihood")
# adjust view
lik_max = np.amax(negative_logliks)
lik_min = np.amin(negative_logliks)
ymin = lik_min - 6.0 * np.log((plt.ylim()[1] - plt.ylim()[0]))
ymax = lik_max + 10.0 * np.log(lik_max - lik_min)
xmin = shrinkages[0]
xmax = shrinkages[-1]
# LW likelihood
plt.vlines(
lw.shrinkage_,
ymin,
-loglik_lw,
color="magenta",
linewidth=3,
label="Ledoit-Wolf estimate",
)
# OAS likelihood
plt.vlines(
oa.shrinkage_, ymin, -loglik_oa, color="purple", linewidth=3, label="OAS estimate"
)
# best CV estimator likelihood
plt.vlines(
cv.best_estimator_.shrinkage,
ymin,
-cv.best_estimator_.score(X_test),
color="cyan",
linewidth=3,
label="Cross-validation best estimate",
)
plt.ylim(ymin, ymax)
plt.xlim(xmin, xmax)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
备注
最大似然估计对应于无收缩,因此表现不佳。Ledoit-Wolf估计的表现非常好,因为它接近最佳估计,并且计算成本不高。在这个例子中,OAS的估计有点远。有趣的是,这两种方法的性能都优于交叉验证,后者的计算成本明显最高。
Total running time of the script: (0分0.334秒)
相关实例
Normal, Ledoit-Wolf and OAS Linear Discriminant Analysis for classification
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _