备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
最近邻分类#
此示例说明如何使用 KNeighborsClassifier .我们在虹膜数据集上训练这样的分类器,并观察所获得的决策边界相对于参数的差异 weights .
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
加载数据#
在本例中,我们使用虹膜数据集。我们将数据拆分为训练和测试数据集。
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = load_iris(as_frame=True)
X = iris.data[["sepal length (cm)", "sepal width (cm)"]]
y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, random_state=0)
K近邻分类器#
我们希望使用k近邻分类器,考虑11个数据点的邻居。由于我们的k近邻模型使用欧几里得距离来寻找最近邻居,因此提前缩放数据非常重要。请参阅标题为 特征缩放的重要性 了解更多详细信息。
因此,我们使用 Pipeline 在使用我们的分类器之前链接一个缩放器。
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
clf = Pipeline(
steps=[("scaler", StandardScaler()), ("knn", KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=11))]
)
决策边界#
现在,我们用不同的参数值来适应两个分类器 weights .我们绘制每个分类器的决策边界以及原始数据集以观察差异。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay
_, axs = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12, 5))
for ax, weights in zip(axs, ("uniform", "distance")):
clf.set_params(knn__weights=weights).fit(X_train, y_train)
disp = DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator(
clf,
X_test,
response_method="predict",
plot_method="pcolormesh",
xlabel=iris.feature_names[0],
ylabel=iris.feature_names[1],
shading="auto",
alpha=0.5,
ax=ax,
)
scatter = disp.ax_.scatter(X.iloc[:, 0], X.iloc[:, 1], c=y, edgecolors="k")
disp.ax_.legend(
scatter.legend_elements()[0],
iris.target_names,
loc="lower left",
title="Classes",
)
_ = disp.ax_.set_title(
f"3-Class classification\n(k={clf[-1].n_neighbors}, weights={weights!r})"
)
plt.show()
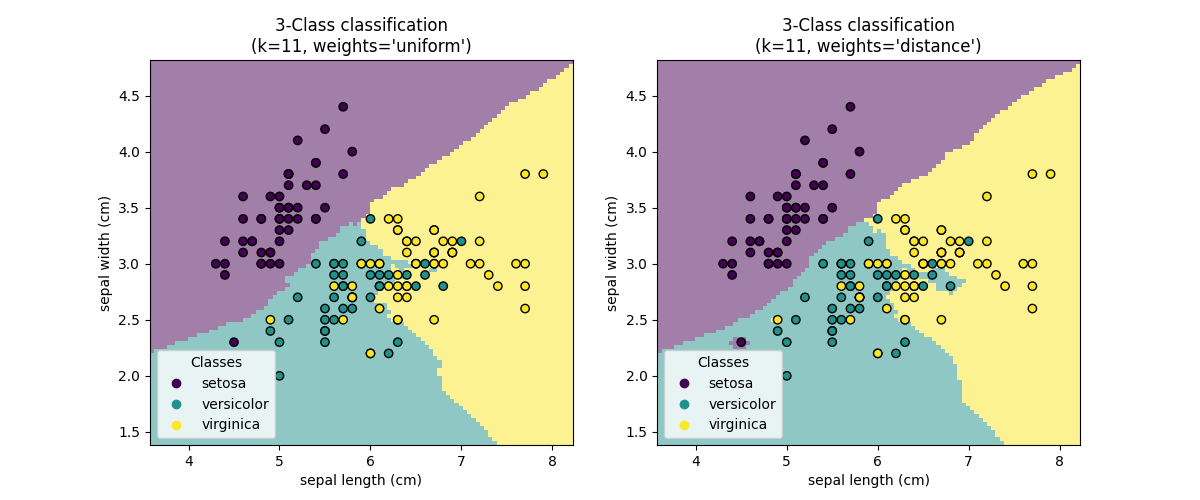
结论#
我们观察到该参数 weights 对决策边界有影响。当 weights="unifom" 所有最近的邻居都会对决定产生相同的影响。而当 weights="distance" 赋予每个邻居的权重与该邻居到查询点的距离的倒数成正比。
In some cases, taking the distance into account might improve the model.
Total running time of the script: (0分0.439秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _