备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
使用树木集合的特征转换#
将您的特征转换为更高维的稀疏空间。然后在这些特征上训练线性模型。
首先在训练集中适应一组树(完全随机树、随机森林或梯度增强树)。然后,为集成中每棵树的每片叶子分配新特征空间中的固定任意特征索引。然后以一次性方式编码这些叶子索引。
每个样本都会经过整个系统中每棵树的决策,最终得到每棵树的一片叶子。通过将这些叶子的特征值设置为1,将其他特征值设置为0来编码样本。
然后,生成的Transformer学习了数据的监督、稀疏、高维分类嵌入。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
首先,我们将创建一个大型数据集并将其分为三组:
训练集成方法的集合,这些方法后来用作特征工程Transformer;
训练线性模型的集合;
一组测试线性模型。
重要的是以这种方式分割数据,以避免泄漏数据的过拟合。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=80_000, random_state=10)
X_full_train, X_test, y_full_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=10
)
X_train_ensemble, X_train_linear, y_train_ensemble, y_train_linear = train_test_split(
X_full_train, y_full_train, test_size=0.5, random_state=10
)
对于每种集成方法,我们将使用10个估计器和3个级别的最大深度。
n_estimators = 10
max_depth = 3
首先,我们将首先在分离的训练集中训练随机森林和梯度提升
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier, RandomForestClassifier
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=n_estimators, max_depth=max_depth, random_state=10
)
random_forest.fit(X_train_ensemble, y_train_ensemble)
gradient_boosting = GradientBoostingClassifier(
n_estimators=n_estimators, max_depth=max_depth, random_state=10
)
_ = gradient_boosting.fit(X_train_ensemble, y_train_ensemble)
注意到 HistGradientBoostingClassifier 远快于 GradientBoostingClassifier 从中间数据集开始 (n_samples >= 10_000 ),而本示例的情况并非如此。
的 RandomTreesEmbedding 是一种无监督的方法,因此不需要独立训练。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomTreesEmbedding
random_tree_embedding = RandomTreesEmbedding(
n_estimators=n_estimators, max_depth=max_depth, random_state=0
)
现在,我们将创建三个管道,将上述嵌入用作预处理阶段。
随机树嵌入可以通过逻辑回归直接流水线化,因为它是标准的scikit-learn Transformer。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
rt_model = make_pipeline(random_tree_embedding, LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000))
rt_model.fit(X_train_linear, y_train_linear)
然后,我们可以通过逻辑回归管道随机森林或梯度提升。但是,要素转换将通过调用方法进行 apply . scikit-learn中的管道预计接到电话 transform .因此,我们将调用包装为 apply 内 FunctionTransformer .
from sklearn.preprocessing import FunctionTransformer, OneHotEncoder
def rf_apply(X, model):
return model.apply(X)
rf_leaves_yielder = FunctionTransformer(rf_apply, kw_args={"model": random_forest})
rf_model = make_pipeline(
rf_leaves_yielder,
OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore"),
LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000),
)
rf_model.fit(X_train_linear, y_train_linear)
def gbdt_apply(X, model):
return model.apply(X)[:, :, 0]
gbdt_leaves_yielder = FunctionTransformer(
gbdt_apply, kw_args={"model": gradient_boosting}
)
gbdt_model = make_pipeline(
gbdt_leaves_yielder,
OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore"),
LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000),
)
gbdt_model.fit(X_train_linear, y_train_linear)
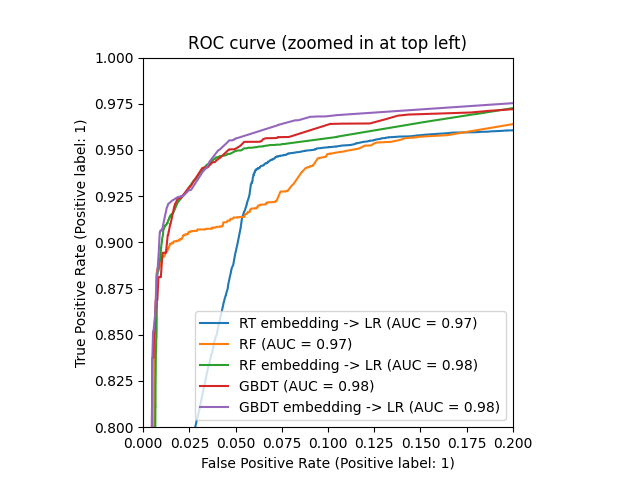
我们最终可以显示所有模型的不同ROC曲线。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import RocCurveDisplay
_, ax = plt.subplots()
models = [
("RT embedding -> LR", rt_model),
("RF", random_forest),
("RF embedding -> LR", rf_model),
("GBDT", gradient_boosting),
("GBDT embedding -> LR", gbdt_model),
]
model_displays = {}
for name, pipeline in models:
model_displays[name] = RocCurveDisplay.from_estimator(
pipeline, X_test, y_test, ax=ax, name=name
)
_ = ax.set_title("ROC curve")

_, ax = plt.subplots()
for name, pipeline in models:
model_displays[name].plot(ax=ax)
ax.set_xlim(0, 0.2)
ax.set_ylim(0.8, 1)
_ = ax.set_title("ROC curve (zoomed in at top left)")
Total running time of the script: (0分2.428秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _