备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
scikit-learn 0.24发布亮点#
我们很高兴宣布scikit-learn 0.24的发布!添加了许多错误修复和改进,以及一些新的关键功能。我们在下面详细介绍了该版本的一些主要功能。 For an exhaustive list of all the changes ,请参阅 release notes .
安装最新版本(使用pip):
pip install --upgrade scikit-learn
或带有conda::
conda install -c conda-forge scikit-learn
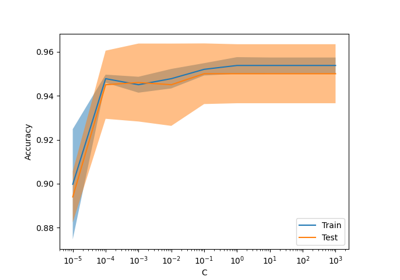
超参数整定的逐次减半估计#
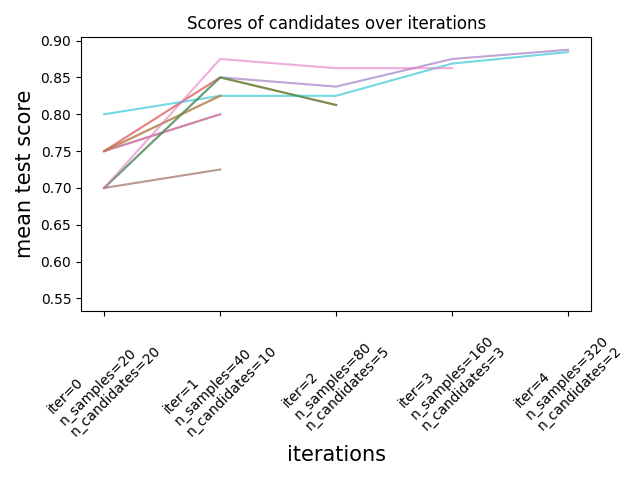
连续减半是一种最先进的方法,现在可以探索参数的空间并确定其最佳组合。 HalvingGridSearchCV 和 HalvingRandomSearchCV 可用作临时替代品 GridSearchCV 和 RandomizedSearchCV .连续减半是一个迭代选择过程,如下图所示。第一次迭代使用少量资源运行,其中资源通常对应于训练样本的数量,但也可以是任意的整参数,例如 n_estimators 在一片随机的森林中。仅为下一次迭代选择参数候选者的一个子集,该迭代将在分配的资源量不断增加的情况下运行。只有候选项的一个子集会持续到迭代过程结束,并且最佳参数候选项是在最后一次迭代中得分最高的参数。
阅读更多的 User Guide (note:连续减半估计值仍然 experimental ).
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import randint
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.experimental import enable_halving_search_cv # noqa: F401
from sklearn.model_selection import HalvingRandomSearchCV
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=700, random_state=rng)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=rng)
param_dist = {
"max_depth": [3, None],
"max_features": randint(1, 11),
"min_samples_split": randint(2, 11),
"bootstrap": [True, False],
"criterion": ["gini", "entropy"],
}
rsh = HalvingRandomSearchCV(
estimator=clf, param_distributions=param_dist, factor=2, random_state=rng
)
rsh.fit(X, y)
rsh.best_params_
{'bootstrap': True, 'criterion': 'gini', 'max_depth': None, 'max_features': 10, 'min_samples_split': 10}
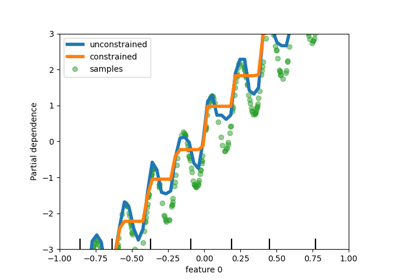
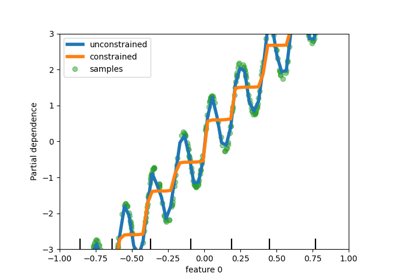
对HistorentBoosting估计器中分类特征的本地支持#
HistGradientBoostingClassifier 和 HistGradientBoostingRegressor 现在有了对分类特征的原生支持:它们可以考虑对无序的分类数据进行拆分。阅读更多的 User Guide .
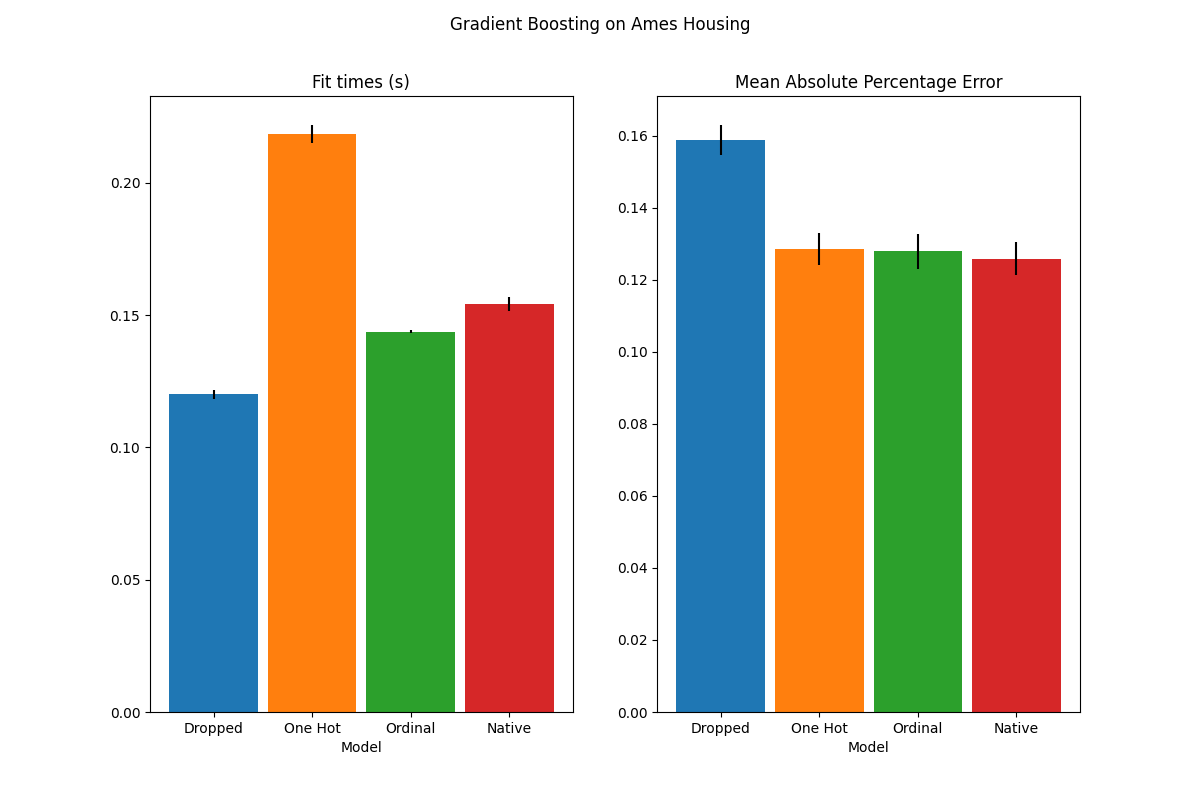
该图显示,对类别特征的新本地支持导致的匹配时间与类别被视为有序量(即简单地顺序编码)的模型相当。原生支持也比单一热编码和有序编码更具表达力。然而,要使用新的 categorical_features 参数,仍然需要对管道内的数据进行预处理,如本文所示 example .
改进HistorentBoosting估计器的性能#
的内存占用 ensemble.HistGradientBoostingRegressor 和 ensemble.HistGradientBoostingClassifier 在致电期间,情况显着改善 fit. In addition, histogram initialization is now done in parallel which results in slight speed improvements. See more in the Benchmark page .
一种新的自训练元估计器#
一种新的自我训练实现,基于 Yarowski's algorithm 现在可以与任何实现 predict_proba .子分类器将充当半监督分类器,允许它从未标记的数据中学习。阅读更多的 User guide .
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.semi_supervised import SelfTrainingClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
iris = datasets.load_iris()
random_unlabeled_points = rng.rand(iris.target.shape[0]) < 0.3
iris.target[random_unlabeled_points] = -1
svc = SVC(probability=True, gamma="auto")
self_training_model = SelfTrainingClassifier(svc)
self_training_model.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
新的SequentialMetureMetrics Transformer#
提供了一个新的迭代Transformer来选择特征: SequentialFeatureSelector .顺序特征选择可以根据交叉验证的分数最大化,一次添加一个特征(向前选择)或从可用特征列表中删除特征(向后选择)。看到 User Guide .
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.feature_selection import SequentialFeatureSelector
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True, as_frame=True)
feature_names = X.columns
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
sfs = SequentialFeatureSelector(knn, n_features_to_select=2)
sfs.fit(X, y)
print(
"Features selected by forward sequential selection: "
f"{feature_names[sfs.get_support()].tolist()}"
)
Features selected by forward sequential selection: ['sepal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
新的PolynomialCountSketch核逼近函数#
新 PolynomialCountSketch 与线性模型一起使用时,逼近特征空间的多项扩展,但使用的内存比 PolynomialFeatures .
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_covtype
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import PolynomialCountSketch
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
X, y = fetch_covtype(return_X_y=True)
pipe = make_pipeline(
MinMaxScaler(),
PolynomialCountSketch(degree=2, n_components=300),
LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000),
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, train_size=5000, test_size=10000, random_state=42
)
pipe.fit(X_train, y_train).score(X_test, y_test)
0.7335
为了进行比较,以下是相同数据的线性基线的得分:
linear_baseline = make_pipeline(MinMaxScaler(), LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000))
linear_baseline.fit(X_train, y_train).score(X_test, y_test)
0.7141
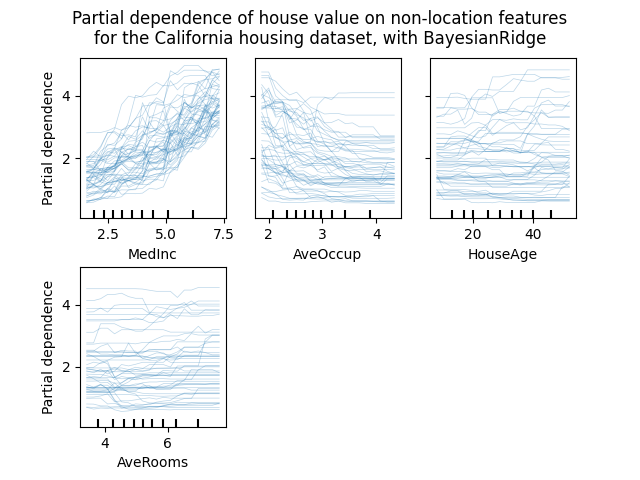
个人条件期望图#
有一种新的部分依赖图可用:个人条件期望(ICE)图。ICE图分别可视化每个样本的预测对特征的依赖性,每个样本有一条线。看到 User Guide
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
# from sklearn.inspection import plot_partial_dependence
from sklearn.inspection import PartialDependenceDisplay
X, y = fetch_california_housing(return_X_y=True, as_frame=True)
features = ["MedInc", "AveOccup", "HouseAge", "AveRooms"]
est = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=10)
est.fit(X, y)
# plot_partial_dependence has been removed in version 1.2. From 1.2, use
# PartialDependenceDisplay instead.
# display = plot_partial_dependence(
display = PartialDependenceDisplay.from_estimator(
est,
X,
features,
kind="individual",
subsample=50,
n_jobs=3,
grid_resolution=20,
random_state=0,
)
display.figure_.suptitle(
"Partial dependence of house value on non-location features\n"
"for the California housing dataset, with BayesianRidge"
)
display.figure_.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3)
一种新的DecisionTreeRegressor Poisson分裂准则#
Poisson回归估计的集成从0.23版本开始继续。 DecisionTreeRegressor 现在支持新的 'poisson' 分裂准则设置 criterion="poisson" 如果您的目标是计数或频率,这可能是一个不错的选择。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
n_samples, n_features = 1000, 20
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X = rng.randn(n_samples, n_features)
# positive integer target correlated with X[:, 5] with many zeros:
y = rng.poisson(lam=np.exp(X[:, 5]) / 2)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=rng)
regressor = DecisionTreeRegressor(criterion="poisson", random_state=0)
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
新的文档改进#
添加了新的示例和文档页面,以不断努力提高对机器学习实践的理解:
示例说明如何 statistically compare the performance of models 评价使用
GridSearchCV,一个 example 主成分回归和偏最小二乘法的比较
Total running time of the script: (0分15.427秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _