备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
具有成本复杂性修剪的后修剪决策树#
的 DecisionTreeClassifier 提供参数,例如 min_samples_leaf 和 max_depth 以防止树木过度生长。成本复杂性修剪提供了另一种控制树大小的选择。在 DecisionTreeClassifier ,这种修剪技术通过成本复杂性参数进行参数化, ccp_alpha .的较大值 ccp_alpha 增加修剪的节点数。这里我们只展示了 ccp_alpha 关于规范树木以及如何选择 ccp_alpha 基于验证分数。
另见 最小成本复杂性修剪 了解有关修剪的详细信息。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
叶片总杂质与修剪树的有效阿尔法#
最小成本复杂性修剪通过迭代找到具有“最弱链接”的节点。最弱的链接以有效阿尔法为特征,其中具有最小有效阿尔法的节点首先被修剪。了解哪些价值观 ccp_alpha scikit-learn提供,可能是合适的 DecisionTreeClassifier.cost_complexity_pruning_path 其在修剪过程的每个步骤返回有效α和相应的总叶杂质。随着α的增加,树的更多部分被修剪,这增加了叶子的总杂质。
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0)
path = clf.cost_complexity_pruning_path(X_train, y_train)
ccp_alphas, impurities = path.ccp_alphas, path.impurities
在下面的图中,最大有效Alpha值被删除,因为它是只有一个节点的平凡树。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(ccp_alphas[:-1], impurities[:-1], marker="o", drawstyle="steps-post")
ax.set_xlabel("effective alpha")
ax.set_ylabel("total impurity of leaves")
ax.set_title("Total Impurity vs effective alpha for training set")
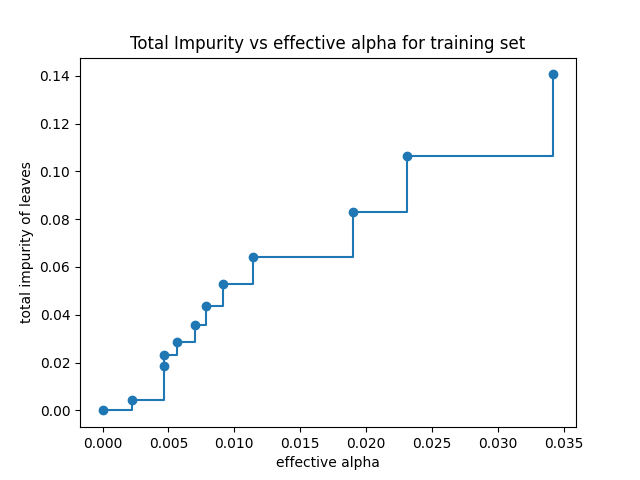
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Total Impurity vs effective alpha for training set')
接下来,我们使用有效的阿尔法来训练决策树。中的最后一个值 ccp_alphas 是修剪整棵树的alpha值,留下树, clfs[-1] ,有一个节点。
clfs = []
for ccp_alpha in ccp_alphas:
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0, ccp_alpha=ccp_alpha)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(clf)
print(
"Number of nodes in the last tree is: {} with ccp_alpha: {}".format(
clfs[-1].tree_.node_count, ccp_alphas[-1]
)
)
Number of nodes in the last tree is: 1 with ccp_alpha: 0.3272984419327777
对于本示例的其余部分,我们删除中的最后一个元素 clfs 和 ccp_alphas ,因为它是只有一个节点的平凡树。在这里,我们表明,随着Alpha的增加,节点数量和树深度会减少。
clfs = clfs[:-1]
ccp_alphas = ccp_alphas[:-1]
node_counts = [clf.tree_.node_count for clf in clfs]
depth = [clf.tree_.max_depth for clf in clfs]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1)
ax[0].plot(ccp_alphas, node_counts, marker="o", drawstyle="steps-post")
ax[0].set_xlabel("alpha")
ax[0].set_ylabel("number of nodes")
ax[0].set_title("Number of nodes vs alpha")
ax[1].plot(ccp_alphas, depth, marker="o", drawstyle="steps-post")
ax[1].set_xlabel("alpha")
ax[1].set_ylabel("depth of tree")
ax[1].set_title("Depth vs alpha")
fig.tight_layout()

训练集和测试集的准确度与alpha#
当 ccp_alpha 设置为零并保持其他默认参数 DecisionTreeClassifier ,树过度匹配,导致100%的训练准确率和88%的测试准确率。随着Alpha的增加,树的更多部分被修剪,从而创建更好地概括的决策树。在本例中,设置 ccp_alpha=0.015 最大限度地提高测试准确性。
train_scores = [clf.score(X_train, y_train) for clf in clfs]
test_scores = [clf.score(X_test, y_test) for clf in clfs]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlabel("alpha")
ax.set_ylabel("accuracy")
ax.set_title("Accuracy vs alpha for training and testing sets")
ax.plot(ccp_alphas, train_scores, marker="o", label="train", drawstyle="steps-post")
ax.plot(ccp_alphas, test_scores, marker="o", label="test", drawstyle="steps-post")
ax.legend()
plt.show()

Total running time of the script: (0分0.340秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _