备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
光谱双集群算法的演示#
此示例演示如何生成棋盘数据集并使用 SpectralBiclustering 算法光谱双集群算法专门设计用于通过同时考虑矩阵的行(样本)和列(特征)来对数据进行集群。它的目标是不仅识别样本之间的模式,而且识别样本子集内的模式,从而检测数据中的局部结构。这使得光谱双集群特别适合特征顺序或排列固定的数据集,例如图像、时间序列或基因组。
生成数据,然后进行混洗并传递到光谱双聚类算法。然后重新排列混洗矩阵的行和列,以绘制找到的双聚类。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成示例数据#
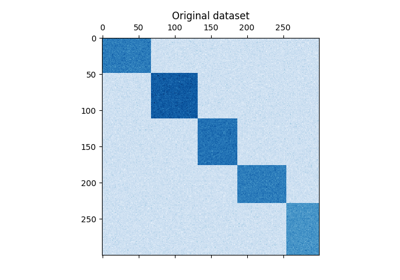
我们使用 make_checkerboard 功能内的每个像素 shape=(300, 300) 用其颜色表示均匀分布的值。噪音是从正态分布添加的,其中选择的值 noise 是标准差。
正如您所看到的,数据分布在12个集群单元中,并且相对较好地区分。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_checkerboard
n_clusters = (4, 3)
data, rows, columns = make_checkerboard(
shape=(300, 300), n_clusters=n_clusters, noise=10, shuffle=False, random_state=42
)
plt.matshow(data, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title("Original dataset")
_ = plt.show()
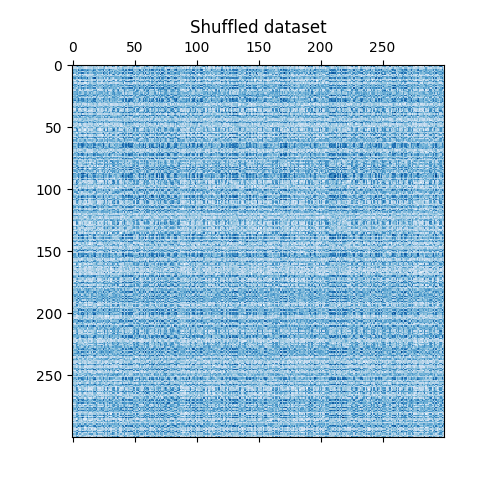
我们对数据进行洗牌,目标是事后使用 SpectralBiclustering .
import numpy as np
# Creating lists of shuffled row and column indices
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
row_idx_shuffled = rng.permutation(data.shape[0])
col_idx_shuffled = rng.permutation(data.shape[1])
我们重新定义洗牌后的数据并绘制它。我们观察到我们丢失了原始数据矩阵的结构。
data = data[row_idx_shuffled][:, col_idx_shuffled]
plt.matshow(data, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title("Shuffled dataset")
_ = plt.show()
拟合 SpectralBiclustering#
我们对模型进行了匹配,并将获得的集群与实际情况进行了比较。请注意,创建模型时,我们指定的集群数量与创建数据集所使用的集群数量相同 (n_clusters = (4, 3) ),这将有助于获得好的结果。
from sklearn.cluster import SpectralBiclustering
from sklearn.metrics import consensus_score
model = SpectralBiclustering(n_clusters=n_clusters, method="log", random_state=0)
model.fit(data)
# Compute the similarity of two sets of biclusters
score = consensus_score(
model.biclusters_, (rows[:, row_idx_shuffled], columns[:, col_idx_shuffled])
)
print(f"consensus score: {score:.1f}")
consensus score: 1.0
分数在0和1之间,其中1对应完美匹配。它显示了双集群的质量。
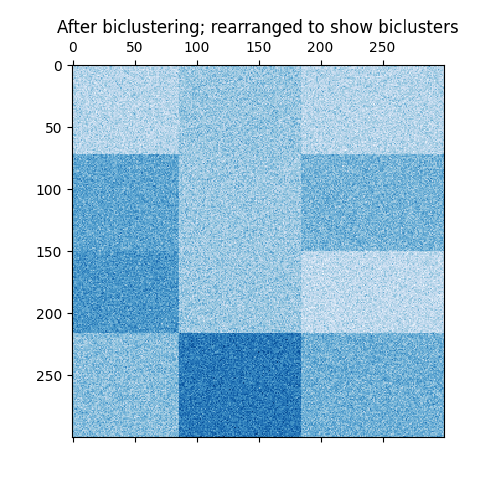
进行绘制的结果#
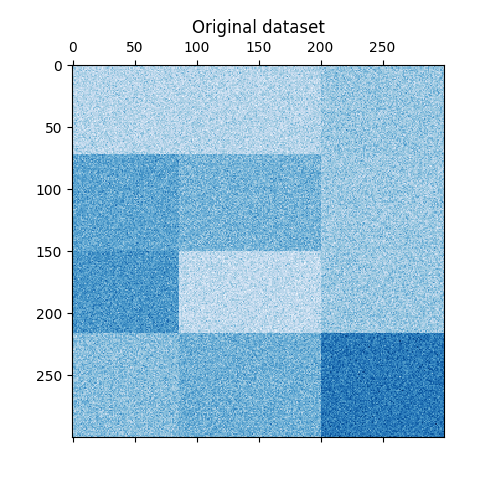
现在,我们根据分配的行和列标签重新排列数据 SpectralBiclustering 按上升顺序建模并再次情节。的 row_labels_ 范围从0到3,而 column_labels_ 范围从0到2,代表每行总共4个集群,每列总共3个集群。
# Reordering first the rows and then the columns.
reordered_rows = data[np.argsort(model.row_labels_)]
reordered_data = reordered_rows[:, np.argsort(model.column_labels_)]
plt.matshow(reordered_data, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title("After biclustering; rearranged to show biclusters")
_ = plt.show()
作为最后一步,我们想要演示模型分配的行标签和列标签之间的关系。因此,我们创建一个网格, numpy.outer ,这需要排序 row_labels_ 和 column_labels_ 并为每个标签添加1,以确保标签从1开始而不是从0开始,以获得更好的可视化。
plt.matshow(
np.outer(np.sort(model.row_labels_) + 1, np.sort(model.column_labels_) + 1),
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
)
plt.title("Checkerboard structure of rearranged data")
plt.show()
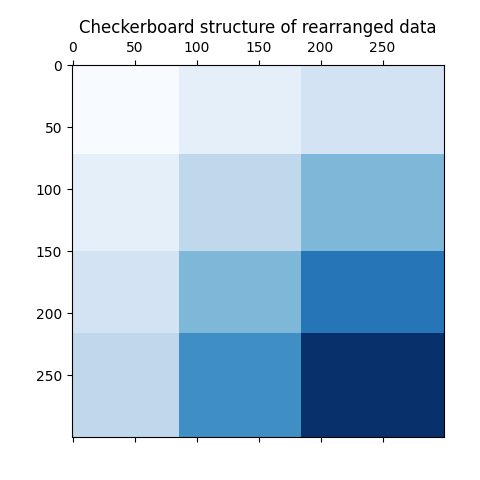
行和列标签载体的外积显示了棋盘结构的表示,其中行和列标签的不同组合由不同的蓝色阴影表示。
Total running time of the script: (0分0.382秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _