备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
scikit-learn 1.0的发布亮点#
我们非常高兴地宣布scikit-learn 1.0正式发布!这个库已经稳定了很长一段时间,发布1.0版本是认识到这一点,并向我们的用户发出信号。除了通常的两个版本弃用周期外,此版本不包括任何中断更改。在未来,我们将尽最大努力保持这种模式。
此版本包括一些新的关键功能以及许多改进和错误修复。我们在下面详细介绍了该版本的一些主要功能。 For an exhaustive list of all the changes ,请参阅 release notes .
安装最新版本(使用pip):
pip install --upgrade scikit-learn
或带有conda::
conda install -c conda-forge scikit-learn
关键词和位置论点#
scikit-learn API公开了许多具有许多输入参数的函数和方法。例如,在此版本之前,可以实例化 HistGradientBoostingRegressor 作为::
HistGradientBoostingRegressor("squared_error", 0.1, 100, 31, None,
20, 0.0, 255, None, None, False, "auto", "loss", 0.1, 10, 1e-7,
0, None)
理解上述代码需要读者查看API文档并检查每个参数的位置和含义。为了提高基于scikit-learn编写的代码的可读性,现在用户必须提供大多数参数及其名称,作为关键字参数,而不是位置参数。例如,上面的代码是::
HistGradientBoostingRegressor(
loss="squared_error",
learning_rate=0.1,
max_iter=100,
max_leaf_nodes=31,
max_depth=None,
min_samples_leaf=20,
l2_regularization=0.0,
max_bins=255,
categorical_features=None,
monotonic_cst=None,
warm_start=False,
early_stopping="auto",
scoring="loss",
validation_fraction=0.1,
n_iter_no_change=10,
tol=1e-7,
verbose=0,
random_state=None,
)
这更具可读性。位置参数自0.23版本以来已被废弃,现在将引发 TypeError .在某些情况下,仍然允许有限数量的立场论点,例如 PCA ,在哪里 PCA(10) 仍然是允许的,但是 PCA(10, False) 不允许。
样条变换器#
将非线性项添加到数据集特征集中的一种方法是使用新的 SplineTransformer .样条是分段多项式,由其多项式次数和节点位置参数化。的 SplineTransformer 实现B样条基础。
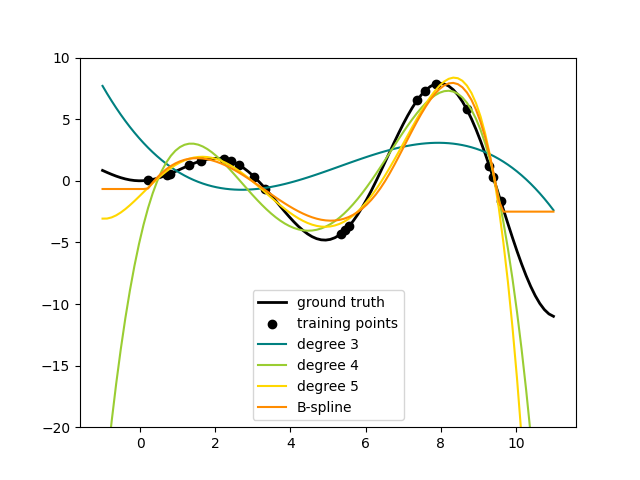
以下代码显示了样条线的作用,有关更多信息,请参阅 User Guide .
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import SplineTransformer
X = np.arange(5).reshape(5, 1)
spline = SplineTransformer(degree=2, n_knots=3)
spline.fit_transform(X)
array([[0.5 , 0.5 , 0. , 0. ],
[0.125, 0.75 , 0.125, 0. ],
[0. , 0.5 , 0.5 , 0. ],
[0. , 0.125, 0.75 , 0.125],
[0. , 0. , 0.5 , 0.5 ]])
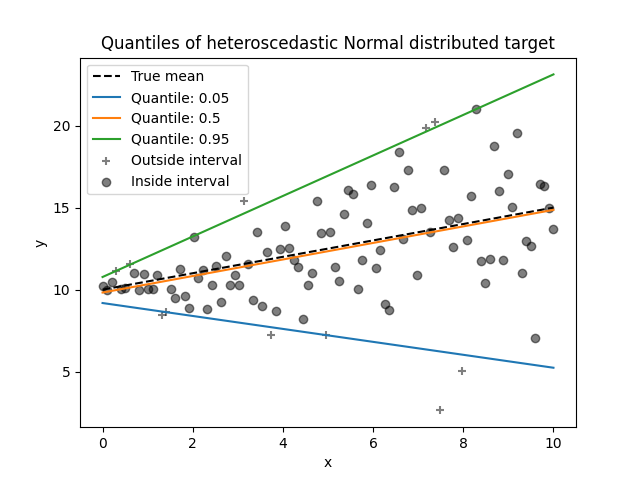
分位数回归#
分位数回归估计的中位数或其他分位数 \(y\) 条件是 \(X\) 而普通最小二乘(OLS)估计条件均值。
作为线性模型,新的 QuantileRegressor 给出线性预测 \(\hat{y}(w, X) = Xw\) 为 \(q\) - 第四分位数, \(q \in (0, 1)\) .权重或系数 \(w\) 然后通过以下最小化问题找到:
这包括弹球损失(也称为线性损失),参见 mean_pinball_loss ,
L1罚分由参数控制 alpha ,类似于 linear_model.Lasso .
请检查以下示例以了解它的工作原理,以及 User Guide 了解更多详细信息。
功能名称支持#
When an estimator is passed a pandas' dataframe during
fit, the estimator will set a feature_names_in_ attribute
containing the feature names. This is a part of
SLEP007.
Note that feature names support is only enabled
when the column names in the dataframe are all strings. feature_names_in_
is used to check that the column names of the dataframe passed in
non-fit, such as predict, are consistent with features in
fit:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
X = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], columns=["a", "b", "c"])
scalar = StandardScaler().fit(X)
scalar.feature_names_in_
array(['a', 'b', 'c'], dtype=object)
的支持 get_feature_names_out 适用于已经有过的变压器 get_feature_names 以及输入和输出之间一一对应的变压器,例如 StandardScaler . get_feature_names_out 在未来的版本中,将向所有其他变压器添加支持。此外, compose.ColumnTransformer.get_feature_names_out 可用于组合其变压器的功能名称:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
X = pd.DataFrame({"pet": ["dog", "cat", "fish"], "age": [3, 7, 1]})
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
[
("numerical", StandardScaler(), ["age"]),
("categorical", OneHotEncoder(), ["pet"]),
],
verbose_feature_names_out=False,
).fit(X)
preprocessor.get_feature_names_out()
array(['age', 'pet_cat', 'pet_dog', 'pet_fish'], dtype=object)
When this preprocessor is used with a pipeline, the feature names used
by the classifier are obtained by slicing and calling
get_feature_names_out:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
y = [1, 0, 1]
pipe = make_pipeline(preprocessor, LogisticRegression())
pipe.fit(X, y)
pipe[:-1].get_feature_names_out()
array(['age', 'pet_cat', 'pet_dog', 'pet_fish'], dtype=object)
更灵活的绘图API#
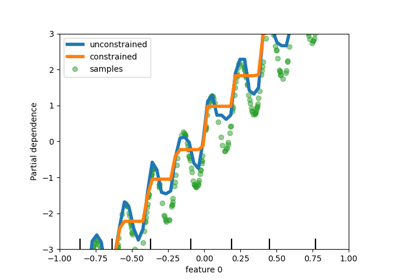
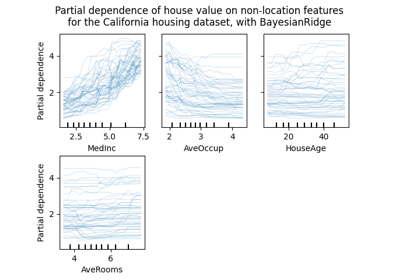
metrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay , metrics.PrecisionRecallDisplay , metrics.DetCurveDisplay ,而且 inspection.PartialDependenceDisplay 现在公开两个类方法: from_estimator 和 from_predictions 这允许用户在给定预测或估计量的情况下创建图。这意味着相应的 plot_* 函数已弃用。请检查 example one 和 example two 了解如何使用新的绘图功能。
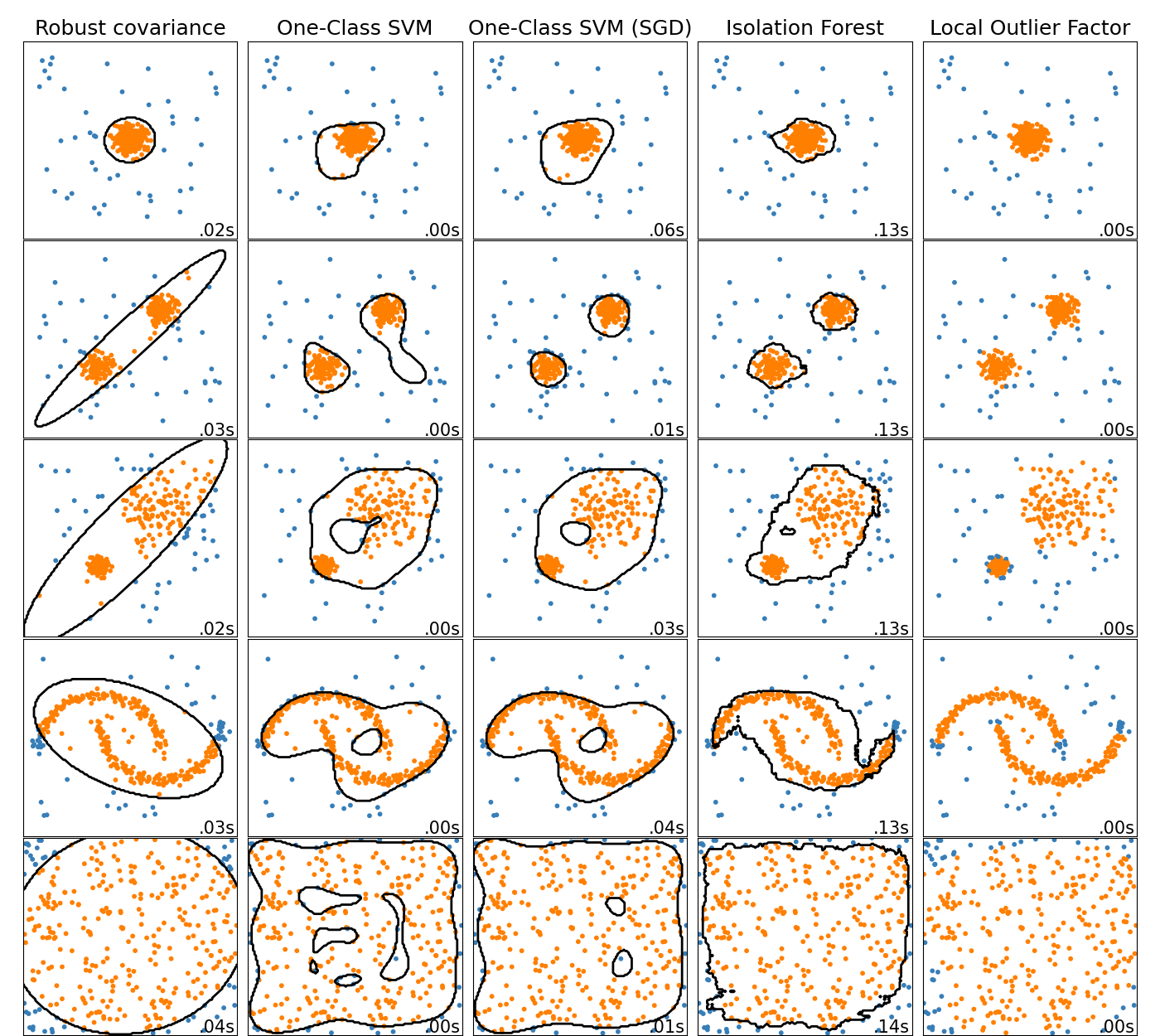
在线一类支持者#
新类 SGDOneClassSVM 使用随机梯度下降实现单类支持机的在线线性版本。结合核逼近技术, SGDOneClassSVM 可用于逼近核化单类支持机的解,在 OneClassSVM ,其适合的时间复杂度与样本数量呈线性关系。请注意,核化的一类支持者的复杂性充其量是样本数量的二次。 SGDOneClassSVM 因此,非常适合具有大量训练样本(> 10,000)的数据集,对于这些数据集,BCD变体可以快几个数量级。请检查这个 example 看看它是如何使用的,以及 User Guide 了解更多详细信息。
基于柱状图的梯度增强模型现已稳定#
HistGradientBoostingRegressor 和 HistGradientBoostingClassifier 不再是实验性的,可以简单地导入并用作::
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingClassifier
新的文档改进#
此版本包括许多文档改进。在2100多个合并的拉取请求中,其中约800个是对我们文档的改进。
Total running time of the script: (0分0.012秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _