备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
单变量特征选择#
该笔记本是使用单变量特征选择来提高有噪数据集分类准确性的一个例子。
在本例中,一些有噪(非信息性)的特征被添加到虹膜数据集中。在应用单变量特征选择之前和之后,使用支持载体机(支持载体机)对数据集进行分类。对于每个特征,我们绘制单变量特征选择的p值以及相应的支持者权重。由此,我们将比较模型准确性并检查单变量特征选择对模型权重的影响。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成示例数据#
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# The iris dataset
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
# Some noisy data not correlated
E = np.random.RandomState(42).uniform(0, 0.1, size=(X.shape[0], 20))
# Add the noisy data to the informative features
X = np.hstack((X, E))
# Split dataset to select feature and evaluate the classifier
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, random_state=0)
单变量特征选择#
单变量特征选择,使用F检验进行特征评分。我们使用默认选择功能来选择四个最重要的功能。
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, f_classif
selector = SelectKBest(f_classif, k=4)
selector.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores = -np.log10(selector.pvalues_)
scores /= scores.max()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
X_indices = np.arange(X.shape[-1])
plt.figure(1)
plt.clf()
plt.bar(X_indices - 0.05, scores, width=0.2)
plt.title("Feature univariate score")
plt.xlabel("Feature number")
plt.ylabel(r"Univariate score ($-Log(p_{value})$)")
plt.show()

在全部功能集中,只有4个原始功能是重要的。我们可以看到,他们在单变量特征选择方面得分最高。
与支持者比较#
没有单变量特征选择
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
clf = make_pipeline(MinMaxScaler(), LinearSVC())
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(
"Classification accuracy without selecting features: {:.3f}".format(
clf.score(X_test, y_test)
)
)
svm_weights = np.abs(clf[-1].coef_).sum(axis=0)
svm_weights /= svm_weights.sum()
Classification accuracy without selecting features: 0.789
单变量特征选择后
clf_selected = make_pipeline(SelectKBest(f_classif, k=4), MinMaxScaler(), LinearSVC())
clf_selected.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(
"Classification accuracy after univariate feature selection: {:.3f}".format(
clf_selected.score(X_test, y_test)
)
)
svm_weights_selected = np.abs(clf_selected[-1].coef_).sum(axis=0)
svm_weights_selected /= svm_weights_selected.sum()
Classification accuracy after univariate feature selection: 0.868
plt.bar(
X_indices - 0.45, scores, width=0.2, label=r"Univariate score ($-Log(p_{value})$)"
)
plt.bar(X_indices - 0.25, svm_weights, width=0.2, label="SVM weight")
plt.bar(
X_indices[selector.get_support()] - 0.05,
svm_weights_selected,
width=0.2,
label="SVM weights after selection",
)
plt.title("Comparing feature selection")
plt.xlabel("Feature number")
plt.yticks(())
plt.axis("tight")
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
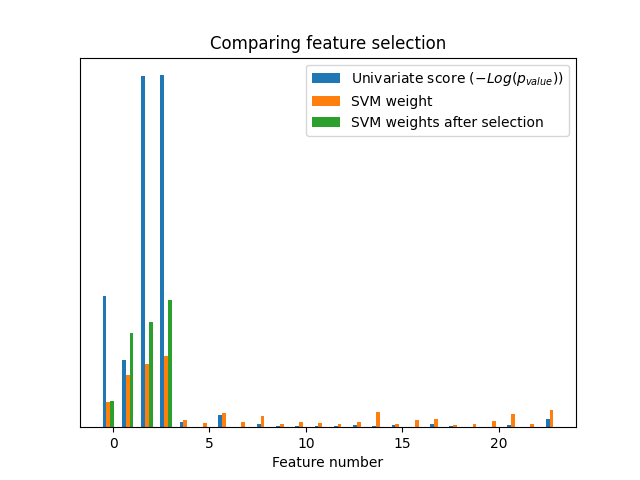
在没有单变量特征选择的情况下,支持者会为前4个原始重要特征分配很大的权重,但也会选择许多非信息特征。在支持者之前应用单变量特征选择可以增加归因于重要特征的支持者权重,从而改善分类。
Total running time of the script: (0分0.128秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _