备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
决策树回归#
In this example, we demonstrate the effect of changing the maximum depth of a decision tree on how it fits to the data. We perform this once on a 1D regression task and once on a multi-output regression task.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
1D回归任务的决策树#
在这里,我们在一维回归任务上拟合一棵树。
的 decision trees 用于在添加噪音观察的情况下匹配sin曲线。结果,它学习逼近sin曲线的局部线性回归。
我们可以看到,如果树的最大深度(由 max_depth 参数)设置得太高,决策树学习训练数据的太细细节并从噪音中学习,即它们过适应。
创建随机1D数据集#
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(5 * rng.rand(80, 1), axis=0)
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
y[::5] += 3 * (0.5 - rng.rand(16))
匹配回归模型#
在这里,我们匹配了两个具有不同最大深度的模型
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
regr_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)
regr_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
regr_1.fit(X, y)
regr_2.fit(X, y)
预测#
获取测试集的预测
X_test = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = regr_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = regr_2.predict(X_test)
绘制结果#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, s=20, edgecolor="black", c="darkorange", label="data")
plt.plot(X_test, y_1, color="cornflowerblue", label="max_depth=2", linewidth=2)
plt.plot(X_test, y_2, color="yellowgreen", label="max_depth=5", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("data")
plt.ylabel("target")
plt.title("Decision Tree Regression")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
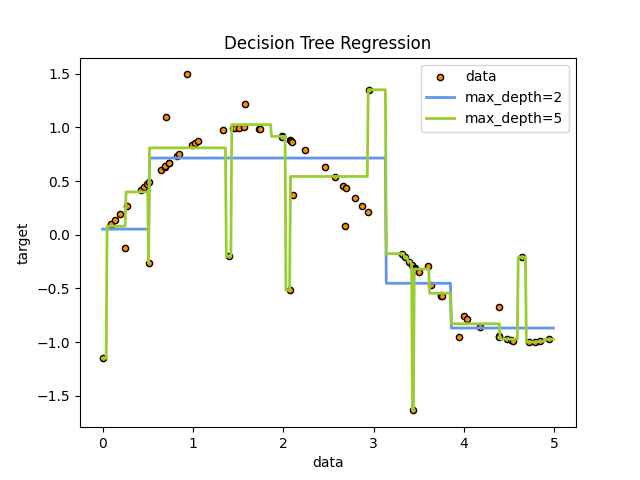
如您所见,深度为5(黄色)的模型学习训练数据的细节,使其过度适合噪音。另一方面,深度为2(蓝色)的模型可以很好地学习数据中的主要趋势,并且不会过度适应。在实际用例中,您需要确保树不会过度适应训练数据,这可以使用交叉验证来完成。
具有多输出目标的决策树回归#
这里 decision trees 用于同时预测噪音 x 和 y 观察一个给定单一基本特征的圆。因此,它学习近似圆的局部线性回归。
我们可以看到,如果树的最大深度(由 max_depth 参数)设置得太高,决策树学习训练数据的太细细节并从噪音中学习,即它们过适应。
创建随机数据集#
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(200 * rng.rand(100, 1) - 100, axis=0)
y = np.array([np.pi * np.sin(X).ravel(), np.pi * np.cos(X).ravel()]).T
y[::5, :] += 0.5 - rng.rand(20, 2)
匹配回归模型#
regr_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)
regr_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
regr_3 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=8)
regr_1.fit(X, y)
regr_2.fit(X, y)
regr_3.fit(X, y)
预测#
获取测试集的预测
X_test = np.arange(-100.0, 100.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = regr_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = regr_2.predict(X_test)
y_3 = regr_3.predict(X_test)
绘制结果#
plt.figure()
s = 25
plt.scatter(y[:, 0], y[:, 1], c="yellow", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="data")
plt.scatter(
y_1[:, 0],
y_1[:, 1],
c="cornflowerblue",
s=s,
edgecolor="black",
label="max_depth=2",
)
plt.scatter(y_2[:, 0], y_2[:, 1], c="red", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="max_depth=5")
plt.scatter(y_3[:, 0], y_3[:, 1], c="blue", s=s, edgecolor="black", label="max_depth=8")
plt.xlim([-6, 6])
plt.ylim([-6, 6])
plt.xlabel("target 1")
plt.ylabel("target 2")
plt.title("Multi-output Decision Tree Regression")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
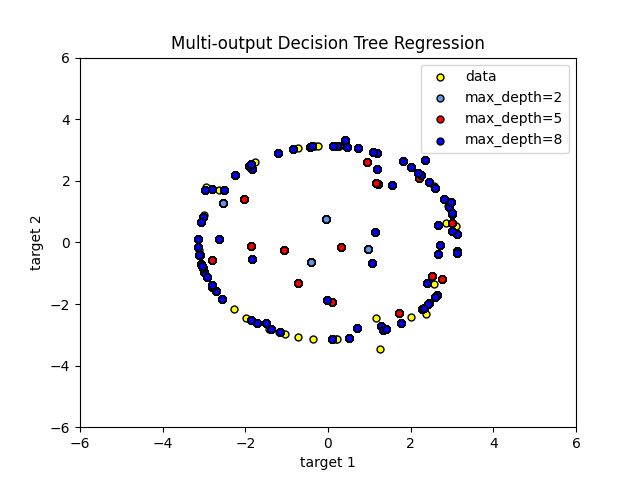
如您所见,的价值越高 max_depth ,模型捕捉到的数据细节就越多。然而,该模型也过度适合数据,并且受到噪音的影响。
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.227 seconds)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _