备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
高斯混合模型选择#
此示例表明可以使用高斯混合模型(GMM)执行模型选择, information-theory criteria .模型选择涉及协方差类型和模型中分量的数量。
在这种情况下,Akaike信息准则(AIC)和Bayes信息准则(BIC)都提供了正确的结果,但我们只演示后者,因为BIC更适合在一组候选者中识别真实模型。与Bayesian程序不同,此类推论是无先验的。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
数据生成#
我们生成两个组件(每个组件包含 n_samples )通过随机抽样返回的标准正态分布 numpy.random.randn .一个组件保持球形,但会发生移动和重新缩放。另一个被变形以具有更通用的协方差矩阵。
import numpy as np
n_samples = 500
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0.0, -0.1], [1.7, 0.4]])
component_1 = np.dot(np.random.randn(n_samples, 2), C) # general
component_2 = 0.7 * np.random.randn(n_samples, 2) + np.array([-4, 1]) # spherical
X = np.concatenate([component_1, component_2])
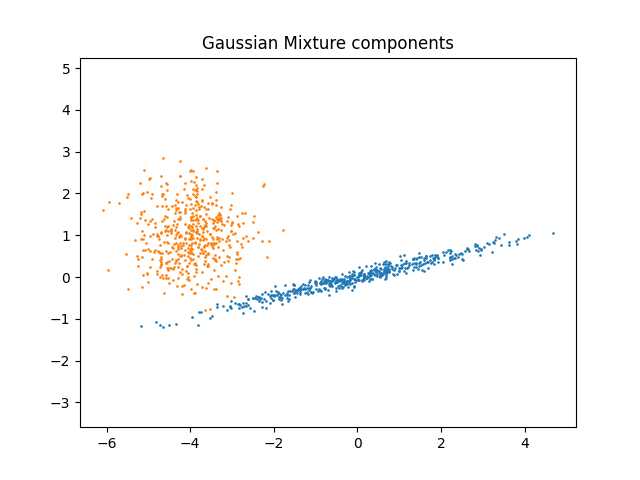
我们可以看到不同的组件:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(component_1[:, 0], component_1[:, 1], s=0.8)
plt.scatter(component_2[:, 0], component_2[:, 1], s=0.8)
plt.title("Gaussian Mixture components")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
模特培训与选拔#
我们将分量的数量从1到6以及要使用的协方差参数类型不同:
"full":每个分量都有自己的一般协方差矩阵。"tied":所有组件共享相同的一般协方差矩阵。"diag":每个分量都有自己的对角协方差矩阵。"spherical":每个分量都有自己的单一方差。
我们对不同的模型进行评分并保留最佳模型(最低的CIC)。这是通过使用 GridSearchCV 以及一个用户定义的分数函数,它返回负的CIC分数,如 GridSearchCV 旨在 maximize 分数(最大化负CIC相当于最小化CIC)。
最佳参数集和估计器存储在 best_parameters_ 和 best_estimator_ ,分别。
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
def gmm_bic_score(estimator, X):
"""Callable to pass to GridSearchCV that will use the BIC score."""
# Make it negative since GridSearchCV expects a score to maximize
return -estimator.bic(X)
param_grid = {
"n_components": range(1, 7),
"covariance_type": ["spherical", "tied", "diag", "full"],
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(
GaussianMixture(), param_grid=param_grid, scoring=gmm_bic_score
)
grid_search.fit(X)
绘制BIC分数#
为了简化绘图,我们可以创建一个 pandas.DataFrame 根据网格搜索完成的交叉验证结果。我们重新颠倒CIC分数的符号,以显示将其最小化的效果。
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(grid_search.cv_results_)[
["param_n_components", "param_covariance_type", "mean_test_score"]
]
df["mean_test_score"] = -df["mean_test_score"]
df = df.rename(
columns={
"param_n_components": "Number of components",
"param_covariance_type": "Type of covariance",
"mean_test_score": "BIC score",
}
)
df.sort_values(by="BIC score").head()
import seaborn as sns
sns.catplot(
data=df,
kind="bar",
x="Number of components",
y="BIC score",
hue="Type of covariance",
)
plt.show()

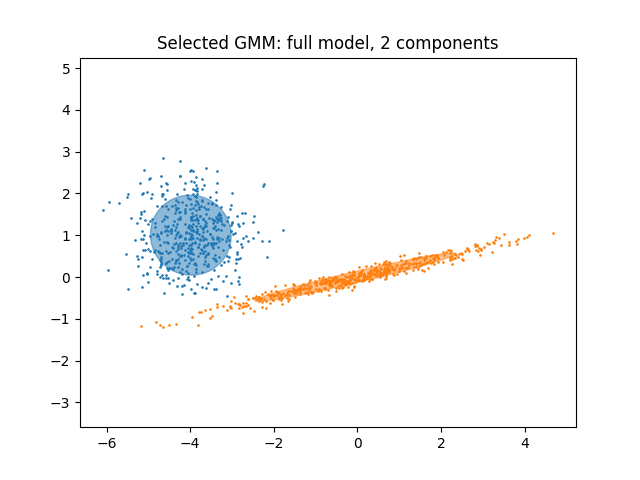
In the present case, the model with 2 components and full covariance (which corresponds to the true generative model) has the lowest BIC score and is therefore selected by the grid search.
绘制最佳模型#
我们绘制一个椭圆来显示所选模型的每个高斯分量。为此,需要找到由 covariances_ 属性这种矩阵的形状取决于 covariance_type :
"full": (n_components,n_features,n_features)"tied": (n_features,n_features)"diag": (n_components,n_features)"spherical": (n_components,)
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
from scipy import linalg
color_iter = sns.color_palette("tab10", 2)[::-1]
Y_ = grid_search.predict(X)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i, (mean, cov, color) in enumerate(
zip(
grid_search.best_estimator_.means_,
grid_search.best_estimator_.covariances_,
color_iter,
)
):
v, w = linalg.eigh(cov)
if not np.any(Y_ == i):
continue
plt.scatter(X[Y_ == i, 0], X[Y_ == i, 1], 0.8, color=color)
angle = np.arctan2(w[0][1], w[0][0])
angle = 180.0 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
v = 2.0 * np.sqrt(2.0) * np.sqrt(v)
ellipse = Ellipse(mean, v[0], v[1], angle=180.0 + angle, color=color)
ellipse.set_clip_box(fig.bbox)
ellipse.set_alpha(0.5)
ax.add_artist(ellipse)
plt.title(
f"Selected GMM: {grid_search.best_params_['covariance_type']} model, "
f"{grid_search.best_params_['n_components']} components"
)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0分1.424秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _