备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
最近邻回归#
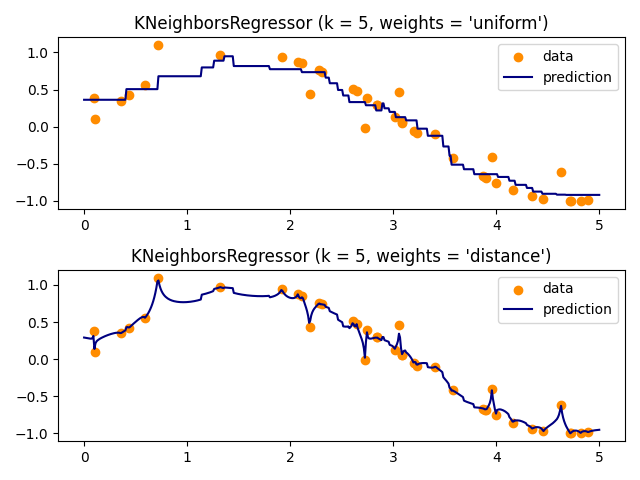
演示使用k-最近邻的回归问题的解决方案以及使用重心和常数权重的目标插值。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成示例数据#
在这里,我们生成一些数据点用于训练模型。我们还在整个训练数据范围内生成数据,以可视化模型在整个区域中的反应。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import neighbors
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X_train = np.sort(5 * rng.rand(40, 1), axis=0)
X_test = np.linspace(0, 5, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
y = np.sin(X_train).ravel()
# Add noise to targets
y[::5] += 1 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(8))
匹配回归模型#
在这里,我们训练一个模型并可视化如何 uniform 和 distance 预测中的权重影响预测值。
n_neighbors = 5
for i, weights in enumerate(["uniform", "distance"]):
knn = neighbors.KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors, weights=weights)
y_ = knn.fit(X_train, y).predict(X_test)
plt.subplot(2, 1, i + 1)
plt.scatter(X_train, y, color="darkorange", label="data")
plt.plot(X_test, y_, color="navy", label="prediction")
plt.axis("tight")
plt.legend()
plt.title("KNeighborsRegressor (k = %i, weights = '%s')" % (n_neighbors, weights))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.149 seconds)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _