备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
用于图像分割的光谱集群#
在本例中,生成具有相连圆的图像,并使用谱集群来分离圆。
在这些设置中, 谱聚类 该方法解决了所谓的“规范化图形切割”的问题:图像被视为连接体素的图形,谱集群算法相当于选择定义区域的图形切割,同时最小化沿着切割的梯度比以及区域的体积。
当算法试图平衡体积(即平衡区域大小)时,如果我们采用不同大小的圆圈,分割就会失败。
此外,由于图像的强度或其梯度中没有有用的信息,因此我们选择在仅被梯度弱告知的图上执行谱聚类。这接近于执行图的Voronoi分区。
此外,我们使用对象的面具来将图形限制为对象的轮廓。在这个例子中,我们感兴趣的是将对象彼此分开,而不是将对象与背景分开。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
生成数据#
import numpy as np
l = 100
x, y = np.indices((l, l))
center1 = (28, 24)
center2 = (40, 50)
center3 = (67, 58)
center4 = (24, 70)
radius1, radius2, radius3, radius4 = 16, 14, 15, 14
circle1 = (x - center1[0]) ** 2 + (y - center1[1]) ** 2 < radius1**2
circle2 = (x - center2[0]) ** 2 + (y - center2[1]) ** 2 < radius2**2
circle3 = (x - center3[0]) ** 2 + (y - center3[1]) ** 2 < radius3**2
circle4 = (x - center4[0]) ** 2 + (y - center4[1]) ** 2 < radius4**2
绘制四个圆圈#
img = circle1 + circle2 + circle3 + circle4
# We use a mask that limits to the foreground: the problem that we are
# interested in here is not separating the objects from the background,
# but separating them one from the other.
mask = img.astype(bool)
img = img.astype(float)
img += 1 + 0.2 * np.random.randn(*img.shape)
将图像转换为具有边缘梯度值的图形。
from sklearn.feature_extraction import image
graph = image.img_to_graph(img, mask=mask)
采用梯度的递减函数,得到接近Voronoi分区的分割
graph.data = np.exp(-graph.data / graph.data.std())
在这里,我们使用arpack解算器执行谱集群,因为amg在这个例子中在数字上不稳定。然后我们绘制结果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import spectral_clustering
labels = spectral_clustering(graph, n_clusters=4, eigen_solver="arpack")
label_im = np.full(mask.shape, -1.0)
label_im[mask] = labels
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
axs[0].matshow(img)
axs[1].matshow(label_im)
plt.show()

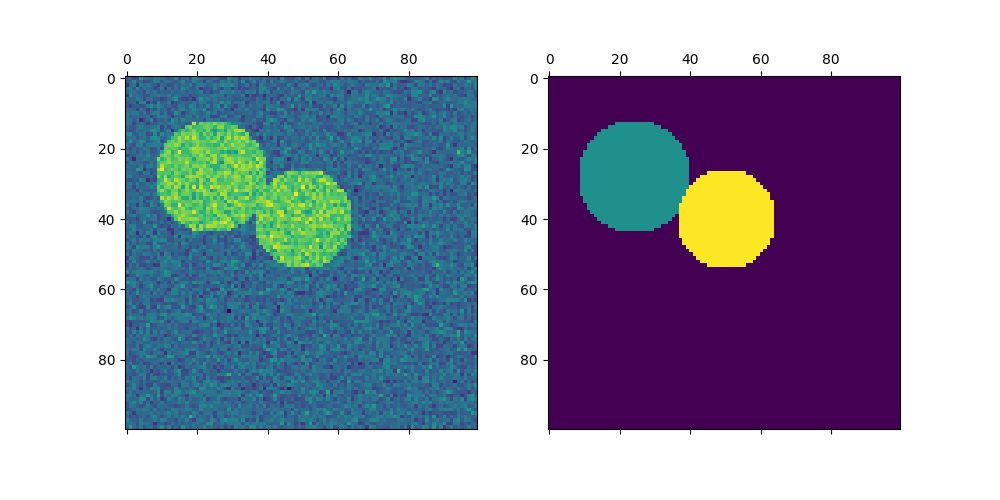
绘制两个圆圈#
Here we repeat the above process but only consider the first two circles we generated. Note that this results in a cleaner separation between the circles as the region sizes are easier to balance in this case.
img = circle1 + circle2
mask = img.astype(bool)
img = img.astype(float)
img += 1 + 0.2 * np.random.randn(*img.shape)
graph = image.img_to_graph(img, mask=mask)
graph.data = np.exp(-graph.data / graph.data.std())
labels = spectral_clustering(graph, n_clusters=2, eigen_solver="arpack")
label_im = np.full(mask.shape, -1.0)
label_im[mask] = labels
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
axs[0].matshow(img)
axs[1].matshow(label_im)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0分0.379秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _