备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码。或者通过浏览器中的MysterLite或Binder运行此示例
GMM检查方法#
高斯混合模型中不同初始化方法的示例
看到 高斯混合模型 有关估计器的更多信息。
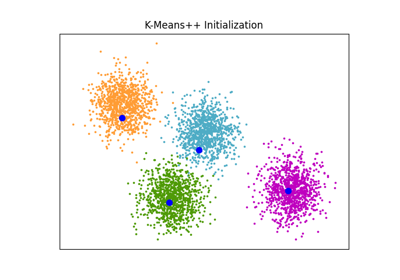
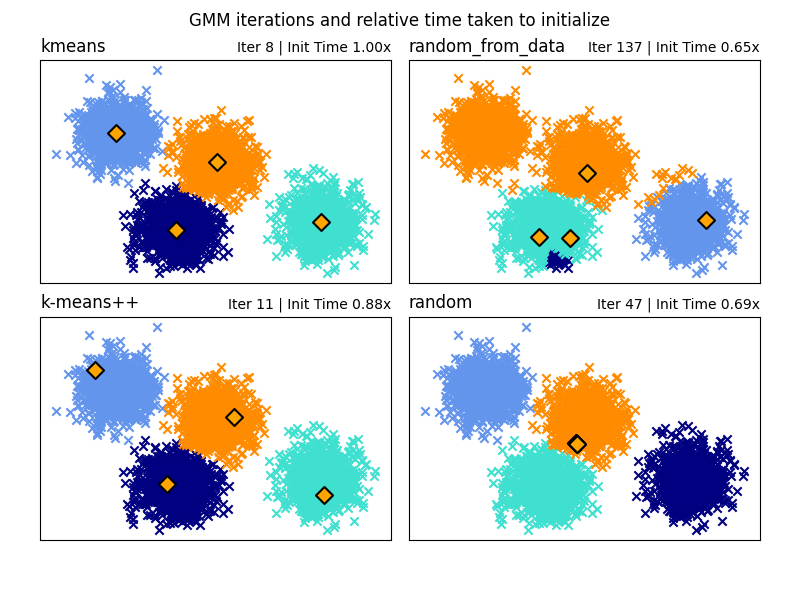
在这里,我们生成一些具有四个易于识别的集群的样本数据。此示例的目的是展示初始化参数的四种不同方法 init_param .
四个初始化是 kmeans (默认), random , random_from_data 和 k-means++ .
橙色钻石代表由 init_param .其余的数据表示为十字,颜色表示GMM完成后的最终相关分类。
每个子图右上角的数字表示GaussianMixture收敛所需的迭代次数以及算法初始化部分运行所需的相对时间。较短的初始化时间往往有更多的迭代收敛。
初始化时间是该方法所花费的时间与默认方法所花费的时间的比率 kmeans 法正如您所看到的,与 kmeans .
在本例中,当初始化为 random_from_data 或 random 该模型需要更多迭代才能收敛。这里 k-means++ 在初始化时间短和收敛GaussianMixture迭代次数少方面都做得很好。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets._samples_generator import make_blobs
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.utils.extmath import row_norms
print(__doc__)
# Generate some data
X, y_true = make_blobs(n_samples=4000, centers=4, cluster_std=0.60, random_state=0)
X = X[:, ::-1]
n_samples = 4000
n_components = 4
x_squared_norms = row_norms(X, squared=True)
def get_initial_means(X, init_params, r):
# Run a GaussianMixture with max_iter=0 to output the initialization means
gmm = GaussianMixture(
n_components=4, init_params=init_params, tol=1e-9, max_iter=0, random_state=r
).fit(X)
return gmm.means_
methods = ["kmeans", "random_from_data", "k-means++", "random"]
colors = ["navy", "turquoise", "cornflowerblue", "darkorange"]
times_init = {}
relative_times = {}
plt.figure(figsize=(4 * len(methods) // 2, 6))
plt.subplots_adjust(
bottom=0.1, top=0.9, hspace=0.15, wspace=0.05, left=0.05, right=0.95
)
for n, method in enumerate(methods):
r = np.random.RandomState(seed=1234)
plt.subplot(2, len(methods) // 2, n + 1)
start = timer()
ini = get_initial_means(X, method, r)
end = timer()
init_time = end - start
gmm = GaussianMixture(
n_components=4, means_init=ini, tol=1e-9, max_iter=2000, random_state=r
).fit(X)
times_init[method] = init_time
for i, color in enumerate(colors):
data = X[gmm.predict(X) == i]
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], color=color, marker="x")
plt.scatter(
ini[:, 0], ini[:, 1], s=75, marker="D", c="orange", lw=1.5, edgecolors="black"
)
relative_times[method] = times_init[method] / times_init[methods[0]]
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.title(method, loc="left", fontsize=12)
plt.title(
"Iter %i | Init Time %.2fx" % (gmm.n_iter_, relative_times[method]),
loc="right",
fontsize=10,
)
plt.suptitle("GMM iterations and relative time taken to initialize")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0分0.815秒)
相关实例
Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery <https://sphinx-gallery.github.io> _