>>> from env_helper import info; info()
页面更新时间: 2024-01-19 23:24:50
运行环境:
Linux发行版本: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm)
操作系统内核: Linux-6.1.0-17-amd64-x86_64-with-glibc2.36
Python版本: 3.11.2
3.2. 霍夫线变换¶
在图片处理中,霍夫变换主要是用来检测图片中的几何形状,包括直线、圆、椭圆等。
在skimage中,霍夫变换是放在tranform模块内,本篇主要讲解霍夫线变换。
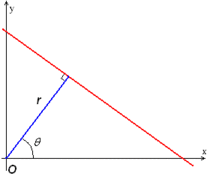
对于平面中的一条直线,在笛卡尔坐标系中,可用 y=mx+b 来表示,其中
m 为斜率, b 为截距。 但是如果直线是一条垂直线,则 m
为无穷大,所有通常我们在另一坐标系中表示直线, 即极坐标系下的
r=xcos(theta)+ysin(theta) 。 即可用 (r,theta)
来表示一条直线。其中 r 为该直线到原点的距离, theta
为该直线的垂线与x轴的夹角。如下图所示。
对于一个给定的点 (x0,y0) , 我们在极坐标下绘出所有通过它的直线
(r,theta) ,
将得到一条正弦曲线。如果将图片中的所有非0点的正弦曲线都绘制出来,则会存在一些交点。
所有经过这个交点的正弦曲线,说明都拥有同样的 (r,theta) ,
意味着这些点在一条直线上。
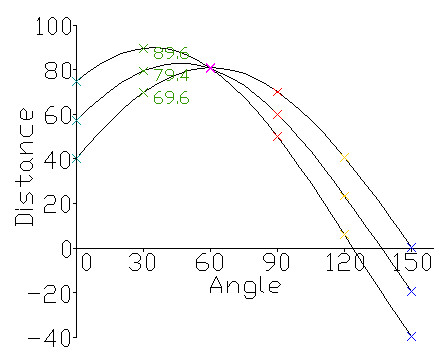
发上图所示,三个点(对应图中的三条正弦曲线)在一条直线上,因为这三个曲线交于一点,具有相同的
(r, theta) 。 霍夫线变换就是利用这种方法来寻找图中的直线。
3.2.1. 霍夫线变换¶
函数:
skimage.transform.hough_line(img)
返回三个值:
h: 霍夫变换累积器theta: 点与x轴的夹角集合,一般为0-179度distance: 点到原点的距离,即上面的所说的r.
例:
>>> import skimage.transform as st
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>>
>>> # 构建测试图片
>>> image = np.zeros((100, 100)) #背景图
>>> idx = np.arange(25, 75) #25-74序列
>>> image[idx[::-1], idx] = 255 # 线条\
>>> image[idx, idx] = 255 # 线条/
>>>
>>> # hough线变换
>>> h, theta, d = st.hough_line(image)
>>>
>>> #生成一个一行两列的窗口(可显示两张图片).
>>> fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 6))
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>>
>>> #显示原始图片
>>> ax0.imshow(image, plt.cm.gray)
>>> ax0.set_title('Input image')
>>> ax0.set_axis_off()
>>>
>>> #显示hough变换所得数据
>>> ax1.imshow(np.log(1 + h))
>>> ax1.set_title('Hough transform')
>>> ax1.set_xlabel('Angles (degrees)')
>>> ax1.set_ylabel('Distance (pixels)')
>>> ax1.axis('image')
(-0.5, 179.5, 284.5, -0.5)
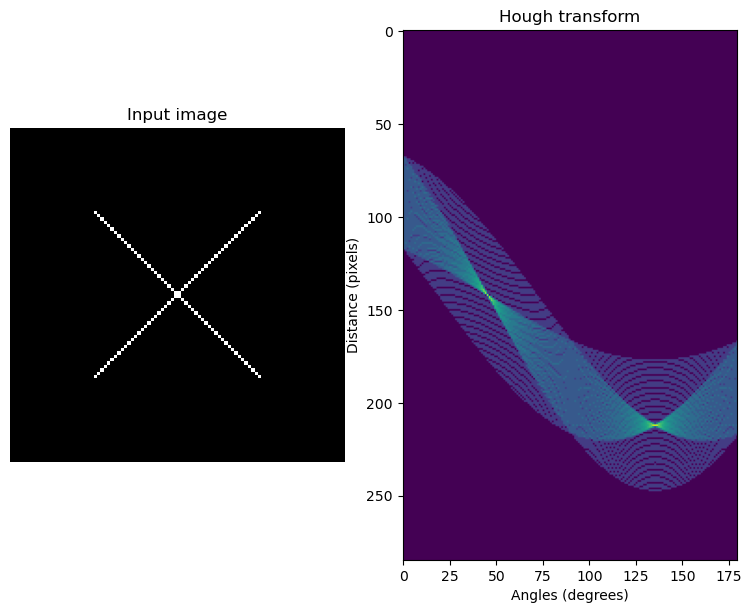
从右边那张图可以看出,有两个交点,说明原图像中有两条直线。
3.2.2. hough_line_peaks() 函数¶
如果我们要把图中的两条直线绘制出来,则需要用到另外一个函数:
skimage.transform.hough_line_peaks(hspace, angles, dists)
用这个函数可以取出峰值点,即交点,也即原图中的直线。
返回的参数与输入的参数一样。我们修改一下上边的程序,在原图中将两直线绘制出来。
>>> import skimage.transform as st
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>>
>>> # 构建测试图片
>>> image = np.zeros((100, 100)) #背景图
>>> idx = np.arange(25, 75) #25-74序列
>>> image[idx[::-1], idx] = 255 # 线条\
>>> image[idx, idx] = 255 # 线条/
>>>
>>> # hough线变换
>>> h, theta, d = st.hough_line(image)
>>>
>>> #生成一个一行三列的窗口(可显示三张图片).
>>> fig, (ax0, ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 6))
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>>
>>> #显示原始图片
>>> ax0.imshow(image, plt.cm.gray)
>>> ax0.set_title('Input image')
>>> ax0.set_axis_off()
>>>
>>> #显示hough变换所得数据
>>> ax1.imshow(np.log(1 + h))
>>> ax1.set_title('Hough transform')
>>> ax1.set_xlabel('Angles (degrees)')
>>> ax1.set_ylabel('Distance (pixels)')
>>> ax1.axis('image')
>>>
>>> #显示检测出的线条
>>> ax2.imshow(image, plt.cm.gray)
>>> row1, col1 = image.shape
>>> for _, angle, dist in zip(*st.hough_line_peaks(h, theta, d)):
>>> y0 = (dist - 0 * np.cos(angle)) / np.sin(angle)
>>> y1 = (dist - col1 * np.cos(angle)) / np.sin(angle)
>>> ax2.plot((0, col1), (y0, y1), '-r')
>>> ax2.axis((0, col1, row1, 0))
>>> ax2.set_title('Detected lines')
>>> ax2.set_axis_off()
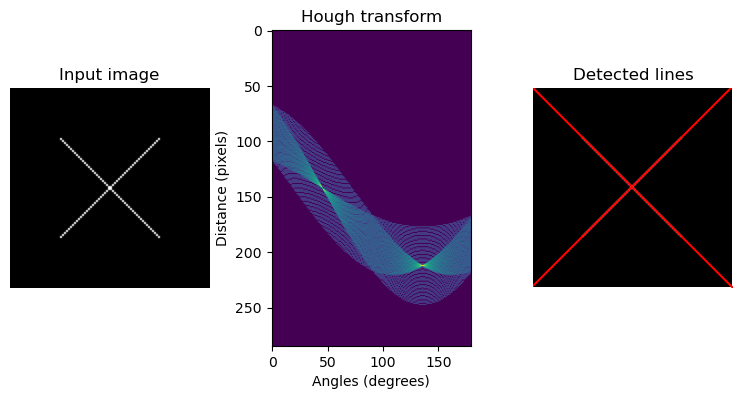
注意,绘制线条的时候,要从极坐标转换为笛卡尔坐标,公式为:
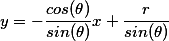
3.2.3. 概率霍夫线变换¶
skimage还提供了另外一个检测直线的霍夫变换函数,概率霍夫线变换:
skimage.transform.probabilistic_hough_line(img, threshold=10, line_length=5,line_gap=3)
参数:
img: 待检测的图像。threshold: 阈值,可先项,默认为10line_length: 检测的最短线条长度,默认为50line_gap: 线条间的最大间隙。增大这个值可以合并破碎的线条。默认为10
返回:
lines : 线条列表, 格式如 ((x0, y0), (x1, y0))
,标明开始点和结束点。
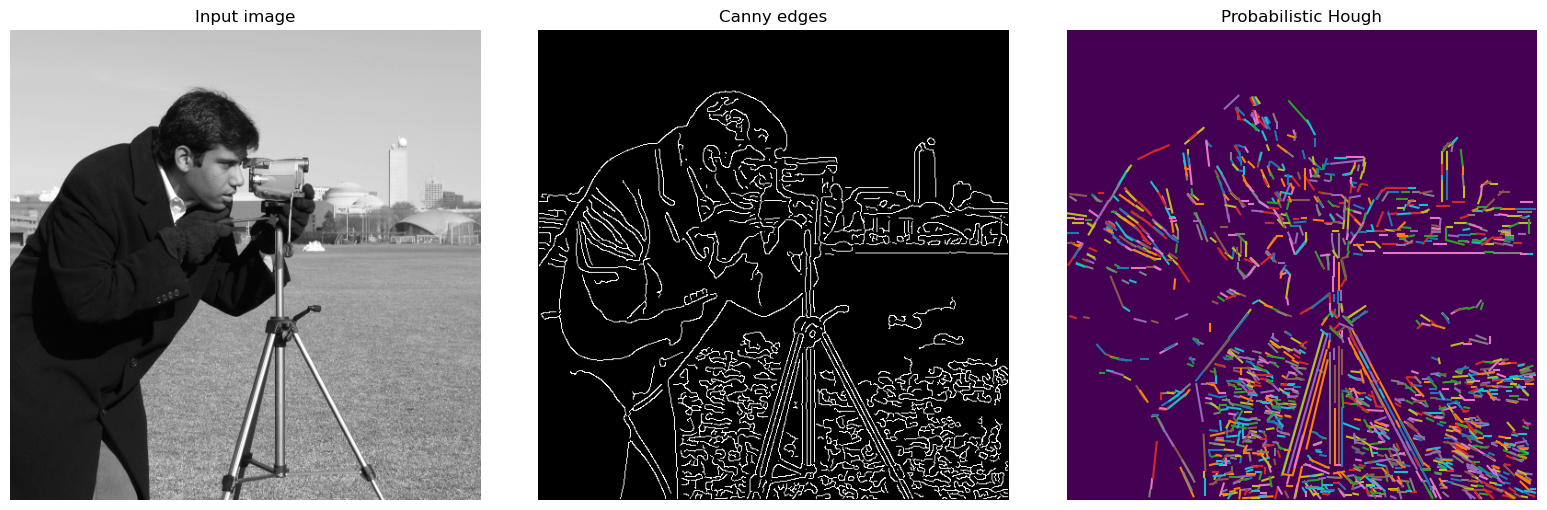
下面,我们用canny算子提取边缘,然后检测哪些边缘是直线?
>>> import skimage.transform as st
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> from skimage import data,feature
>>>
>>> #使用Probabilistic Hough Transform.
>>> image = data.camera()
>>> edges = feature.canny(image, sigma=2, low_threshold=1, high_threshold=25)
>>> lines = st.probabilistic_hough_line(edges, threshold=10, line_length=5,line_gap=3)
>>>
>>> # 创建显示窗口.
>>> fig, (ax0, ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(16, 6))
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>>
>>> #显示原图像
>>> ax0.imshow(image, plt.cm.gray)
>>> ax0.set_title('Input image')
>>> ax0.set_axis_off()
>>>
>>> #显示canny边缘
>>> ax1.imshow(edges, plt.cm.gray)
>>> ax1.set_title('Canny edges')
>>> ax1.set_axis_off()
>>>
>>> #用plot绘制出所有的直线
>>> ax2.imshow(edges * 0)
>>> for line in lines:
>>> p0, p1 = line
>>> ax2.plot((p0[0], p1[0]), (p0[1], p1[1]))
>>> row2, col2 = image.shape
>>> ax2.axis((0, col2, row2, 0))
>>> ax2.set_title('Probabilistic Hough')
>>> ax2.set_axis_off()
>>> plt.show()
