>>> from env_helper import info; info()
页面更新时间: 2024-01-19 23:06:10
运行环境:
Linux发行版本: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm)
操作系统内核: Linux-6.1.0-17-amd64-x86_64-with-glibc2.36
Python版本: 3.11.2
5.12. 控制参数美化可视化结果¶
在使用可视化技术探索数据集特征时,最好有令人愉悦的绘图。 可视化对于向观众传达定量见解也至关重要,在这种情况下,更需要有能够吸引注意力并吸引观众的数字。
Matplotlib 是高度可定制的,但很难知道要调整哪些设置才能获得有吸引力的绘图。 Seaborn 带有许多自定义主题和一个高级界面,用于控制 matplotlib 图形的外观。
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import seaborn as sns
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> sns.__version__
'0.12.2'
让我们定义一个简单的函数来绘制一些偏移正弦波,这将有助于我们看到我们可以调整的不同风格参数。
>>> def sinplot(n=10, flip=1):
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 14, 100)
>>> for i in range(1, n + 1):
>>> plt.plot(x, np.sin(x + i * .5) * (n + 2 - i) * flip)
这是 matplotlib 默认值的绘图:
>>> sinplot()
要切换到 seaborn 默认值,只需调用set_theme()函数即可。
>>> sns.set_theme()
>>> sinplot()
注意 , 在0.8之前的seaborn版本中, set_theme()
在导入时被调用。在以后的版本中,必须显式调用它。
Seaborn将matplotlib参数分成两个独立的组。第一组设定情节的美学风格,第二组衡量人物的各种元素,使其容易融入不同的语境。
操作这些参数的接口是两对函数。要控制样式,请使用 axes_style() 和
set_style() 函数。 要缩放绘图,请使用 plotting_context() 和
set_context() 函数。
在这两种情况下,第一个函数返回一个参数字典,第二个函数设置matplotlib默认值。
5.12.1. Seaborn 风格主题¶
Seaborn 有五个预设的主题: darkgrid , whitegrid , dark ,
white , 和 ticks 。
它们都适合不同的应用和个人偏好。默认的主题是 darkgrid 。
如上所述,网格有助于将图用作定量信息的查找表,而白色和灰色有助于防止网格与表示数据的线条竞争。
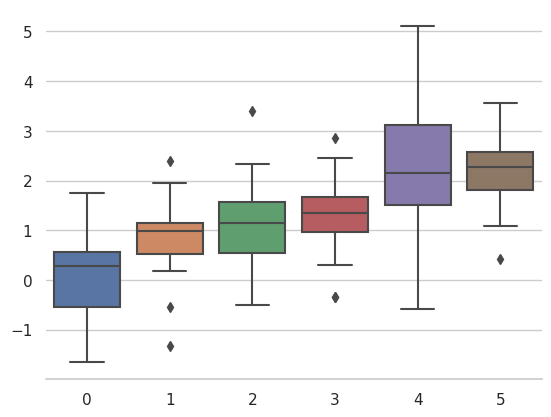
whitegrid 的主题是类似的,但它更适合于具有大量数据元素的图:
>>> sns.set_style("whitegrid")
>>> data = np.random.normal(size=(20, 6)) + np.arange(6) / 2
>>> sns.boxplot(data=data);
对于许多绘图(尤其是对于谈话等设置,您主要希望使用数字来提供数据中模式的印象),网格就不太必要了。
>>> sns.set_style("dark")
>>> sinplot()
>>> sns.set_style("white")
>>> sinplot()
有时您可能想为绘图提供一些额外的结构,这就是 tick 派上用场的地方:
>>> sns.set_style("ticks")
>>> sinplot()
5.12.2. 去除上侧与左侧数轴¶
white 和 ticks
风格都可以去除顶部和右侧数轴,这是不必须的。可以调用 Seaborn 函数
despine() 来移除它们:
>>> sinplot()
>>> sns.despine()
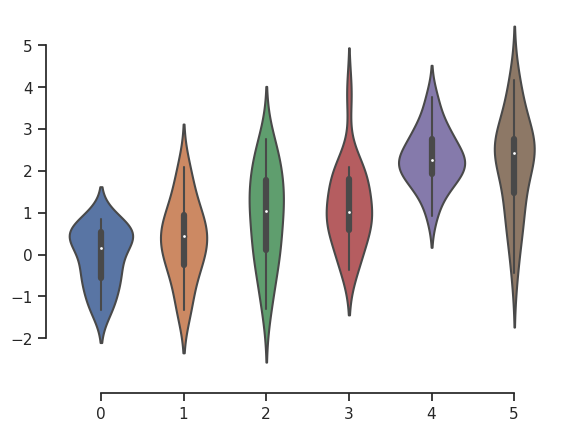
当刻度没有覆盖整个轴的范围时, trim 参数将限制剩余刻度的范围。
>>> f, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> sns.violinplot(data=data)
>>> sns.despine(offset=10, trim=True);
你还可以通过对 despine() 的附加参数来控制哪些 spine 被移除:
>>> sns.set_style("whitegrid")
>>> sns.boxplot(data=data, palette="deep")
>>> sns.despine(left=True)
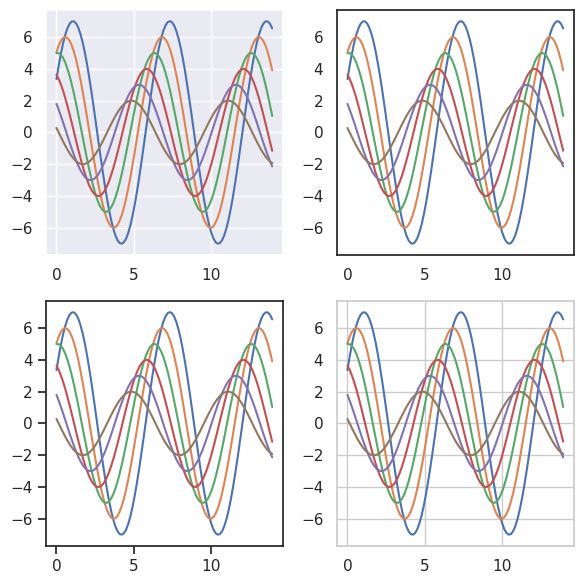
5.12.3. 临时设置图形样式¶
虽然来回切换很容易,但是您也可以在 with 语句中使用 axes_style()
函数来临时设置绘图参数。
这也允许你用不同风格的轴来制作图形:
>>> f = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
>>> gs = f.add_gridspec(2, 2)
>>>
>>> with sns.axes_style("darkgrid"):
>>> ax = f.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
>>> sinplot(6)
>>>
>>> with sns.axes_style("white"):
>>> ax = f.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
>>> sinplot(6)
>>>
>>> with sns.axes_style("ticks"):
>>> ax = f.add_subplot(gs[1, 0])
>>> sinplot(6)
>>>
>>> with sns.axes_style("whitegrid"):
>>> ax = f.add_subplot(gs[1, 1])
>>> sinplot(6)
>>>
>>> f.tight_layout()
5.12.4. 覆盖seaborn样式的元素¶
如果你想自定义seaborn样式,你可以将一个参数字典传递给 axes_style()
和 set_style() 的 rc 参数。
请注意,您只能通过此方法覆盖作为样式定义一部分的参数。(然而,更高级的set_theme()函数接受一个包含所有matplotlib参数的字典)。
如果你想查看包含哪些参数,你可以只调用不带参数的函数,这将返回当前设置:
>>> sns.axes_style()
{'axes.facecolor': 'white',
'axes.edgecolor': '.8',
'axes.grid': True,
'axes.axisbelow': True,
'axes.labelcolor': '.15',
'figure.facecolor': 'white',
'grid.color': '.8',
'grid.linestyle': '-',
'text.color': '.15',
'xtick.color': '.15',
'ytick.color': '.15',
'xtick.direction': 'out',
'ytick.direction': 'out',
'lines.solid_capstyle': <CapStyle.round: 'round'>,
'patch.edgecolor': 'w',
'patch.force_edgecolor': True,
'image.cmap': 'rocket',
'font.family': ['sans-serif'],
'font.sans-serif': ['Arial',
'DejaVu Sans',
'Liberation Sans',
'Bitstream Vera Sans',
'sans-serif'],
'xtick.bottom': False,
'xtick.top': False,
'ytick.left': False,
'ytick.right': False,
'axes.spines.left': True,
'axes.spines.bottom': True,
'axes.spines.right': True,
'axes.spines.top': True}
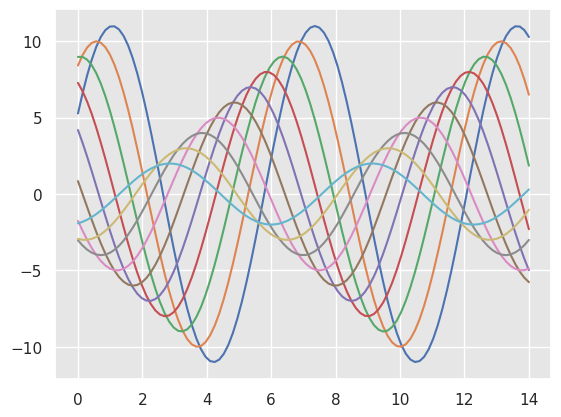
然后,您可以设置这些参数的不同版本:
>>> sns.set_style("darkgrid", {"axes.facecolor": ".9"})
>>> sinplot()
5.12.5. 缩放绘图元素¶
一组单独的参数控制绘图元素的比例,这应该允许您使用相同的代码来制作适合在适合较大或较小绘图的设置中使用的绘图。
首先,让我们通过调用set_theme()来重置默认参数:
>>> sns.set_theme()
四种预设的语境,按相对大小排序,分别是paper,
notebook,talk,
poster。notebook样式是默认的,在上面的图中使用。
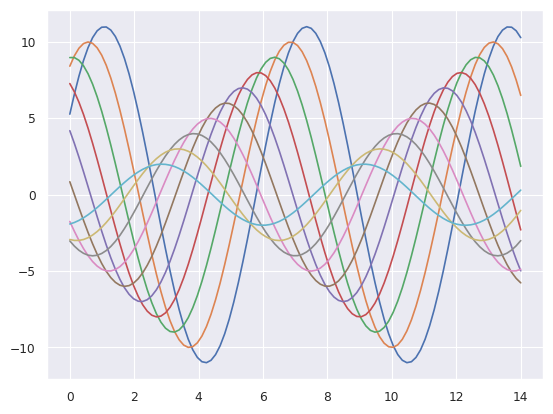
>>> sns.set_context("paper")
>>> sinplot()
>>> sns.set_context("talk")
>>> sinplot()
>>> sns.set_context("poster")
>>> sinplot()
您现在所知道的关于样式函数的大部分知识应该转移到上下文函数中。
您可以使用其中一个名称调用set_context()来设置参数,并且可以通过提供一个参数值字典来覆盖这些参数。
您还可以在更改上下文时独立缩放字体元素的大小。(此选项也可通过顶级set()函数获得)。
>>> sns.set_context("notebook", font_scale=1.5, rc={"lines.linewidth": 2.5})
>>> sinplot()
类似地,您可以临时控制嵌套在with语句下的图形的大小。
样式和上下文都可以用set()函数快速配置。此函数还设置默认调色板,但这将在本教程的下一节中更详细地介绍。