A-Star寻路#
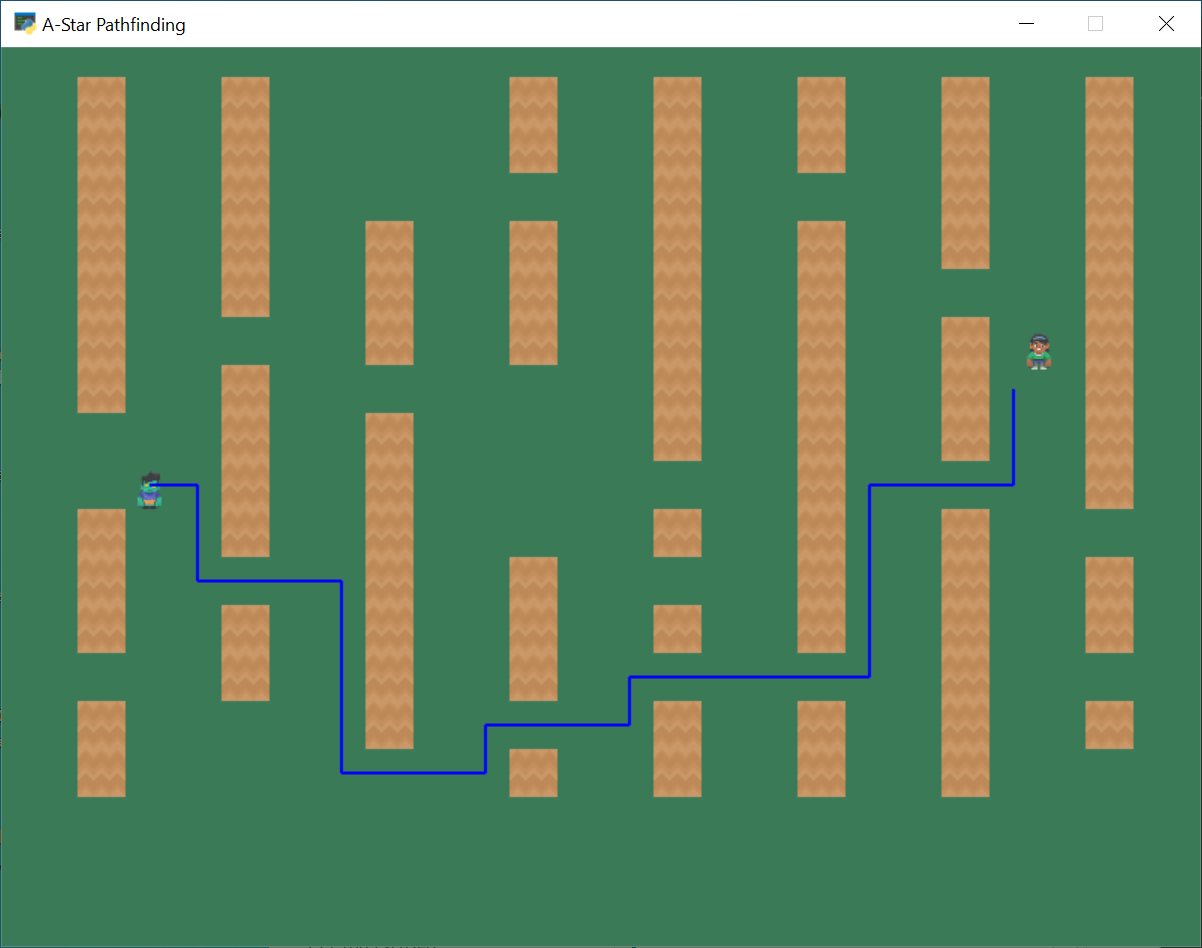
解释#
A星寻路可以用来找到一种绕过障碍物从一个地点到另一个地点的方法。本例仅根据返回的坐标绘制路径。如果你想让敌人沿着这条路走,请参见 沿着一条路走的精灵 。
来源#
astar_pathfinding.py#
1"""
2A-Star Path-finding
3
4Artwork from https://kenney.nl
5
6If Python and Arcade are installed, this example can be run from the command line with:
7python -m arcade.examples.astar_pathfinding
8"""
9
10import arcade
11from arcade import camera
12import random
13
14SPRITE_IMAGE_SIZE = 128
15SPRITE_SCALING = 0.25
16SPRITE_SIZE = int(SPRITE_IMAGE_SIZE * SPRITE_SCALING)
17
18SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
19SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
20SCREEN_TITLE = "A-Star Path-finding"
21
22MOVEMENT_SPEED = 5
23
24VIEWPORT_MARGIN = 100
25
26
27class MyGame(arcade.Window):
28 """
29 Main application class.
30 """
31
32 def __init__(self, width, height, title):
33 """
34 Initializer
35 """
36
37 # Call the parent class initializer
38 super().__init__(width, height, title)
39
40 # Variables that will hold sprite lists
41 self.player_list = None
42 self.wall_list = None
43 self.enemy_list = None
44
45 # Set up the player info
46 self.player = None
47
48 # Track the current state of what key is pressed
49 self.left_pressed = False
50 self.right_pressed = False
51 self.up_pressed = False
52 self.down_pressed = False
53
54 self.physics_engine = None
55
56 # --- Related to paths
57 # List of points that makes up a path between two points
58 self.path = None
59 # List of points we checked to see if there is a barrier there
60 self.barrier_list = None
61
62 # Set the window background color
63 self.background_color = arcade.color.AMAZON
64
65 # Camera
66 self.cam = None
67
68 def setup(self):
69 """ Set up the game and initialize the variables. """
70
71 # Sprite lists
72 self.player_list = arcade.SpriteList()
73 self.wall_list = arcade.SpriteList(use_spatial_hash=True,
74 spatial_hash_cell_size=128)
75 self.enemy_list = arcade.SpriteList()
76
77 # Set up the player
78 resource = ":resources:images/animated_characters/" \
79 "female_person/femalePerson_idle.png"
80 self.player = arcade.Sprite(resource, scale=SPRITE_SCALING)
81 self.player.center_x = SPRITE_SIZE * 5
82 self.player.center_y = SPRITE_SIZE * 1
83 self.player_list.append(self.player)
84
85 # Set enemies
86 resource = ":resources:images/animated_characters/zombie/zombie_idle.png"
87 enemy = arcade.Sprite(resource, scale=SPRITE_SCALING)
88 enemy.center_x = SPRITE_SIZE * 4
89 enemy.center_y = SPRITE_SIZE * 7
90 self.enemy_list.append(enemy)
91
92 spacing = SPRITE_SIZE * 3
93 for column in range(10):
94 for row in range(15):
95 sprite = arcade.Sprite(":resources:images/tiles/grassCenter.png",
96 scale=SPRITE_SCALING)
97
98 x = (column + 1) * spacing
99 y = (row + 1) * sprite.height
100
101 sprite.center_x = x
102 sprite.center_y = y
103 if random.randrange(100) > 30:
104 self.wall_list.append(sprite)
105
106 self.physics_engine = arcade.PhysicsEngineSimple(self.player,
107 self.wall_list)
108
109 # --- Path related
110 # This variable holds the travel-path. We keep it as an attribute so
111 # we can calculate it in on_update, and draw it in on_draw.
112 self.path = None
113 # Grid size for calculations. The smaller the grid, the longer the time
114 # for calculations. Make sure the grid aligns with the sprite wall grid,
115 # or some openings might be missed.
116 grid_size = SPRITE_SIZE
117
118 # Calculate the playing field size. We can't generate paths outside of
119 # this.
120 playing_field_left_boundary = -SPRITE_SIZE * 2
121 playing_field_right_boundary = SPRITE_SIZE * 35
122 playing_field_top_boundary = SPRITE_SIZE * 17
123 playing_field_bottom_boundary = -SPRITE_SIZE * 2
124
125 # This calculates a list of barriers. By calculating it here in the
126 # init, we are assuming this list does not change. In this example,
127 # our walls don't move, so that is ok. If we want moving barriers (such as
128 # moving platforms or enemies) we need to recalculate. This can be an
129 # time-intensive process depending on the playing field size and grid
130 # resolution.
131
132 # Note: If the enemy sprites are the same size, we only need to calculate
133 # one of these. We do NOT need a different one for each enemy. The sprite
134 # is just used for a size calculation.
135 self.barrier_list = arcade.AStarBarrierList(enemy,
136 self.wall_list,
137 grid_size,
138 playing_field_left_boundary,
139 playing_field_right_boundary,
140 playing_field_bottom_boundary,
141 playing_field_top_boundary)
142
143 self.cam = camera.Camera2D()
144
145 def on_draw(self):
146 """
147 Render the screen.
148 """
149 self.cam.use()
150
151 # This command has to happen before we start drawing
152 self.clear()
153
154 # Draw all the sprites.
155 self.player_list.draw()
156 self.wall_list.draw()
157 self.enemy_list.draw()
158
159 if self.path:
160 arcade.draw_line_strip(self.path, arcade.color.BLUE, 2)
161
162 def on_update(self, delta_time):
163 """ Movement and game logic """
164
165 # Calculate speed based on the keys pressed
166 self.player.change_x = 0
167 self.player.change_y = 0
168
169 if self.up_pressed and not self.down_pressed:
170 self.player.change_y = MOVEMENT_SPEED
171 elif self.down_pressed and not self.up_pressed:
172 self.player.change_y = -MOVEMENT_SPEED
173 if self.left_pressed and not self.right_pressed:
174 self.player.change_x = -MOVEMENT_SPEED
175 elif self.right_pressed and not self.left_pressed:
176 self.player.change_x = MOVEMENT_SPEED
177
178 # Update the character
179 self.physics_engine.update()
180
181 # Calculate a path to the player
182 enemy = self.enemy_list[0]
183 # Set to True if we can move diagonally. Note that diagonal movement
184 # might cause the enemy to clip corners.
185 self.path = arcade.astar_calculate_path(enemy.position,
186 self.player.position,
187 self.barrier_list,
188 diagonal_movement=False)
189 # print(self.path,"->", self.player.position)
190
191 # --- Manage Scrolling ---
192
193 # Scroll left
194 left_boundary = self.cam.left + VIEWPORT_MARGIN
195 if self.player.left < left_boundary:
196 self.cam.left -= left_boundary - self.player.left
197
198 # Scroll right
199 right_boundary = self.cam.right - VIEWPORT_MARGIN
200 if self.player.right > right_boundary:
201 self.cam.right += self.player.right - right_boundary
202
203 # Scroll up
204 top_boundary = self.cam.top - VIEWPORT_MARGIN
205 if self.player.top > top_boundary:
206 self.cam.top += self.player.top - top_boundary
207
208 # Scroll down
209 bottom_boundary = self.cam.bottom + VIEWPORT_MARGIN
210 if self.player.bottom < bottom_boundary:
211 self.cam.bottom -= bottom_boundary - self.player.bottom
212
213 # Make sure our boundaries are integer values. While the view port does
214 # support floating point numbers, for this application we want every pixel
215 # in the view port to map directly onto a pixel on the screen. We don't want
216 # any rounding errors.
217
218 def on_key_press(self, key, modifiers):
219 """Called whenever a key is pressed. """
220
221 if key == arcade.key.UP:
222 self.up_pressed = True
223 elif key == arcade.key.DOWN:
224 self.down_pressed = True
225 elif key == arcade.key.LEFT:
226 self.left_pressed = True
227 elif key == arcade.key.RIGHT:
228 self.right_pressed = True
229
230 def on_key_release(self, key, modifiers):
231 """Called when the user releases a key. """
232
233 if key == arcade.key.UP:
234 self.up_pressed = False
235 elif key == arcade.key.DOWN:
236 self.down_pressed = False
237 elif key == arcade.key.LEFT:
238 self.left_pressed = False
239 elif key == arcade.key.RIGHT:
240 self.right_pressed = False
241
242
243def main():
244 """ Main function """
245 window = MyGame(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, SCREEN_TITLE)
246 window.setup()
247 arcade.run()
248
249
250if __name__ == "__main__":
251 main()