为Mars创建新的坐标框架类#
此示例描述了如何对行星体进行子分类和定义自定义坐标系,该坐标系可以通过测地或体心表示来描述,如中所讨论的 定义新框架 和 创建您自己的大地测量表示和身体中心表示 .
请注意,我们在这里使用框架仅用于存储坐标。使用它来确定,例如要将望远镜指向地球上观察奥林匹斯山的位置,需要将框架添加到传递图中,这超出了本示例的范围。
为此,首先我们需要定义 BaseGeodeticRepresentation 和 BaseBodycentricRepresentation ,然后是的一个子集 BaseCoordinateFrame 使用之前定义的表示。
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from astropy import units as u
>>> from astropy.coordinates.baseframe import BaseCoordinateFrame
>>> from astropy.coordinates.representation import CartesianRepresentation
>>> from astropy.coordinates.representation.geodetic import (
... BaseBodycentricRepresentation,
... BaseGeodeticRepresentation,
... )
>>> from astropy.visualization import quantity_support
第一步是创建一个新类,并使其成为 BaseGeodeticRepresentation .使用大地测量纬度,赤道线跨度从0度到360度,它代表了火星球体与火星大地水准面(水洼面)的最佳匹配:
>>> class MarsBestFitAeroid(BaseGeodeticRepresentation):
... """A Spheroidal representation of Mars that minimized deviations with respect to the
... areoid following
... Ardalan A. A, R. Karimi, and E. W. Grafarend (2010)
... https://doi.org/10.1007/s11038-009-9342-7
... """
... _equatorial_radius = 3395.4280 * u.km
... _flattening = 0.5227617843759314 * u.percent
现在让我们定义一个新的大地测量表示,它是从MarsBestFitAeroid获得的,但由行星中心纬度描述:
>>> class MarsBestFitOcentricAeroid(BaseBodycentricRepresentation):
... """A Spheroidal planetocentric representation of Mars that minimized deviations with
... respect to the areoid following
... Ardalan A. A, R. Karimi, and E. W. Grafarend (2010)
... https://doi.org/10.1007/s11038-009-9342-7
... """
... _equatorial_radius = 3395.4280 * u.km
... _flattening = 0.5227617843759314 * u.percent
作为比较,我们定义了一个新的球形框架表示,我们可以基于 BaseBodycentricRepresentation 也:
>>> class MarsSphere(BaseGeodeticRepresentation):
... """A Spherical representation of Mars."""
... _equatorial_radius = 3395.4280 * u.km
... _flattening = 0.0 * u.percent
新的行星体固定参考系将使用之前定义的表示来描述:
>>> class MarsCoordinateFrame(BaseCoordinateFrame):
... """A reference system for Mars."""
... name = "Mars"
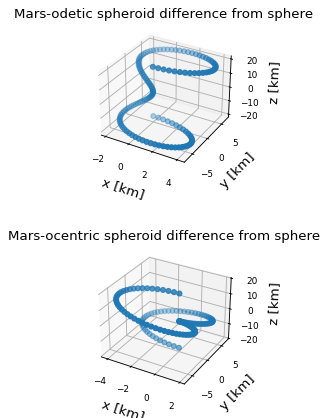
现在,我们绘制旋转木马表示的每个分量相对于球形模型之间的差异,假设物体表面上的点 (height = 0 ):
>>> mars_sphere = MarsCoordinateFrame(
... lon=np.linspace(0, 360, 128) * u.deg,
... lat=np.linspace(-90, 90, 128) * u.deg,
... representation_type=MarsSphere,
... )
>>> mars = MarsCoordinateFrame(
... lon=np.linspace(0, 360, 128) * u.deg,
... lat=np.linspace(-90, 90, 128) * u.deg,
... representation_type=MarsBestFitAeroid,
... )
>>> mars_ocentric = MarsCoordinateFrame(
... lon=np.linspace(0, 360, 128) * u.deg,
... lat=np.linspace(-90, 90, 128) * u.deg,
... representation_type=MarsBestFitOcentricAeroid,
... )
>>> xyz_sphere = mars_sphere.represent_as(CartesianRepresentation)
>>> xyz = mars.represent_as(CartesianRepresentation)
>>> xyz_ocentric = mars_ocentric.represent_as(CartesianRepresentation)
>>> with quantity_support():
... fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
... ax[0].scatter(*((xyz - xyz_sphere).xyz << u.km))
... ax[0].tick_params(labelsize=8)
... ax[0].set(xlabel="x [km]", ylabel="y [km]", zlabel="z [km]")
... ax[0].set_title("Mars-odetic spheroid difference from sphere")
... ax[1].scatter(*((xyz_ocentric - xyz_sphere).xyz << u.km))
... ax[1].tick_params(labelsize=8)
... ax[1].set(xlabel="x [km]", ylabel="y [km]", zlabel="z [km]")
... ax[1].set_title("Mars-ocentric spheroid difference from sphere")
... plt.draw()