备注
点击 here 下载完整的示例代码
克努斯英里#
miles_graph() returns an undirected graph over 128 US cities. The
cities each have location and population data. The edges are labeled with the
distance between the two cities.
此示例在的第1.1节中描述
唐纳德E.克努特,“斯坦福图形:组合计算平台”,ACM出版社,纽约,1993年。http://www cs faculty.stanford.edu/~knuth/sgb.html
数据文件位于:
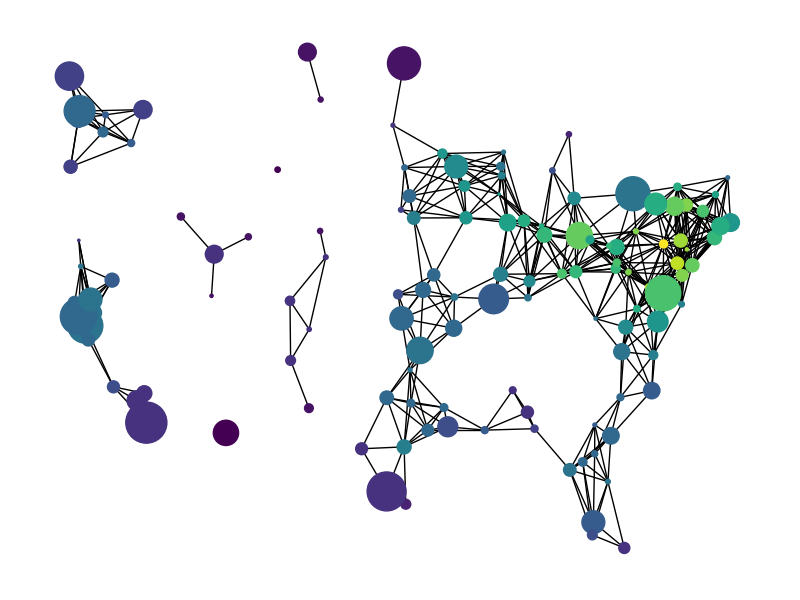
出:
Loaded miles_dat.txt containing 128 cities.
Graph with 128 nodes and 8128 edges
import gzip
import re
# Ignore any warnings related to downloading shpfiles with cartopy
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx
def miles_graph():
"""Return the cites example graph in miles_dat.txt
from the Stanford GraphBase.
"""
# open file miles_dat.txt.gz (or miles_dat.txt)
fh = gzip.open("knuth_miles.txt.gz", "r")
G = nx.Graph()
G.position = {}
G.population = {}
cities = []
for line in fh.readlines():
line = line.decode()
if line.startswith("*"): # skip comments
continue
numfind = re.compile(r"^\d+")
if numfind.match(line): # this line is distances
dist = line.split()
for d in dist:
G.add_edge(city, cities[i], weight=int(d))
i = i + 1
else: # this line is a city, position, population
i = 1
(city, coordpop) = line.split("[")
cities.insert(0, city)
(coord, pop) = coordpop.split("]")
(y, x) = coord.split(",")
G.add_node(city)
# assign position - Convert string to lat/long
G.position[city] = (-float(x) / 100, float(y) / 100)
G.population[city] = float(pop) / 1000.0
return G
G = miles_graph()
print("Loaded miles_dat.txt containing 128 cities.")
print(G)
# make new graph of cites, edge if less then 300 miles between them
H = nx.Graph()
for v in G:
H.add_node(v)
for (u, v, d) in G.edges(data=True):
if d["weight"] < 300:
H.add_edge(u, v)
# draw with matplotlib/pylab
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
# nodes colored by degree sized by population
node_color = [float(H.degree(v)) for v in H]
# Use cartopy to provide a backdrop for the visualization
try:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.io.shapereader as shpreader
ax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], projection=ccrs.LambertConformal(), frameon=False)
ax.set_extent([-125, -66.5, 20, 50], ccrs.Geodetic())
# Add map of countries & US states as a backdrop
for shapename in ("admin_1_states_provinces_lakes_shp", "admin_0_countries"):
shp = shpreader.natural_earth(
resolution="110m", category="cultural", name=shapename
)
ax.add_geometries(
shpreader.Reader(shp).geometries(),
ccrs.PlateCarree(),
facecolor="none",
edgecolor="k",
)
# NOTE: When using cartopy, use matplotlib directly rather than nx.draw
# to take advantage of the cartopy transforms
ax.scatter(
*np.array([v for v in G.position.values()]).T,
s=[G.population[v] for v in H],
c=node_color,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
zorder=100 # Ensure nodes lie on top of edges/state lines
)
# Plot edges between the cities
for edge in H.edges():
edge_coords = np.array([G.position[v] for v in edge])
ax.plot(
edge_coords[:, 0],
edge_coords[:, 1],
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
linewidth=0.75,
color="k",
)
except ImportError:
# If cartopy is unavailable, the backdrop for the plot will be blank;
# though you should still be able to discern the general shape of the US
# from graph nodes and edges!
nx.draw(
H,
G.position,
node_size=[G.population[v] for v in H],
node_color=node_color,
with_labels=False,
)
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间: (0分0.083秒)