scipy.signal.correlate2d¶
- scipy.signal.correlate2d(in1, in2, mode='full', boundary='fill', fillvalue=0)[源代码]¶
使两个二维数组相互关联。
互相关 in1 和 in2 其输出大小由 mode ,以及由以下条件确定的边界条件 boundary 和 fillvalue 。
- 参数
- in1array_like
第一次输入。
- in2array_like
第二个输入。应具有与的维度数量相同的维度 in1 。
- modestr{‘完整’,‘有效’,‘相同’},可选
指示输出大小的字符串:
full输出是输入的全离散线性互相关。(默认)
valid输出只包含那些不依赖于补零的元素。在“有效”模式下, in1 或 in2 必须在每个维度上至少与其他维度一样大。
same输出的大小与 in1 ,相对于“完整”输出居中。
- boundarystr{‘Fill’,‘WRAP’,‘symm’},可选
指示如何处理边界的标志:
fill用填充值填充输入数组。(默认)
wrap圆形边界条件。
symm对称边界条件。
- fillvalue标量,可选
要填充输入数组的值。默认值为0。
- 退货
- correlate2dndarray
包含以下项的离散线性互相关子集的二维数组 in1 使用 in2 。
注意事项
当使用具有偶数长度输入的“相同”模式时,
correlate和correlate2d不同:它们之间有1个索引偏移。示例
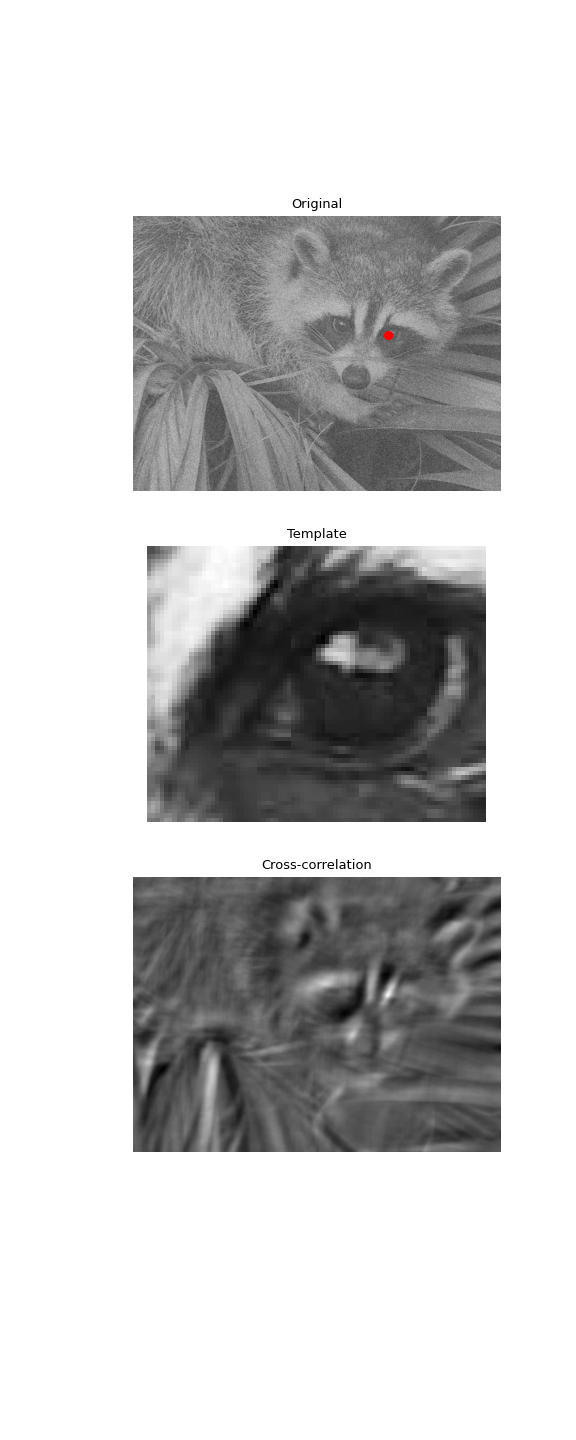
使用2D互相关在噪声图像中查找模板的位置:
>>> from scipy import signal >>> from scipy import misc >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> face = misc.face(gray=True) - misc.face(gray=True).mean() >>> template = np.copy(face[300:365, 670:750]) # right eye >>> template -= template.mean() >>> face = face + rng.standard_normal(face.shape) * 50 # add noise >>> corr = signal.correlate2d(face, template, boundary='symm', mode='same') >>> y, x = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(corr), corr.shape) # find the match
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, (ax_orig, ax_template, ax_corr) = plt.subplots(3, 1, ... figsize=(6, 15)) >>> ax_orig.imshow(face, cmap='gray') >>> ax_orig.set_title('Original') >>> ax_orig.set_axis_off() >>> ax_template.imshow(template, cmap='gray') >>> ax_template.set_title('Template') >>> ax_template.set_axis_off() >>> ax_corr.imshow(corr, cmap='gray') >>> ax_corr.set_title('Cross-correlation') >>> ax_corr.set_axis_off() >>> ax_orig.plot(x, y, 'ro') >>> fig.show()