注解
Click here 下载完整的示例代码
创建带注释的热图¶
通常需要将依赖于两个独立变量的数据显示为彩色编码图像图。这通常被称为热图。如果数据是绝对的,这将被称为绝对热图。
Matplotlib imshow 功能使这些图的制作特别容易。
下面的示例演示如何使用注释创建热图。我们将从一个简单的示例开始,并将其扩展为可用的通用函数。
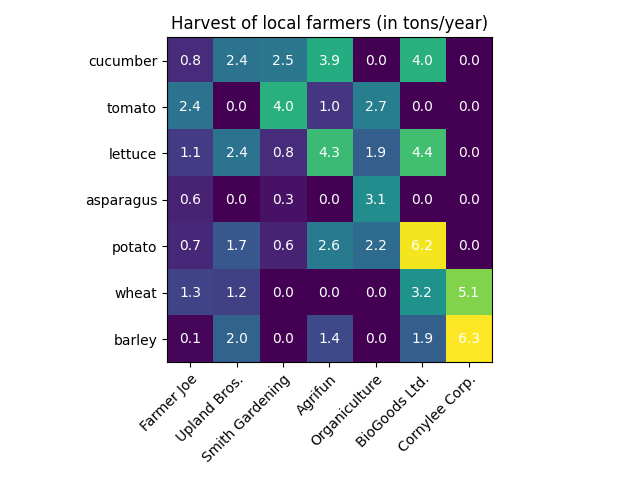
简单的分类热图¶
我们可以先定义一些数据。我们需要的是一个二维列表或数组,它将数据定义为颜色代码。然后我们还需要两个列表或类别数组;当然,这些列表中的元素数量需要沿着各自的轴匹配数据。热天本身就是一个 imshow 根据我们的类别绘制标签。请注意,必须同时设置两个勾号位置 (set_xticks )以及刻度线标签 (set_xticklabels 否则,它们就会失去同步。位置只是升序整数,而滴答标签是要显示的标签。最后,我们可以通过创建 Text 在每个单元格中显示该单元格的值。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
vegetables = ["cucumber", "tomato", "lettuce", "asparagus",
"potato", "wheat", "barley"]
farmers = ["Farmer Joe", "Upland Bros.", "Smith Gardening",
"Agrifun", "Organiculture", "BioGoods Ltd.", "Cornylee Corp."]
harvest = np.array([[0.8, 2.4, 2.5, 3.9, 0.0, 4.0, 0.0],
[2.4, 0.0, 4.0, 1.0, 2.7, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.1, 2.4, 0.8, 4.3, 1.9, 4.4, 0.0],
[0.6, 0.0, 0.3, 0.0, 3.1, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.7, 1.7, 0.6, 2.6, 2.2, 6.2, 0.0],
[1.3, 1.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.2, 5.1],
[0.1, 2.0, 0.0, 1.4, 0.0, 1.9, 6.3]])
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = ax.imshow(harvest)
# We want to show all ticks...
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(farmers)))
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(len(vegetables)))
# ... and label them with the respective list entries
ax.set_xticklabels(farmers)
ax.set_yticklabels(vegetables)
# Rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45, ha="right",
rotation_mode="anchor")
# Loop over data dimensions and create text annotations.
for i in range(len(vegetables)):
for j in range(len(farmers)):
text = ax.text(j, i, harvest[i, j],
ha="center", va="center", color="w")
ax.set_title("Harvest of local farmers (in tons/year)")
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
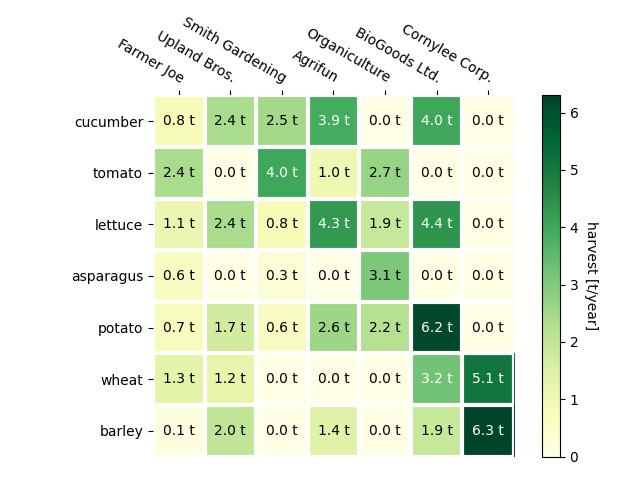
使用助手函数代码样式¶
如中所述 Coding styles 人们可能希望重用这些代码来为不同的输入数据和/或在不同的轴上创建某种heatmap。我们创建了一个函数,将数据、行和列标签作为输入,并允许用于自定义绘图的参数
在这里,除了上面的内容,我们还想创建一个颜色条,并将标签放在heatmap的上方而不是下方。注释应根据阈值获得不同的颜色,以便与像素颜色形成更好的对比。最后,我们关闭周围的轴,并创建一个白色网格线来分隔单元格。
def heatmap(data, row_labels, col_labels, ax=None,
cbar_kw={}, cbarlabel="", **kwargs):
"""
Create a heatmap from a numpy array and two lists of labels.
Parameters
----------
data
A 2D numpy array of shape (N, M).
row_labels
A list or array of length N with the labels for the rows.
col_labels
A list or array of length M with the labels for the columns.
ax
A `matplotlib.axes.Axes` instance to which the heatmap is plotted. If
not provided, use current axes or create a new one. Optional.
cbar_kw
A dictionary with arguments to `matplotlib.Figure.colorbar`. Optional.
cbarlabel
The label for the colorbar. Optional.
**kwargs
All other arguments are forwarded to `imshow`.
"""
if not ax:
ax = plt.gca()
# Plot the heatmap
im = ax.imshow(data, **kwargs)
# Create colorbar
cbar = ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax, **cbar_kw)
cbar.ax.set_ylabel(cbarlabel, rotation=-90, va="bottom")
# We want to show all ticks...
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(data.shape[1]))
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(data.shape[0]))
# ... and label them with the respective list entries.
ax.set_xticklabels(col_labels)
ax.set_yticklabels(row_labels)
# Let the horizontal axes labeling appear on top.
ax.tick_params(top=True, bottom=False,
labeltop=True, labelbottom=False)
# Rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=-30, ha="right",
rotation_mode="anchor")
# Turn spines off and create white grid.
for edge, spine in ax.spines.items():
spine.set_visible(False)
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(data.shape[1]+1)-.5, minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(data.shape[0]+1)-.5, minor=True)
ax.grid(which="minor", color="w", linestyle='-', linewidth=3)
ax.tick_params(which="minor", bottom=False, left=False)
return im, cbar
def annotate_heatmap(im, data=None, valfmt="{x:.2f}",
textcolors=("black", "white"),
threshold=None, **textkw):
"""
A function to annotate a heatmap.
Parameters
----------
im
The AxesImage to be labeled.
data
Data used to annotate. If None, the image's data is used. Optional.
valfmt
The format of the annotations inside the heatmap. This should either
use the string format method, e.g. "$ {x:.2f}", or be a
`matplotlib.ticker.Formatter`. Optional.
textcolors
A pair of colors. The first is used for values below a threshold,
the second for those above. Optional.
threshold
Value in data units according to which the colors from textcolors are
applied. If None (the default) uses the middle of the colormap as
separation. Optional.
**kwargs
All other arguments are forwarded to each call to `text` used to create
the text labels.
"""
if not isinstance(data, (list, np.ndarray)):
data = im.get_array()
# Normalize the threshold to the images color range.
if threshold is not None:
threshold = im.norm(threshold)
else:
threshold = im.norm(data.max())/2.
# Set default alignment to center, but allow it to be
# overwritten by textkw.
kw = dict(horizontalalignment="center",
verticalalignment="center")
kw.update(textkw)
# Get the formatter in case a string is supplied
if isinstance(valfmt, str):
valfmt = matplotlib.ticker.StrMethodFormatter(valfmt)
# Loop over the data and create a `Text` for each "pixel".
# Change the text's color depending on the data.
texts = []
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
for j in range(data.shape[1]):
kw.update(color=textcolors[int(im.norm(data[i, j]) > threshold)])
text = im.axes.text(j, i, valfmt(data[i, j], None), **kw)
texts.append(text)
return texts
上面的内容现在可以让我们保持实际的情节创建非常紧凑。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im, cbar = heatmap(harvest, vegetables, farmers, ax=ax,
cmap="YlGn", cbarlabel="harvest [t/year]")
texts = annotate_heatmap(im, valfmt="{x:.1f} t")
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
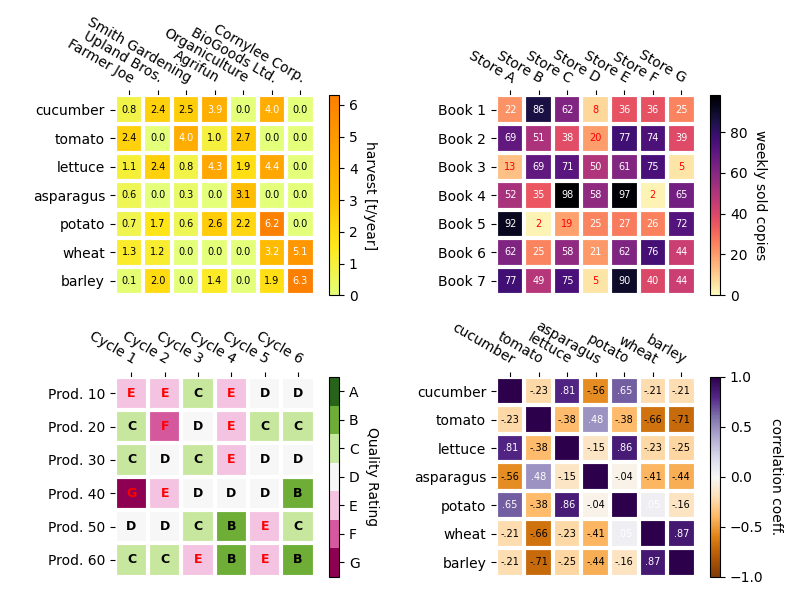
一些更复杂的热图例子¶
在下面,我们将展示先前创建的函数的多功能性,方法是将它应用于不同的情况和使用不同的参数。
np.random.seed(19680801)
fig, ((ax, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 6))
# Replicate the above example with a different font size and colormap.
im, _ = heatmap(harvest, vegetables, farmers, ax=ax,
cmap="Wistia", cbarlabel="harvest [t/year]")
annotate_heatmap(im, valfmt="{x:.1f}", size=7)
# Create some new data, give further arguments to imshow (vmin),
# use an integer format on the annotations and provide some colors.
data = np.random.randint(2, 100, size=(7, 7))
y = ["Book {}".format(i) for i in range(1, 8)]
x = ["Store {}".format(i) for i in list("ABCDEFG")]
im, _ = heatmap(data, y, x, ax=ax2, vmin=0,
cmap="magma_r", cbarlabel="weekly sold copies")
annotate_heatmap(im, valfmt="{x:d}", size=7, threshold=20,
textcolors=("red", "white"))
# Sometimes even the data itself is categorical. Here we use a
# `matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm` to get the data into classes
# and use this to colorize the plot, but also to obtain the class
# labels from an array of classes.
data = np.random.randn(6, 6)
y = ["Prod. {}".format(i) for i in range(10, 70, 10)]
x = ["Cycle {}".format(i) for i in range(1, 7)]
qrates = list("ABCDEFG")
norm = matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm(np.linspace(-3.5, 3.5, 8), 7)
fmt = matplotlib.ticker.FuncFormatter(lambda x, pos: qrates[::-1][norm(x)])
im, _ = heatmap(data, y, x, ax=ax3,
cmap=plt.get_cmap("PiYG", 7), norm=norm,
cbar_kw=dict(ticks=np.arange(-3, 4), format=fmt),
cbarlabel="Quality Rating")
annotate_heatmap(im, valfmt=fmt, size=9, fontweight="bold", threshold=-1,
textcolors=("red", "black"))
# We can nicely plot a correlation matrix. Since this is bound by -1 and 1,
# we use those as vmin and vmax. We may also remove leading zeros and hide
# the diagonal elements (which are all 1) by using a
# `matplotlib.ticker.FuncFormatter`.
corr_matrix = np.corrcoef(harvest)
im, _ = heatmap(corr_matrix, vegetables, vegetables, ax=ax4,
cmap="PuOr", vmin=-1, vmax=1,
cbarlabel="correlation coeff.")
def func(x, pos):
return "{:.2f}".format(x).replace("0.", ".").replace("1.00", "")
annotate_heatmap(im, valfmt=matplotlib.ticker.FuncFormatter(func), size=7)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
工具书类¶
以下函数和方法的用法如本例所示:
出:
<function colorbar at 0x7faa00ce1ea0>
脚本的总运行时间: (0分3.116秒)
关键词:matplotlib代码示例,codex,python plot,pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery