注解
Click here 下载完整的示例代码
起源 和 程度 在里面 imshow¶
imshow() 允许您渲染图像(二维数组,它将被颜色映射(基于 norm 和 cmap )或者一个3D-RGB(a)数组,它将按原样使用到数据空间中的矩形区域。最终渲染中图像的方向由控制 起源 和 程度 Kwargs(和结果的属性 AxesImage 实例)和轴的数据限制。
这个 程度 Kwarg控制图像将填充的数据坐标中的边界框,指定为 (left, right, bottom, top) 在里面 数据坐标 , the 起源 Kwarg控制图像如何填充该边界框,最终渲染图像中的方向也受轴限制的影响。
提示
下面的大部分代码用于向绘图添加标签和信息性文本。描述的影响 起源 和 程度 可以在图中看到,无需遵循所有代码详细信息。
为了快速理解,您可能希望跳过下面的代码详细信息,直接继续讨论结果。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
def index_to_coordinate(index, extent, origin):
"""Return the pixel center of an index."""
left, right, bottom, top = extent
hshift = 0.5 * np.sign(right - left)
left, right = left + hshift, right - hshift
vshift = 0.5 * np.sign(top - bottom)
bottom, top = bottom + vshift, top - vshift
if origin == 'upper':
bottom, top = top, bottom
return {
"[0, 0]": (left, bottom),
"[M', 0]": (left, top),
"[0, N']": (right, bottom),
"[M', N']": (right, top),
}[index]
def get_index_label_pos(index, extent, origin, inverted_xindex):
"""
Return the desired position and horizontal alignment of an index label.
"""
if extent is None:
extent = lookup_extent(origin)
left, right, bottom, top = extent
x, y = index_to_coordinate(index, extent, origin)
is_x0 = index[-2:] == "0]"
halign = 'left' if is_x0 ^ inverted_xindex else 'right'
hshift = 0.5 * np.sign(left - right)
x += hshift * (1 if is_x0 else -1)
return x, y, halign
def get_color(index, data, cmap):
"""Return the data color of an index."""
val = {
"[0, 0]": data[0, 0],
"[0, N']": data[0, -1],
"[M', 0]": data[-1, 0],
"[M', N']": data[-1, -1],
}[index]
return cmap(val / data.max())
def lookup_extent(origin):
"""Return extent for label positioning when not given explicitly."""
if origin == 'lower':
return (-0.5, 6.5, -0.5, 5.5)
else:
return (-0.5, 6.5, 5.5, -0.5)
def set_extent_None_text(ax):
ax.text(3, 2.5, 'equals\nextent=None', size='large',
ha='center', va='center', color='w')
def plot_imshow_with_labels(ax, data, extent, origin, xlim, ylim):
"""Actually run ``imshow()`` and add extent and index labels."""
im = ax.imshow(data, origin=origin, extent=extent)
# extent labels (left, right, bottom, top)
left, right, bottom, top = im.get_extent()
if xlim is None or top > bottom:
upper_string, lower_string = 'top', 'bottom'
else:
upper_string, lower_string = 'bottom', 'top'
if ylim is None or left < right:
port_string, starboard_string = 'left', 'right'
inverted_xindex = False
else:
port_string, starboard_string = 'right', 'left'
inverted_xindex = True
bbox_kwargs = {'fc': 'w', 'alpha': .75, 'boxstyle': "round4"}
ann_kwargs = {'xycoords': 'axes fraction',
'textcoords': 'offset points',
'bbox': bbox_kwargs}
ax.annotate(upper_string, xy=(.5, 1), xytext=(0, -1),
ha='center', va='top', **ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(lower_string, xy=(.5, 0), xytext=(0, 1),
ha='center', va='bottom', **ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(port_string, xy=(0, .5), xytext=(1, 0),
ha='left', va='center', rotation=90,
**ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(starboard_string, xy=(1, .5), xytext=(-1, 0),
ha='right', va='center', rotation=-90,
**ann_kwargs)
ax.set_title('origin: {origin}'.format(origin=origin))
# index labels
for index in ["[0, 0]", "[0, N']", "[M', 0]", "[M', N']"]:
tx, ty, halign = get_index_label_pos(index, extent, origin,
inverted_xindex)
facecolor = get_color(index, data, im.get_cmap())
ax.text(tx, ty, index, color='white', ha=halign, va='center',
bbox={'boxstyle': 'square', 'facecolor': facecolor})
if xlim:
ax.set_xlim(*xlim)
if ylim:
ax.set_ylim(*ylim)
def generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents, xlim=None, ylim=None):
N = len(extents)
fig = plt.figure(tight_layout=True)
fig.set_size_inches(6, N * (11.25) / 5)
gs = GridSpec(N, 5, figure=fig)
columns = {'label': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 0]) for j in range(N)],
'upper': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 1:3]) for j in range(N)],
'lower': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 3:5]) for j in range(N)]}
x, y = np.ogrid[0:6, 0:7]
data = x + y
for origin in ['upper', 'lower']:
for ax, extent in zip(columns[origin], extents):
plot_imshow_with_labels(ax, data, extent, origin, xlim, ylim)
columns['label'][0].set_title('extent=')
for ax, extent in zip(columns['label'], extents):
if extent is None:
text = 'None'
else:
left, right, bottom, top = extent
text = (f'left: {left:0.1f}\nright: {right:0.1f}\n'
f'bottom: {bottom:0.1f}\ntop: {top:0.1f}\n')
ax.text(1., .5, text, transform=ax.transAxes, ha='right', va='center')
ax.axis('off')
return columns
默认范围¶
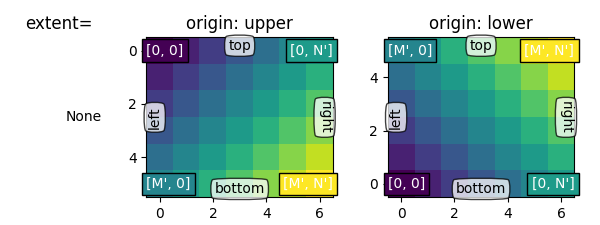
首先,让我们看一下默认值 extent=None
generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents=[None])
出:
{'label': [<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'extent='}>], 'upper': [<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'origin: upper'}>], 'lower': [<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'origin: lower'}>]}
通常,对于形状数组(m,n),第一个索引沿垂直方向运行,第二个索引沿水平方向运行。像素中心位于0到 N' = N - 1 水平,从0到 M' = M - 1 垂直地。 起源 确定如何在边界框中填充数据。
为了 origin='lower' :
- [0, 0] 位于(左、下)
- [M′,0] 位于(左上)
- [0,N’] 位于(右、下)
- [M’,N’] 位于(右上)
origin='upper' 反转垂直轴方向和填充:
- [0, 0] 位于(左上)
- [M′,0] 位于(左、下)
- [0,N’] 位于(右上)
- [M’,N’] 位于(右、下)
总的来说, [0, 0] 指数以及受 起源 :
| 起源 | [0, 0] 位置 | 程度 |
|---|---|---|
| 上面的 | 左上角 | (-0.5, numcols-0.5, numrows-0.5, -0.5) |
| 降低 | 左下角 | (-0.5, numcols-0.5, -0.5, numrows-0.5) |
默认值为 起源 是由 rcParams["image.origin"] (default: 'upper') 默认为 'upper' 匹配数学和计算机图形图像索引约定中的矩阵索引约定。
显式范围¶
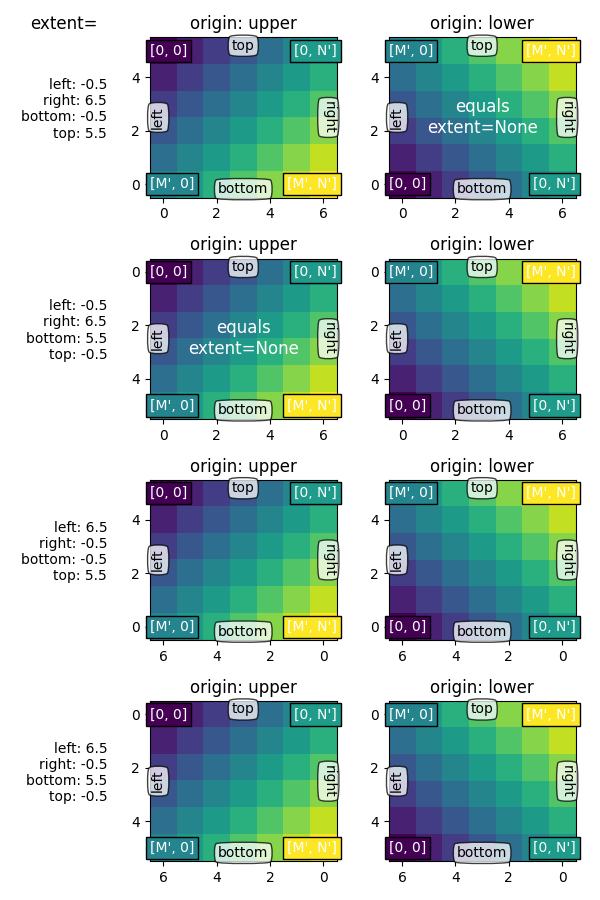
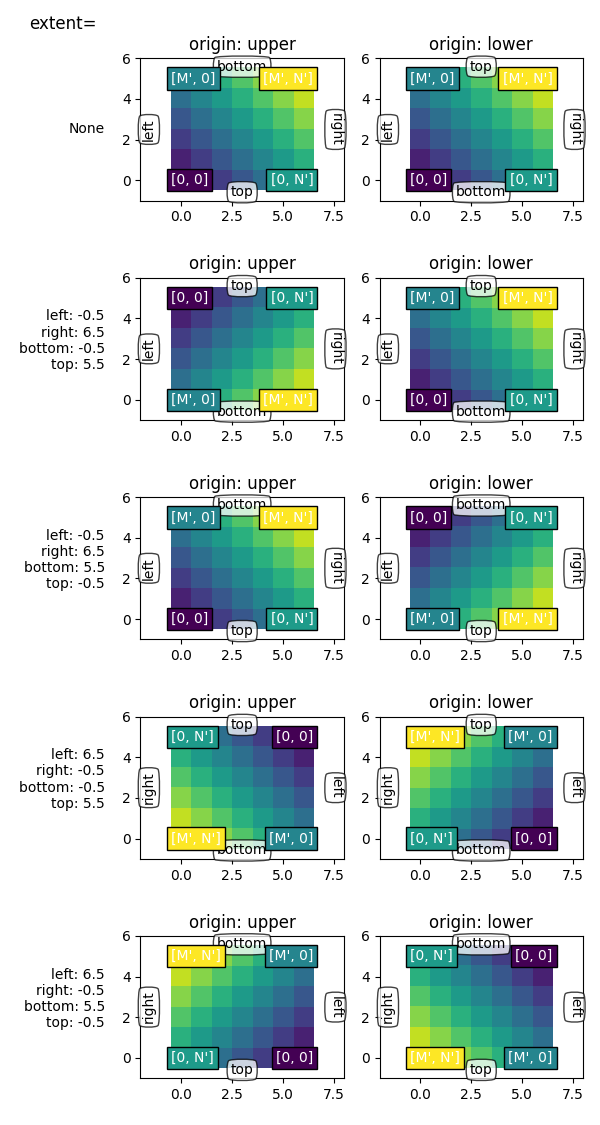
通过设置 程度 我们定义图像区域的坐标。对底层图像数据进行插值/重采样以填充该区域。
如果轴设置为自动缩放,则轴的视图限制设置为与 程度 这样可以确保 (left, bottom) 在轴的左下角!但是,这可能会使轴反转,因此它们不会在“自然”方向上增加。
显式范围和轴限制¶
如果我们通过显式设置来固定轴限制 set_xlim / set_ylim ,我们强制确定轴的大小和方向。这可以将图像的“左-右”和“上-下”感觉与屏幕上的方向分离。
在下面的示例中,我们选择了比范围稍大的限制(注意轴内的白色区域)。
当我们像前面的例子一样保留范围时,坐标(0,0)现在显式地放在左下角,值向上和向右增加(从观察者的角度)。我们可以看到:
- 坐标系
(left, bottom)定位图像,然后将其填充到框中(right, top)指向数据空间。 - 第一列总是最靠近“左”。
- 起源 控制第一行是否最接近“top”或“bottom”。
- 图像可以沿任一方向反转。
- 图像的“左-右”和“上-下”感觉可能与屏幕上的方向分离。
脚本的总运行时间: (0分3.163秒)
关键词:matplotlib代码示例,codex,python plot,pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery