注解
Click here 下载完整的示例代码
曲线网格演示¶
自定义网格和刻度线。
这个例子演示了如何使用 GridHelperCurveLinear 通过在网格上应用转换来定义自定义网格和记号线。如第二张图所示,这可以用于在矩形框中创建极轴投影。
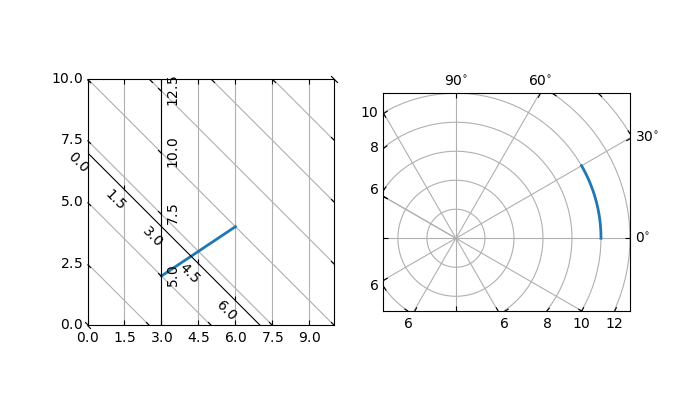
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.projections import PolarAxes
from matplotlib.transforms import Affine2D
from mpl_toolkits.axisartist import (
angle_helper, Subplot, SubplotHost, ParasiteAxesAuxTrans)
from mpl_toolkits.axisartist.grid_helper_curvelinear import (
GridHelperCurveLinear)
def curvelinear_test1(fig):
"""
Grid for custom transform.
"""
def tr(x, y):
x, y = np.asarray(x), np.asarray(y)
return x, y - x
def inv_tr(x, y):
x, y = np.asarray(x), np.asarray(y)
return x, y + x
grid_helper = GridHelperCurveLinear((tr, inv_tr))
ax1 = Subplot(fig, 1, 2, 1, grid_helper=grid_helper)
# ax1 will have a ticks and gridlines defined by the given
# transform (+ transData of the Axes). Note that the transform of
# the Axes itself (i.e., transData) is not affected by the given
# transform.
fig.add_subplot(ax1)
xx, yy = tr([3, 6], [5, 10])
ax1.plot(xx, yy, linewidth=2.0)
ax1.set_aspect(1)
ax1.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 10)
ax1.axis["t"] = ax1.new_floating_axis(0, 3)
ax1.axis["t2"] = ax1.new_floating_axis(1, 7)
ax1.grid(True, zorder=0)
def curvelinear_test2(fig):
"""
Polar projection, but in a rectangular box.
"""
# PolarAxes.PolarTransform takes radian. However, we want our coordinate
# system in degree
tr = Affine2D().scale(np.pi/180, 1) + PolarAxes.PolarTransform()
# Polar projection, which involves cycle, and also has limits in
# its coordinates, needs a special method to find the extremes
# (min, max of the coordinate within the view).
extreme_finder = angle_helper.ExtremeFinderCycle(
nx=20, ny=20, # Number of sampling points in each direction.
lon_cycle=360, lat_cycle=None,
lon_minmax=None, lat_minmax=(0, np.inf),
)
# Find grid values appropriate for the coordinate (degree, minute, second).
grid_locator1 = angle_helper.LocatorDMS(12)
# Use an appropriate formatter. Note that the acceptable Locator and
# Formatter classes are a bit different than that of Matplotlib, which
# cannot directly be used here (this may be possible in the future).
tick_formatter1 = angle_helper.FormatterDMS()
grid_helper = GridHelperCurveLinear(
tr, extreme_finder=extreme_finder,
grid_locator1=grid_locator1, tick_formatter1=tick_formatter1)
ax1 = SubplotHost(fig, 1, 2, 2, grid_helper=grid_helper)
# make ticklabels of right and top axis visible.
ax1.axis["right"].major_ticklabels.set_visible(True)
ax1.axis["top"].major_ticklabels.set_visible(True)
# let right axis shows ticklabels for 1st coordinate (angle)
ax1.axis["right"].get_helper().nth_coord_ticks = 0
# let bottom axis shows ticklabels for 2nd coordinate (radius)
ax1.axis["bottom"].get_helper().nth_coord_ticks = 1
fig.add_subplot(ax1)
ax1.set_aspect(1)
ax1.set_xlim(-5, 12)
ax1.set_ylim(-5, 10)
ax1.grid(True, zorder=0)
# A parasite axes with given transform
ax2 = ParasiteAxesAuxTrans(ax1, tr, "equal")
# note that ax2.transData == tr + ax1.transData
# Anything you draw in ax2 will match the ticks and grids of ax1.
ax1.parasites.append(ax2)
ax2.plot(np.linspace(0, 30, 51), np.linspace(10, 10, 51), linewidth=2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 4))
curvelinear_test1(fig)
curvelinear_test2(fig)
plt.show()
关键词:matplotlib代码示例,codex,python plot,pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery