matplotlib.transforms¶

Matplotlib包含用于确定画布上绘制的所有元素的最终位置的任意几何变换的框架。
转换被组成树 TransformNode 其实际值取决于其子级的对象。当孩子的内容发生变化时,他们的父母将自动失效。下次访问失效的转换时,将重新计算以反映这些更改。这种无效/缓存方法可以防止不必要的转换重新编译,并有助于提高交互性能。
例如,下面是用于将数据绘制到图表的转换树的图:
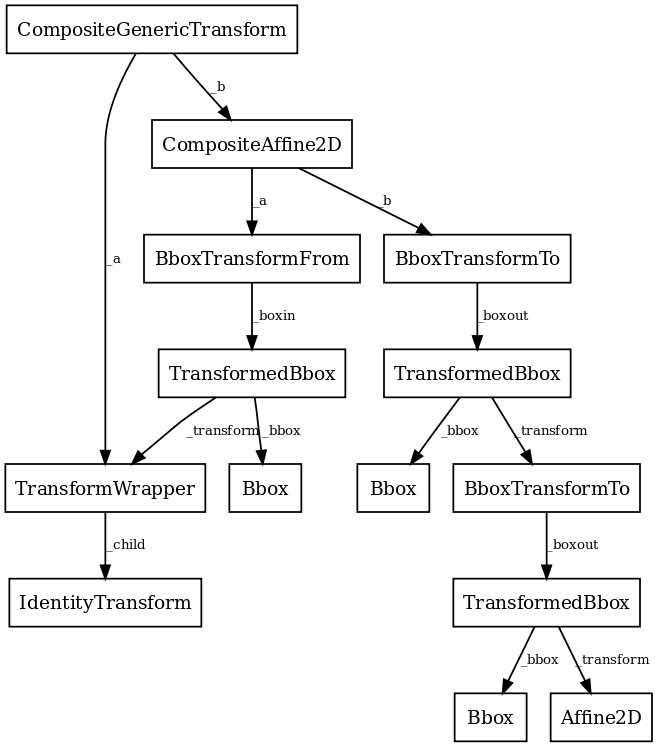
该框架既可用于仿射转换,也可用于非仿射转换。但是,为了提高速度,我们希望尽可能使用后端渲染器执行仿射转换。因此,在一组数据上只执行转换的仿射或非仿射部分是可能的。仿射总是假定发生在非仿射之后。对于任何转换:
full transform == non-affine part + affine part
后端不应该自己处理非仿射转换。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2D(matrix=None, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase可变的二维仿射变换。
从3x3 numpy float数组初始化仿射转换:
a c e b d f 0 0 1
如果 矩阵 为“无”,使用标识转换初始化。
-
__init__(matrix=None, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 从3x3 numpy float数组初始化仿射转换:
a c e b d f 0 0 1
如果 矩阵 为“无”,使用标识转换初始化。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
static
identity()[源代码]¶ 返回一个新的
Affine2D对象,它是标识转换。除非此转换稍后会发生变化,否则请考虑使用
IdentityTransform改为类。
-
rotate(theta)[源代码]¶ 将旋转(以弧度)添加到此转换中。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
rotate_around(x, y, theta)[源代码]¶ 添加围绕点(x,y)的旋转(以弧度为单位)。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
rotate_deg(degrees)[源代码]¶ 将旋转(以度为单位)添加到此转换中。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
rotate_deg_around(x, y, degrees)[源代码]¶ 在适当位置围绕点(X,Y)添加旋转(以度为单位)。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
scale(sx, sy=None)[源代码]¶ 在适当位置添加比例。
如果 sy 为“无”,在两个 x -和 y -方向。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
set(other)[源代码]¶ 从另一个已冻结的副本设置此转换
Affine2DBase对象。
-
skew(xShear, yShear)[源代码]¶ 在适当位置添加倾斜。
X剪 和 YS剪力 剪切角是沿着 x -和 y -轴,分别以弧度表示。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
skew_deg(xShear, yShear)[源代码]¶ 在适当位置添加倾斜。
X剪 和 YS剪力 剪切角是沿着 x -和 y -轴,分别以度为单位。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
translate(tx, ty)[源代码]¶ 在适当位置添加翻译。
返回 self ,因此此方法可以很容易地与对
rotate(),rotate_deg(),translate()和scale().
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase(*args, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.AffineBase所有二维仿射变换的基类。
使用3x3 numpy数组执行二维仿射转换:
a c e b d f 0 0 1
此类提供只读接口。对于可变的二维仿射变换,请使用
Affine2D.此类的子类通常只需要重写构造函数和
get_matrix()生成自定义3x3矩阵。参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
has_inverse= True¶
-
input_dims= 2¶
-
inverted()[源代码]¶ 返回相应的逆变换。
它坚持住了
x == self.inverted().transform(self.transform(x)).此方法的返回值应视为临时值。对…的更新 self 不会对其反向副本进行相应的更新。
-
property
is_separable¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
static
matrix_from_values(a, b, c, d, e, f)[源代码]¶ [Deprecated] 以3x3 numpy数组的形式创建一个新的转换矩阵:
a c e b d f 0 0 1
笔记
3.2 版后已移除.
-
output_dims= 2¶
-
transform_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅对给定的值数组应用此变换的仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常是不可操作的。在仿射变换中,这相当于
transform(values).参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.AffineBase(*args, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Transform任何维数的所有仿射变换的基类。
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__hash__= None¶
-
__init__(*args, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
is_affine= True¶
-
transform(values)[源代码]¶ 将此转换应用于给定的 价值观 .
参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_affine(values)[源代码]¶ 仅对给定的值数组应用此变换的仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常是不可操作的。在仿射变换中,这相当于
transform(values).参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_non_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅应用此变换的非仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常等价于
transform(values). 在仿射变换中,这总是一个不运算。参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_path(path)[源代码]¶ Apply the transform to
Pathpath, returning a newPath.在某些情况下,此转换可能会将曲线插入以直线段开始的路径中。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.AffineDeltaTransform(transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase用于在点对之间变换位移的变换包装器。
此类用于转换成对点之间的位移(“位置增量”)(例如
offset_transform属于Collections) :给定变换t这样的话t = AffineDeltaTransform(t) + offset,AffineDeltaTransform满足AffineDeltaTransform(a - b) == AffineDeltaTransform(a) - AffineDeltaTransform(b).这是通过强制变换矩阵的偏移分量为零来实现的。
这个类从3.3开始是实验性的,API可能会改变。
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__init__(transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.Bbox(points, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.BboxBase可变边界框。
实例
从已知边界创建
默认构造函数接受边界“点”
[[xmin, ymin], [xmax, ymax]].>>> Bbox([[1, 1], [3, 7]]) Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [3.0, 7.0]])
或者,可以从展平点数组创建Bbox,即所谓的“范围”
(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)>>> Bbox.from_extents(1, 1, 3, 7) Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [3.0, 7.0]])
或者从“边界”
(xmin, ymin, width, height).>>> Bbox.from_bounds(1, 1, 2, 6) Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [3.0, 7.0]])
从点集合创建
用于累积bbox的“empty”对象是null bbox,它是空集的替代对象。
>>> Bbox.null() Bbox([[inf, inf], [-inf, -inf]])
将点添加到空bbox将得到这些点的bbox。
>>> box = Bbox.null() >>> box.update_from_data_xy([[1, 1]]) >>> box Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0]]) >>> box.update_from_data_xy([[2, 3], [3, 2]], ignore=False) >>> box Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [3.0, 3.0]])
设置
ignore=True相当于从空bbox重新开始。>>> box.update_from_data_xy([[1, 1]], ignore=True) >>> box Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0]])
警告
建议始终指定
ignore明确地。如果不是,则默认值为ignore可以通过访问Bbox的代码随时更改,例如使用ignore.Properties of the ``null`` bbox
注解
当前的行为
Bbox.null()这可能令人惊讶,因为它不具备“空集”的所有属性,因此在数学意义上也不像“零”对象。我们可能会在将来改变这一点(有一个折旧期)。空bbox是交叉点的标识
>>> Bbox.intersection(Bbox([[1, 1], [3, 7]]), Bbox.null()) Bbox([[1.0, 1.0], [3.0, 7.0]])
除了它本身,它返回完整的空间。
>>> Bbox.intersection(Bbox.null(), Bbox.null()) Bbox([[-inf, -inf], [inf, inf]])
包含null的并集将始终返回完整的空间(而不是另一个集!)
>>> Bbox.union([Bbox([[0, 0], [0, 0]]), Bbox.null()]) Bbox([[-inf, -inf], [inf, inf]])
参数: - points恩达雷
窗体的2x2 numpy数组
[[x0, y0], [x1, y1]].
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
ignore(value)[源代码]¶ 设置后续调用是否应忽略框的现有边界
update_from_data_xy().- 价值布尔
- 什么时候?
True,后续呼叫update_from_data_xy()将忽略Bbox. - 什么时候?
False,后续呼叫update_from_data_xy()将包括Bbox.
- 什么时候?
-
property
intervalx¶ 一对 x 定义边界框的坐标。
不能保证从左到右排序。
-
property
intervaly¶ 一对 y 定义边界框的坐标。
不能保证从下到上进行排序。
-
property
minpos¶
-
property
minposx¶
-
property
minposy¶
-
property
p0¶ 第一对( x , y )定义边界框的坐标。
这不保证是左下角(为此,使用
min)
-
property
p1¶ 第二对( x , y )定义边界框的坐标。
不能保证这是右上角(为此,使用
max)
-
update_from_data_xy(xy, ignore=None, updatex=True, updatey=True)[源代码]¶ 更新
Bbox基于传入的数据。更新后,边界将为正 宽度 和 高度 ; x0 和 y0 将是最小值。参数:
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BboxBase(shorthand_name=None)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.TransformNode所有边界框的基类。
这个类是不变的;
Bbox是一个可变的子类。规范化表示是两点,对它们的排序没有限制。提供了方便的属性来获取左、下、右和上边缘以及宽度和高度,但这些属性没有显式存储。
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
coefs= {'C': (0.5, 0.5), 'E': (1.0, 0.5), 'N': (0.5, 1.0), 'NE': (1.0, 1.0), 'NW': (0, 1.0), 'S': (0.5, 0), 'SE': (1.0, 0), 'SW': (0, 0), 'W': (0, 0.5)}¶
-
property
height¶ 边界框的(有符号的)高度。
-
property
intervalx¶ 一对 x 定义边界框的坐标。
不能保证从左到右排序。
-
property
intervaly¶ 一对 y 定义边界框的坐标。
不能保证从下到上进行排序。
-
is_affine= True¶
-
is_bbox= True¶
-
property
max¶ 边界框的右上角。
-
property
min¶ 边界框的左下角。
-
shrunk_to_aspect(box_aspect, container=None, fig_aspect=1.0)[源代码]¶ 返回的副本
Bbox收缩,使其尽可能大,同时具有所需的纵横比, box_aspect . 如果方框坐标是相对的(即较大方框的分数,如图形),则该图形的物理纵横比用 fig_aspect ,这样 box_aspect 也可以以绝对尺寸的比率给出,而不是相对尺寸。
-
property
size¶ 边界框的(有符号的)宽度和高度。
-
property
width¶ 边界框的(有符号的)宽度。
-
property
xmax¶ 边界框的右边缘。
-
property
xmin¶ 边界框的左边缘。
-
property
ymax¶ 边界框的上边缘。
-
property
ymin¶ 边界框的底边。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BboxTransform(boxin, boxout, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBaseBboxTransform线性变换点Bbox到另一个。创建新的
BboxTransform线性变换点 博信 到 箱出 .-
__init__(boxin, boxout, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 创建新的
BboxTransform线性变换点 博信 到 箱出 .
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
is_separable= True¶
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BboxTransformFrom(boxin, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBaseBboxTransformFrom从给定的线性变换点Bbox到单元边界框。参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__init__(boxin, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
is_separable= True¶
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BboxTransformTo(boxout, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBaseBboxTransformTo是将点从单元边界框线性转换为给定值的转换。Bbox.创建新的
BboxTransformTo将点从单元边界框线性转换为 箱出 .-
__init__(boxout, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 创建新的
BboxTransformTo将点从单元边界框线性转换为 箱出 .
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
is_separable= True¶
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BboxTransformToMaxOnly(boxout, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.BboxTransformToBboxTransformTo是将点从单元边界框线性转换为给定值的转换。Bbox具有固定的左上角(0,0)。创建新的
BboxTransformTo将点从单元边界框线性转换为 箱出 .-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BlendedAffine2D(x_transform, y_transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms._BlendedMixin,matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase“混合”转换使用一个转换 x -方向和另一个转换 y -方向。
此版本是对两个子转换都属于类型的情况的优化
Affine2DBase.使用创建新的“混合”变换 x_transform 转换 x 轴和 y_transform 转换 y 轴。
两个 x_transform 和 y_transform 必须是二维仿射变换。
通常不直接调用此构造函数,而是使用
blended_transform_factory函数,它可以自动确定要创建哪种混合转换。-
__init__(x_transform, y_transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 使用创建新的“混合”变换 x_transform 转换 x 轴和 y_transform 转换 y 轴。
两个 x_transform 和 y_transform 必须是二维仿射变换。
通常不直接调用此构造函数,而是使用
blended_transform_factory函数,它可以自动确定要创建哪种混合转换。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
is_separable= True¶
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.BlendedGenericTransform(x_transform, y_transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms._BlendedMixin,matplotlib.transforms.Transform“混合”转换使用一个转换 x -方向和另一个转换 y -方向。
这个“通用”版本可以处理 x -和 y -方向。
使用创建新的“混合”变换 x_transform 转换 x 轴和 y_transform 转换 y 轴。
通常不直接调用此构造函数,而是使用
blended_transform_factory函数,它可以自动确定要创建哪种混合转换。-
__init__(x_transform, y_transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 使用创建新的“混合”变换 x_transform 转换 x 轴和 y_transform 转换 y 轴。
通常不直接调用此构造函数,而是使用
blended_transform_factory函数,它可以自动确定要创建哪种混合转换。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
contains_branch(other)[源代码]¶ 返回给定的转换是否是此转换的子树。
此例程使用转换相等来标识子树,因此在许多情况下,将使用对象ID。
对于给定转换表示整个转换的情况,返回true。
-
property
depth¶ 返回已链接在一起以形成此转换实例的转换数。
注解
对于复合变换的特殊情况,返回两个变换的最大深度。
-
property
has_inverse¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
input_dims= 2¶
-
inverted()[源代码]¶ 返回相应的逆变换。
它坚持住了
x == self.inverted().transform(self.transform(x)).此方法的返回值应视为临时值。对…的更新 self 不会对其反向副本进行相应的更新。
-
property
is_affine¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
is_separable= True¶
-
output_dims= 2¶
-
pass_through= True¶
-
transform_non_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅应用此变换的非仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常等价于
transform(values). 在仿射变换中,这总是一个不运算。参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.CompositeAffine2D(a, b, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase应用变换形成的复合变换 a 然后变换 b .
此版本是一个优化,它处理以下情况: a 和 b 是二维仿射。
Create a new composite transform that is the result of applying
Affine2DBasea thenAffine2DBaseb.通常不会直接调用此构造函数,而是编写
a + b相反,它将自动选择要创建的最佳类型的复合变换实例。-
__init__(a, b, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ Create a new composite transform that is the result of applying
Affine2DBasea thenAffine2DBaseb.通常不会直接调用此构造函数,而是编写
a + b相反,它将自动选择要创建的最佳类型的复合变换实例。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
property
depth¶ 返回已链接在一起以形成此转换实例的转换数。
注解
对于复合变换的特殊情况,返回两个变换的最大深度。
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.CompositeGenericTransform(a, b, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Transform应用变换形成的复合变换 a 然后变换 b .
这个“通用”版本可以处理任意两个转换。
创建一个新的复合变换,该变换是应用变换的结果 a 然后变换 b .
通常不会直接调用此构造函数,而是编写
a + b相反,它将自动选择要创建的最佳类型的复合变换实例。-
__hash__= None¶
-
__init__(a, b, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 创建一个新的复合变换,该变换是应用变换的结果 a 然后变换 b .
通常不会直接调用此构造函数,而是编写
a + b相反,它将自动选择要创建的最佳类型的复合变换实例。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
property
depth¶ 返回已链接在一起以形成此转换实例的转换数。
注解
对于复合变换的特殊情况,返回两个变换的最大深度。
-
property
has_inverse¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
inverted()[源代码]¶ 返回相应的逆变换。
它坚持住了
x == self.inverted().transform(self.transform(x)).此方法的返回值应视为临时值。对…的更新 self 不会对其反向副本进行相应的更新。
-
property
is_affine¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
property
is_separable¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
pass_through= True¶
-
transform_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅对给定的值数组应用此变换的仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常是不可操作的。在仿射变换中,这相当于
transform(values).参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.IdentityTransform(*args, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase一个特殊的类,它以快速的方式完成一件事,即身份转换。
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
inverted()[源代码]¶ 返回相应的逆变换。
它坚持住了
x == self.inverted().transform(self.transform(x)).此方法的返回值应视为临时值。对…的更新 self 不会对其反向副本进行相应的更新。
-
transform(points)[源代码]¶ 将此转换应用于给定的 价值观 .
参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅对给定的值数组应用此变换的仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常是不可操作的。在仿射变换中,这相当于
transform(values).参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_non_affine(points)[源代码]¶ 仅应用此变换的非仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常等价于
transform(values). 在仿射变换中,这总是一个不运算。参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_path(path)[源代码]¶ Apply the transform to
Pathpath, returning a newPath.在某些情况下,此转换可能会将曲线插入以直线段开始的路径中。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.LockableBbox(bbox, x0=None, y0=None, x1=None, y1=None, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.BboxBaseA
Bbox其中一些元素可能被锁定在某些值上。当子边界框更改时,此bbox的边界将相应更新,但锁定的元素除外。
参数: - bbox :
Bbox盒子 要包装的子边界框。
- x0浮动或无
X0或无的锁定值保持未锁定。
- y0浮动或无
Y0的锁定值,或“无”保持未锁定。
- x1浮动或无
x1的锁定值,或无以保持解锁。
- y1浮动或无
Y1的锁定值,或无以保持解锁。
-
__init__(bbox, x0=None, y0=None, x1=None, y1=None, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 参数: - bbox :
Bbox盒子 要包装的子边界框。
- x0浮动或无
X0或无的锁定值保持未锁定。
- y0浮动或无
Y0的锁定值,或“无”保持未锁定。
- x1浮动或无
x1的锁定值,或无以保持解锁。
- y1浮动或无
Y1的锁定值,或无以保持解锁。
- bbox :
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
property
locked_x0¶ 浮动或无:用于锁定的X0的值。
-
property
locked_x1¶ 浮动或无:用于锁定x1的值。
-
property
locked_y0¶ 浮动或无:用于锁定Y0的值。
-
property
locked_y1¶ 浮动或无:用于锁定的y1的值。
- bbox :
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.ScaledTranslation(xt, yt, scale_trans, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Affine2DBase转化为 xt 和 yt 之后 xt 和 yt 改变了 scale_trans .
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__init__(xt, yt, scale_trans, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.Transform(shorthand_name=None)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.TransformNode所有人的基本阶级
TransformNode实际执行转换的实例。所有非仿射转换都应该是这个类的子类。新的仿射变换应该是
Affine2D.此类的子类应重写以下成员(至少):
input_dimsoutput_dimstransform()inverted()(如果存在相反的情况)
如果默认值不合适,可以重写以下属性:
is_separable(对于1d->1d变换,默认为True,否则为False)has_inverse(如果inverted()重写,否则为False)
如果转换需要对
matplotlib.path.Path对象,例如在曾经有线段的地方添加曲线,它应该覆盖:参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__add__(other)[源代码]¶ 将两个变换组合在一起 self 其次是 其他 .
A + B返回变换C以便C.transform(x) == B.transform(A.transform(x)).
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__sub__(other)[源代码]¶ 撰写 self 与之相反的 其他 ,取消相同的条款(如果有):
# In general: A - B == A + B.inverted() # (but see note regarding frozen transforms below). # If A "ends with" B (i.e. A == A' + B for some A') we can cancel # out B: (A' + B) - B == A' # Likewise, if B "starts with" A (B = A + B'), we can cancel out A: A - (A + B') == B'.inverted() == B'^-1
取消(而不是天真地返回
A + B.inverted())其重要性有多种原因:- 在计算B的逆时,它避免了浮点误差:
B - B保证完全抵消(导致身份转换),而B + B.inverted()可能会有一个小的epsilon。 B.inverted()始终返回冻结的转换:如果计算A + B + B.inverted()后来变异了B然后B.inverted()不会更新,最后两个学期也不会取消;另一方面,A + B - B永远等于A即使B是变异的。
- 在计算B的逆时,它避免了浮点误差:
-
contains_branch(other)[源代码]¶ 返回给定的转换是否是此转换的子树。
此例程使用转换相等来标识子树,因此在许多情况下,将使用对象ID。
对于给定转换表示整个转换的情况,返回true。
-
contains_branch_seperately(other_transform)[源代码]¶ 返回给定分支是否是每个独立维度上此转换的子树。
此方法的一个常见用途是标识转换是否是包含轴数据转换的混合转换。例如。::
x_isdata, y_isdata = trans.contains_branch_seperately(ax.transData)
-
property
depth¶ 返回已链接在一起以形成此转换实例的转换数。
注解
对于复合变换的特殊情况,返回两个变换的最大深度。
-
has_inverse= False¶ 如果此转换具有相应的逆转换,则为true。
-
input_dims= None¶ 此转换的输入维度数。必须在子类中被重写(用整数)。
-
inverted()[源代码]¶ 返回相应的逆变换。
它坚持住了
x == self.inverted().transform(self.transform(x)).此方法的返回值应视为临时值。对…的更新 self 不会对其反向副本进行相应的更新。
-
is_separable= False¶ 如果此转换在X和Y维度中是可分离的,则为真。
-
output_dims= None¶ 此转换的输出维度数。必须在子类中被重写(用整数)。
-
transform(values)[源代码]¶ 将此转换应用于给定的 价值观 .
参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_affine(values)[源代码]¶ 仅对给定的值数组应用此变换的仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常是不可操作的。在仿射变换中,这相当于
transform(values).参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_angles(angles, pts, radians=False, pushoff=1e-05)[源代码]¶ 变换固定在特定位置的一组角度。
参数: - angles(N,)类数组
要变换的角度。
- pts(n,2)类似阵列
角度锚定的点。
- radiansbool,默认值:False
是否 角 是弧度或度。
- pushoff浮动
对于每个点 pts 和角度 角 ,通过变换一段长度来计算变换后的角度 推送 从该点开始,使该角度相对于水平轴,然后测量水平轴与转换段之间的角度。
返回: - (N,)数组
-
transform_bbox(bbox)[源代码]¶ 转换给定的边界框。
有关包括缓存在内的更智能的转换(Matplotlib中的一个常见要求),请参见
TransformedBbox.
-
transform_non_affine(values)[源代码]¶ 仅应用此变换的非仿射部分。
transform(values)总是等价于transform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).在非仿射变换中,这通常等价于
transform(values). 在仿射变换中,这总是一个不运算。参数: - values数组
输入值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxinput_dims)
返回: - 数组
输出值为NumPy数组的长度
input_dims或形状(nxoutput_dims),取决于输入。
-
transform_path(path)[源代码]¶ Apply the transform to
Pathpath, returning a newPath.在某些情况下,此转换可能会将曲线插入以直线段开始的路径中。
-
transform_path_affine(path)[源代码]¶ Apply the affine part of this transform to
Pathpath, returning a newPath.transform_path(path)等于transform_path_affine(transform_path_non_affine(values)).
-
transform_path_non_affine(path)[源代码]¶ Apply the non-affine part of this transform to
Pathpath, returning a newPath.transform_path(path)等于transform_path_affine(transform_path_non_affine(values)).
-
transform_point(point)[源代码]¶ 返回变换后的点。
此函数仅用于向后兼容;更通用的
transform方法能够同时转换点列表和单个点。该点按长度顺序给出。
input_dims. 转换后的点作为长度序列返回output_dims.
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.TransformNode(shorthand_name=None)[源代码]¶ 基类:
object任何参与转换树并需要使其父级无效或被无效的对象的基类。这包括不是真正变换的类,例如边界框,因为有些变换依赖于边界框来计算它们的值。
参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
INVALID= 3¶
-
INVALID_AFFINE= 2¶
-
INVALID_NON_AFFINE= 1¶
-
__deepcopy__(*args)¶
-
__dict__= mappingproxy({'__module__': 'matplotlib.transforms', '__doc__': '\n The base class for anything that participates in the transform tree\n and needs to invalidate its parents or be invalidated. This includes\n classes that are not really transforms, such as bounding boxes, since some\n transforms depend on bounding boxes to compute their values.\n ', '_gid': 0, 'INVALID_NON_AFFINE': 1, 'INVALID_AFFINE': 2, 'INVALID': 3, 'is_affine': False, 'is_bbox': False, 'pass_through': False, '__init__': <function TransformNode.__init__>, '__getstate__': <function TransformNode.__getstate__>, '__setstate__': <function TransformNode.__setstate__>, '__copy__': <function TransformNode.__copy__>, '__deepcopy__': <function TransformNode.__copy__>, 'invalidate': <function TransformNode.invalidate>, '_invalidate_internal': <function TransformNode._invalidate_internal>, 'set_children': <function TransformNode.set_children>, 'frozen': <function TransformNode.frozen>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'TransformNode' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'TransformNode' objects>, '__annotations__': {}})¶
-
__init__(shorthand_name=None)[源代码]¶ 参数: - shorthand_nameSTR
表示转换的“名称”的字符串。除了提高
str(transform)当debug=true时。
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__weakref__¶ 对象的弱引用列表(如果已定义)
-
invalidate()[源代码]¶ 使此无效
TransformNode并引发其祖先的伤残。应在转换更改时调用。
-
is_affine= False¶
-
is_bbox= False¶
-
pass_through= False¶ 如果“通过”为真,则所有祖先都将始终无效,即使“自我”已经无效。
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.TransformWrapper(child)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.Transform一个包含单个子转换并与之等效的助手类。
如果在运行时必须将转换树的节点替换为其他类型的转换,则此功能非常有用。此类允许该替换正确触发无效。
TransformWrapper实例在其整个生命周期内必须具有相同的输入和输出维度,因此子转换只能替换为具有相同维度的另一个子转换。小孩 答:
Transform实例。这个孩子以后可能会被set().-
__hash__= None¶
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
property
has_inverse¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
property
is_affine¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
property
is_separable¶ 布尔(x)->布尔
当参数x为真时返回真,否则返回假。内建的true和false是类bool的唯一两个实例。bool类是int类的子类,不能被子类化。
-
pass_through= True¶
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.TransformedBbox(bbox, transform, **kwargs)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.BboxBaseA
Bbox通过给定的转换自动转换。当子边界框或变换更改时,此边界框的边界将相应更新。参数: -
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
__str__()¶ 返回str(self)。
-
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.TransformedPatchPath(patch)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.TransformedPathA
TransformedPatchPath缓存的非仿射转换副本Patch. 当转换的非仿射部分或修补程序更改时,此缓存副本将自动更新。参数: - 补丁 :
Patch补丁
-
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
- 补丁 :
-
class
matplotlib.transforms.TransformedPath(path, transform)[源代码]¶ 基类:
matplotlib.transforms.TransformNodeA
TransformedPath缓存的非仿射转换副本Path. 当转换的非仿射部分更改时,此缓存副本将自动更新。注解
此类认为路径是不可变的。对路径顶点/代码的任何更新都不会触发转换重新计算。
参数: -
__module__= 'matplotlib.transforms'¶
-
get_transformed_points_and_affine()[源代码]¶ 返回子路径的副本,其中已应用转换的非仿射部分,以及完成转换所需的路径的仿射部分。不像
get_transformed_path_and_affine(),不执行插值。
-
-
matplotlib.transforms.blended_transform_factory(x_transform, y_transform)[源代码]¶ 使用创建新的“混合”变换 x_transform 转换 x 轴和 y_transform 转换 y 轴。
对于两个子转换都是仿射的情况,将返回混合转换的更快版本。
-
matplotlib.transforms.composite_transform_factory(a, b)[源代码]¶ 创建一个新的复合变换,这是应用变换A的结果,然后是变换B。
对于两个子变换都是仿射变换或其中一个子变换是标识变换的情况,将提供混合变换的快捷版本。
也可以使用“+”运算符创建复合转换,例如:
c = a + b
-
matplotlib.transforms.interval_contains(interval, val)[源代码]¶ 检查间隔是否包括给定值。
参数: - interval(浮标,浮标)
间隔的端点。
- val浮动
要检查的值在间隔内。
返回: - 布尔
是否 val 在 间隔 .
-
matplotlib.transforms.interval_contains_open(interval, val)[源代码]¶ 检查(不包括端点)间隔是否包含给定值。
参数: - interval(浮标,浮标)
间隔的端点。
- val浮动
要检查的值在间隔内。
返回: - 布尔
是否 val 在 间隔 .
-
matplotlib.transforms.nonsingular(vmin, vmax, expander=0.001, tiny=1e-15, increasing=True)[源代码]¶ 根据需要修改范围的端点以避免奇点。
参数: - VMN,Vmax浮动
初始端点。
- expander浮动,默认值:0.001
分数 vmin 和 vmax 如果原始间隔太小,则根据 tiny .
- tiny浮动,默认值:1e-15
间隔与其端点的最大绝对值之比的阈值。如果间隔小于此值,它将被扩展。该值应在1e-15或更大范围内;否则间隔将接近双精度分辨率限制。
- increasingbool,默认值:True
如果为真,则交换 vmin , vmax 如果 vmin > vmax .
返回: - VMN,Vmax浮动
端点,必要时展开和/或交换。如果输入是inf或nan,或者两个输入都是0或非常接近于零,则返回- 扩展器 , 扩展器 .