注解
此笔记本可在此处下载: 02_CNN_1_Beauty.ipynb
MECA653学实干
从现有数据集创建简单的美容检测器
Hints: https://github.com/ustcqidi/BeautyPredict
问题陈述
我们将有一个网络摄像头输入。我们怎么才能算出美貌分数呢?
如何学习什么是美?
让我们使用卷积神经网络。
# Fix tensorflow without GPU :( old cuda-10 but cuda-11.2 mismatch
# 1. Install miniconda
# 2. Install cuda-toolkit 11.2
# 3. Install cudnn 8.1
# 4. Install tensorflow-gpu
# !wget -nc https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
# !bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -b -u
# !$HOME/miniconda3/bin/conda init bash
# !conda install cudatoolkit=11.2 -c conda-forge
# !conda install cudnn=8.1 -c conda-forge
# !python3 -m ipykernel install --user --name=base
# !$HOME/miniconda3/bin/pip3 install ipywidgets matplotlib pandas Pillow scipy tensorflow-gpu # tf-nightly-gpu
from io import BytesIO
import urllib
from PIL import Image
import IPython
try:
import ipywidgets as widgets
from ipywidgets import interact, interact_manual
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('ipywidgets is not installed.')
@interact
def predict_from_url(URL='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c0/Nicolas_Cage_Deauville_2013.jpg'):
with urllib.request.urlopen(URL) as url: # Download an image from an URL in RAM memory
img_size = 128
img = Image.open(BytesIO(url.read())).convert('RGB')
img = img.resize((img_size, img_size), Image.BILINEAR)
IPython.display.display(img) # Display the image
# Preprocess image
# img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.img_to_array(img)
# img = preprocess_input(img)
# img = np.expand_dims(img, axis = 0)
# prediction = model.predict(img)[0][0] # Use da model
# print('Predicted beauty:', prediction)
interactive(children=(Text(value='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c0/Nicolas_Cage_Deauville_2…
1.创建数据集
%%capture
![ ! -d 'datasets' ] && echo 'datasets dir not found, will create' && mkdir datasets
![ ! -d 'logs' ] && echo 'logs dir not found, will create' && mkdir logs
![ ! -d 'models' ] && echo 'models dir not found, will create' && mkdir 'models'
![ ! -d './datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2' ] && echo './datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2 not found, will download & unzip it' && wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/circulosmeos/gdown.pl/master/gdown.pl && perl gdown.pl 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w0TorBfTIqbquQVd6k3h_77ypnrvfGwf' './datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2.1.zip' && unzip -n -q -d './datasets/' './datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2.1.zip' && rm -f datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2.1.zip
我们现在将定义一些PATH变量来轻松访问数据集:
import os
dataset_path = os.path.relpath("datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2")
txt_file_path = os.path.join(dataset_path, "train_test_files", "All_labels.txt")
images_path = os.path.join(dataset_path, "Images")
assert os.path.exists(dataset_path)
assert os.path.exists(txt_file_path)
assert os.path.exists(images_path)
print("dataset_path:", dataset_path)
print("txt_file_path:", txt_file_path)
print("images_path:", images_path)
dataset_path: datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2
txt_file_path: datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2/train_test_files/All_labels.txt
images_path: datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2/Images
1.1浏览数据集
我们来看看里面有什么 ``datasets/SCUT-FBP5500_v2/train_test_files/All_labels.txt`` 。
txt_file_path 变量。import pandas as pd
# Mean rate by the 60th raters
df = "add your code to read the textfile in 'txt_file_path' with pandas"
# (columns should be names=["filename", "rating"] and the separator between columns should be a space))'
# WARNING: We will use the column names you just define next.
# By default it's set to "filename" and "rating".
# Next are some useful exploratory statistics:
# Check the 5th first row
# df.head()
# Describe the dataset
# df.describe()
# Rates histogram
# df.rating.hist(bins=30, density=1)
问题
平均评分是多少?
问题
评级范围是多少?
最低费率
最高速率
2.定义卷积神经网络
2.1.创建数据集加载器
为了训练一个神经网络,我们需要给它提供大量的图像作为输入。
import tensorflow as tf
import pkg_resources
for i, gpu in enumerate(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')):
print('Gpu %d:' % i, gpu)
print()
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')[0], True)
# Set mixed precision
if pkg_resources.parse_version(tf.__version__) < pkg_resources.parse_version("2.4.0"):
tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental.set_policy("mixed_float16")
print("Mixed precision policy:", tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental.global_policy())
else:
tf.keras.mixed_precision.set_global_policy("mixed_float16")
print("Mixed precision policy:", tf.keras.mixed_precision.global_policy())
Gpu 0: PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')
INFO:tensorflow:Mixed precision compatibility check (mixed_float16): OK
Your GPU will likely run quickly with dtype policy mixed_float16 as it has compute capability of at least 7.0. Your GPU: GeForce RTX 3090, compute capability 8.6
Mixed precision policy: <Policy "mixed_float16">
import numpy as np
import time
from tensorflow.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2 import MobileNetV2, preprocess_input
# from tensorflow.keras.applications.mobilenet_v3 import MobileNetV3Small, preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
image_size = 128 # This low-resolution to increase speed
batch_size = 128 # This is the number of images per batches
validation_split = 0.2 # 0.2 -> 20% in validation, 80% in train
training_steps_per_epoch = (len(df) * (1 - validation_split)) // batch_size
validation_steps = (len(df) * validation_split) // batch_size
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input, # This is what modify image color for ImageNet normalization
validation_split=validation_split,
fill_mode = 'nearest',
# rotation_range=30,
# width_shift_range=0.10,
# height_shift_range=0.10,
horizontal_flip=True,
vertical_flip=False,
# shear_range=0.05, # Shear angle in counter-clockwise direction as radians.
zoom_range=[0.7, 1.2], # Float [1-value, 1+value] or [lower, upper] of random zoom.
# brightness_range=[0.5, 1.8] # Takes 100ms! Random ratio [lower, upper] of brightness change.
)
train_generator = datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
subset='training',
dataframe=df,
directory=images_path,
x_col='filename', # name of col in data frame that contains file names
y_col='rating', # name of col with labels
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
class_mode='raw', # 'raw' is for regression, 'categorical' for classification task
)
validation_generator = datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
subset='validation',
dataframe=df,
directory=images_path,
x_col='filename', # name of col in data frame that contains file names
y_col='rating', # name of col with labels
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
class_mode='raw' # 'raw' is for regression, 'categorical' for classification task
)
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
lambda: train_generator,
output_types=(tf.float32, tf.float32), # int32
output_shapes=([None, image_size, image_size, 3], [None]) # None instead of a fixed batch_size for variable batch_size
)
validation_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
lambda: train_generator,
output_types=(tf.float32, tf.float32),
output_shapes=([None, image_size, image_size, 3], [None]) # None instead of a fixed batch_size for variable batch_size
)
Found 4400 validated image filenames.
Found 1100 validated image filenames.
2.2-尝试并优化数据集加载器
现在,您可以通过计算一批图像来尝试数据集加载器。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Display the dataset
train_generator.image_data_generator.preprocessing_function=None # Remove preprocessing
t1 = time.time()
x_batch, y_batch = next(train_generator)
print("Batch generation duration: %.2fs" % float(time.time()-t1))
train_generator.image_data_generator.preprocessing_function = preprocess_input # Enable preprocessing
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), dpi=50)
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=.01, right=1.2, top=0.9, hspace=0.2)
for i, (image, label) in enumerate(zip(x_batch[:32], y_batch[:32])):
plt.subplot(4, 8, i + 1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(image.astype(np.uint8))
plt.title("N°%i | Beauty: %.2f" % (i, label))
Batch generation duration: 0.39s

您可以看到图像已被修改:变形、亮度、对比度。
这就是所谓的 数据增强 。
问题
你能选择更好的增强参数吗?
2.3.定义神经网络
我们将使用 迁移学习 。
迁移学习意味着我们使用 pre-trained model ,但删除了预先培训的 last 图层。
我们添加自定义的最后一层 在上面 预先训练好的模型
然后我们只训练最后一个自定义图层
最后,我们可以对整个模型进行微调
选择好最后一层很重要 架构 。
你可以 hand-tune 此选项,或使用 AutoML (贝叶斯/遗传搜索)。
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation, Dense, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
learning_rate = 0.001
def create_model():
# Create a new neural networks model.
model = Sequential(name='beautyNet')
# Add a pre-trained model, without the last layer
model.add(
MobileNetV2(
include_top=False,
input_shape=(image_size, image_size, 3),
pooling='avg',
weights='imagenet')
)
# 1st layer as Dense with ReLu
model.add(Dense(2, activation='relu'))
# Add a stochastic regularization to avoid overfitting
model.add(Dropout(rate=0.1))
# Last layer as Dense for regression
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
# Do not train the first layer model, as it is already pre-trained
model.layers[0].trainable = False
# Compile the model with an optimizer
model.compile(
loss='mean_squared_error', # 'mean_absolute_error', 'kullback_leibler_divergence'
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
)
return model
model = create_model()
model.summary()
Model: "beautyNet"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
mobilenetv2_1.00_128 (Functi (None, 1280) 2257984
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 8) 10248
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 8) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 1) 9
=================================================================
Total params: 2,268,241
Trainable params: 10,257
Non-trainable params: 2,257,984
_________________________________________________________________
3.神经网络的训练
我们将使用 迁移学习 。
迁移学习意味着我们使用 pre-trained model ,但删除了预先培训的 last 图层。
我们添加自定义的最后一层 在上面 预先训练好的模型
然后我们只训练最后一个自定义图层
最后,我们可以对整个模型进行微调
选择好最后一层很重要 架构 。
你可以 hand-tune 模型体系结构和超参数,或使用 AutoML (贝叶斯/遗传搜索)。
import multiprocessing
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau
n_epochs = 20
initial_epoch = 0
callbacks = [
EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=1e-3,
patience=10,
verbose=1,
),
ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.2,
patience=1,
cooldown=1,
min_lr=0.00001
),
ModelCheckpoint(
filepath='beauty_model_untuned_epoch{epoch:02d}.h5',
monitor='val_loss',
save_best_only=True,
verbose=1
)
]
t_start = time.time()
history = model.fit(
train_dataset,
epochs=n_epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
initial_epoch=initial_epoch,
steps_per_epoch=training_steps_per_epoch,
validation_data=validation_dataset,
validation_steps=validation_steps,
workers=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
)
print('Training duration: %.2fs' % float(time.time()-t_start))
Epoch 1/20
34/34 [==============================] - 35s 750ms/step - loss: 6.7363 - val_loss: 0.7023
Epoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 0.70233, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch01.h5
Epoch 2/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 513ms/step - loss: 1.0485 - val_loss: 0.4525
Epoch 00002: val_loss improved from 0.70233 to 0.45248, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch02.h5
Epoch 3/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 514ms/step - loss: 0.8943 - val_loss: 0.4391
Epoch 00003: val_loss improved from 0.45248 to 0.43915, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch03.h5
Epoch 4/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 514ms/step - loss: 0.8333 - val_loss: 0.3691
Epoch 00004: val_loss improved from 0.43915 to 0.36914, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch04.h5
Epoch 5/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 507ms/step - loss: 0.8411 - val_loss: 0.3352
Epoch 00005: val_loss improved from 0.36914 to 0.33523, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch05.h5
Epoch 6/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 517ms/step - loss: 0.7894 - val_loss: 0.3365
Epoch 00006: val_loss did not improve from 0.33523
Epoch 7/20
34/34 [==============================] - 18s 518ms/step - loss: 0.7231 - val_loss: 0.3016
Epoch 00007: val_loss improved from 0.33523 to 0.30162, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch07.h5
Epoch 8/20
34/34 [==============================] - 18s 520ms/step - loss: 0.8204 - val_loss: 0.3275
Epoch 00008: val_loss did not improve from 0.30162
Epoch 9/20
34/34 [==============================] - 18s 519ms/step - loss: 0.7342 - val_loss: 0.3100
Epoch 00009: val_loss did not improve from 0.30162
Epoch 10/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 509ms/step - loss: 0.7954 - val_loss: 0.3160
Epoch 00010: val_loss did not improve from 0.30162
Epoch 11/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 515ms/step - loss: 0.7924 - val_loss: 0.3228
Epoch 00011: val_loss did not improve from 0.30162
Epoch 12/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 514ms/step - loss: 0.7879 - val_loss: 0.2954
Epoch 00012: val_loss improved from 0.30162 to 0.29541, saving model to beauty_model_untuned_epoch12.h5
Epoch 13/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 513ms/step - loss: 0.8064 - val_loss: 0.3118
Epoch 00013: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 14/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 517ms/step - loss: 0.7649 - val_loss: 0.3405
Epoch 00014: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 15/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 507ms/step - loss: 0.7561 - val_loss: 0.3332
Epoch 00015: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 16/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 513ms/step - loss: 0.7468 - val_loss: 0.3339
Epoch 00016: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 17/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 517ms/step - loss: 0.7216 - val_loss: 0.3088
Epoch 00017: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 18/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 516ms/step - loss: 0.7925 - val_loss: 0.3528
Epoch 00018: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 19/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 516ms/step - loss: 0.7778 - val_loss: 0.3010
Epoch 00019: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Epoch 20/20
34/34 [==============================] - 17s 507ms/step - loss: 0.8443 - val_loss: 0.3242
Epoch 00020: val_loss did not improve from 0.29541
Training duration: 366.17s
# Evaluate (WARNING: you should use normaly unseen data)
test_loss = model.evaluate(train_generator, verbose=1)
print('Test loss: {:0.2f}'.format(test_loss))
35/35 [==============================] - 14s 396ms/step - loss: 0.2630
Test loss: 0.26
现在可以保存最终模型。
4.保存/加载训练好的模型
# Load a model from local checkpoints
epoch_id = 20
model_loaded = tf.keras.models.load_model('beauty_model_untuned_epoch%d.h5' % epoch_id)
# Save the final model
models_path = os.path.relpath("models")
assert os.path.exists(models_path)
# Save the final model
model.save(os.path.join(models_path, "beauty_model_untuned")) # creates a HDF5 file 'final_beauty_model.h5'
INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: models/beauty_model_untuned/assets
import os
import tensorflow as tf
# Load the final model
models_path = os.path.relpath("models")
model_loaded = tf.keras.models.load_model(os.path.join(models_path, "beauty_model_untuned"))
5.使用您的型号
# Predict on a new image
from io import BytesIO
import urllib
from PIL import Image
import IPython
import ipywidgets as widgets
from ipywidgets import interact, interact_manual
@interact
def predict_from_url(URL='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c0/Nicolas_Cage_Deauville_2013.jpg'):
with urllib.request.urlopen(URL) as url: # Download an image from an URL in RAM memory
img_size = 128
img = Image.open(BytesIO(url.read())).convert('RGB')
img = img.resize((img_size, img_size), Image.BILINEAR)
# Preprocess image
img_array = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.img_to_array(img) # Convert PIL image to np.array
img_batch = np.expand_dims(img_array, axis=0) # Add a batch dim
img_preprocessed = preprocess_input(img_batch) # Normalize
y_predicted = model.predict(img_preprocessed) # Predict with your model
IPython.display.display(img) # Display the image
print("Predicted beauty score:", y_predicted.flatten())
interactive(children=(Text(value='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c0/Nicolas_Cage_Deauville_2…
6.在简单的Web应用程序中本地运行您的模型
我们可以使用Python包将Kera模型转换为TensorFlow.js格式 tensorflowjs 。
阅读有关以下内容的更多信息 converting Keras models to tfjs 。
live_demo 文件夹。!$HOME/miniconda3/bin/pip3 install -q tensorflowjs
import tensorflowjs as tfjs
tf.keras.backend.clear_session() # Clean up variable names before exporting
# Convert model
model = tf.keras.models.load_model(os.path.join(models_path, "beauty_model_untuned"))
tfjs.converters.save_keras_model(model, "live_demo/model/",
quantization_dtype_map={"uint8": "*"})
# Write an index.html file
with open('live_demo/index.html', 'w') as f:
f.write('''
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs@latest"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow-models/mobilenet"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/semantic-ui@2.4.2/dist/semantic.min.css" />
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/semantic-ui@2.4.2/dist/semantic.min.js"></script>
<style type="text/css">
.app_container {
width: 500px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;}
.ui .card {width: 90vw !important;}
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.button_container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: space-around;
margin: 15px;
}
#output {
font-size: 2em !important;
}
body {
background-color: linen;
}
.stream {
display: flex;
overflow: hidden;
}
.card {
min-width: 320px;
}
</style>
<title>BeautyNet</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ui one column centered grid" style="margin: 20px 0">
<div class="app_container">
<h1>BeautyNet</h1>
<div class="ui card">
<div class="stream">
<video width="100%" height="100%" autoplay playsinline muted id="webcam"></video>
</div>
<div class="content" id="content">
<div class="button_container">
<button class="ui primary button" id="capture">Save</button>
<button class="ui button" id="stop">Stop</button>
</div>
<div class="ui sub header" id="output"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const modelPath = './model/model.json';
const imageSize = 128;
const predictionInterval = 500;
var webcamElement = document.getElementById("webcam");
var output = document.getElementById("output");
var captureButton = document.getElementById("capture");
var stopButton = document.getElementById("stop");
var stopped = false;
let model = null;
async function setupWebcam() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const navigatorAny = navigator;
navigator.getUserMedia = navigator.getUserMedia ||
navigatorAny.webkitGetUserMedia || navigatorAny.mozGetUserMedia ||
navigatorAny.msGetUserMedia;
if (navigator.getUserMedia) {
navigator.getUserMedia({
video: true
},
stream => {
webcamElement.srcObject = stream;
webcamElement.addEventListener("loadeddata", resolve, false);
},
error => reject());
} else {
reject();
}
});
}
async function predictImage() {
const img = await getWebcamImage();
let result = tf.tidy(() => {
const input = img.reshape([1, imageSize, imageSize, 3]);
return model.predict(input);
});
img.dispose(); // Dispose the tensor to release the memory.
let prediction = await result.data();
result.dispose(); // Dispose the tensor to release the memory.
output.innerText = `score: ${(prediction[0]).toFixed(1)}\n`;
}
async function getWebcamImage() {
const img = (await webcam.capture()).toFloat();
const normalized = img.div(127).sub(1);
return normalized;
}
let webcam = null;
let predictInterval;
(async () => {
// Load the model
tf.loadLayersModel(modelPath)
.then(response => {
model = response;
console.log("Model successfully loaded!");
})
.catch(error => output.textContent = "ERROR :" + error.message +
" Fix: put your model in a ./model/ folder")
await setupWebcam();
webcam = await tf.data.webcam(webcamElement, {
resizeWidth: imageSize,
resizeHeight: imageSize,
});
// Setup prediction every 500 ms
predictInterval = setInterval(predictImage, predictionInterval);
})();
captureButton.addEventListener("click", async function () {
const img = await getWebcamImage();
let result = tf.tidy(() => {
const input = img.reshape([1, imageSize, imageSize, 3]);
return model.predict(input);
});
img.dispose(); // Dispose the tensor to release the memory.
let prediction = await result.data();
result.dispose(); // Dispose the tensor to release the memory.
console.log("score", prediction[0]);
output.innerText = `score: ${(prediction[0]).toFixed(1)}\n`;
const div = document.createElement('div');
div.innerText = `score: ${(prediction[0]).toFixed(3)}\n`;
div.className = "description";
document.getElementById("content").appendChild(div);
});
stopButton.addEventListener("click", function () {
if (stopped == false) {
clearInterval(predictInterval);
stream = webcamElement.srcObject;
tracks = stream.getTracks();
tracks.forEach(function (track) {
track.stop();
});
stopButton.innerText = "Restart";
stopped = true;
console.log("Stop prediction");
} else {
(async () => {
await setupWebcam();
webcam = await tf.data.webcam(webcamElement, {
resizeWidth: imageSize,
resizeHeight: imageSize,
});
predictInterval = setInterval(predictImage, predictionInterval);
stopButton.innerText = "Stop";
stopped = false;
console.log("Prediction restarted");
})();
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
''')
!zip -r live_demo.zip live_demo
from IPython.display import FileLink
FileLink("live_demo.zip")
updating: live_demo/ (stored 0%)
updating: live_demo/index.html (deflated 63%)
updating: live_demo/model/ (stored 0%)
updating: live_demo/model/model.json (deflated 92%)
updating: live_demo/model/group1-shard1of1.bin (deflated 19%)
7.改善意见
!$HOME/miniconda3/bin/pip3 install -U tensorflow-addons
Requirement already up-to-date: tensorflow-addons in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (0.12.1)
Requirement already satisfied, skipping upgrade: typeguard>=2.7 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from tensorflow-addons) (2.7.1)
import datetime
import psutil
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, TensorBoard
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import tensorflow_addons as tfa
# Cache dataset to RAM (WARNING: could OOM)
train_dataset = train_dataset.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
validation_dataset = validation_dataset.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
# Trace memory usage
class MemoryCallback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
bts = process.memory_info().rss # in bytes
# vbts = psutil.virtual_memory().used # in bytes
print(' RAM:', (bts / 1024) // 1024, 'MB')
process = psutil.Process(os.getpid())
# More epochs
n_epochs = 20
# Change learning rate over time
cyclic_rate_schelduler = tfa.optimizers.cyclical_learning_rate.Triangular2CyclicalLearningRate(
initial_learning_rate=1e-4,
maximal_learning_rate=0.005,
# step_size=4 * training_steps_per_epoch,
step_size=training_steps_per_epoch // 2,
# scale_fn=lambda x: 1.,
scale_mode='cycle',
name='Triangular2CyclicalScheduler'
)
# Better optimizer
radam = tfa.optimizers.RectifiedAdam(learning_rate=cyclic_rate_schelduler)
ranger = tfa.optimizers.Lookahead(radam)
# Better loss
model.compile(optimizer=ranger, loss='mean_absolute_error') # 'mean_absolute_percentage_error', 'mean_squared_error', 'kullback_leibler_divergence'
# Train with all these new things
t_start = time.time()
history = model.fit(
train_dataset,
epochs=n_epochs,
callbacks=[*callbacks, MemoryCallback()],
initial_epoch=initial_epoch,
steps_per_epoch=training_steps_per_epoch,
validation_data=validation_dataset,
validation_steps=validation_steps,
workers=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
)
print("Training duration: %.2fs" % float(time.time()-t_start))
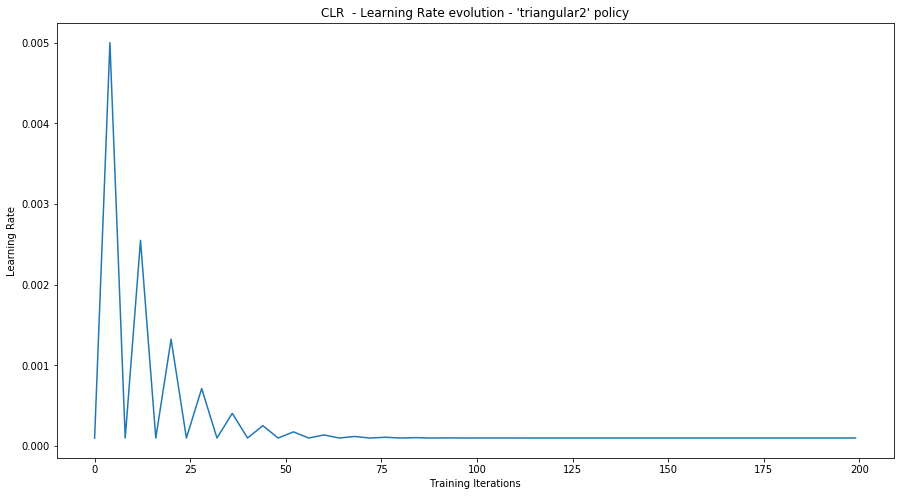
# View the learning rate evolution during training
plt.figure(1, figsize=(15, 8))
plt.xlabel("Training Iterations")
plt.ylabel("Learning Rate")
plt.title("CLR - Learning Rate evolution - 'triangular2' policy")
plt.plot(range(0, n_epochs), [cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in range(0, n_epochs)])
plt.show()
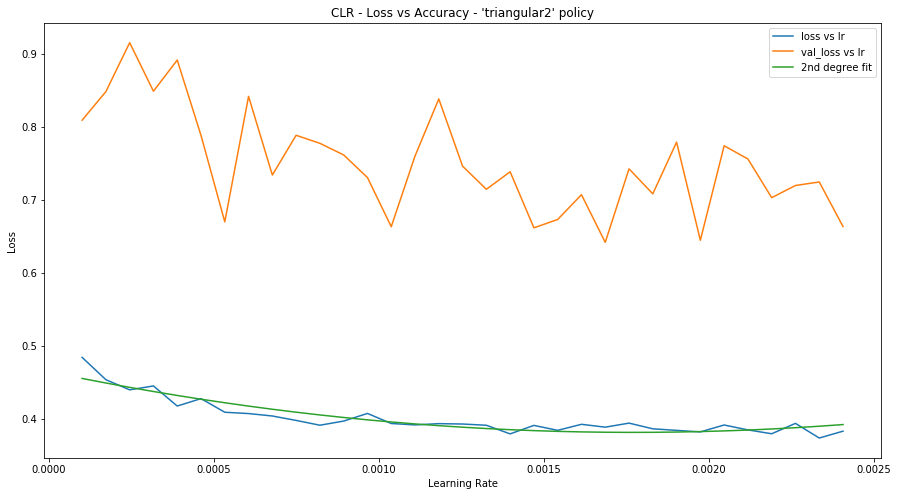
# View the learning rate evolution during training regarding the loss
plt.figure(1, figsize=(15, 8))
plt.xlabel("Learning Rate")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.title("CLR - Loss vs Accuracy - 'triangular2' policy")
plt.plot([cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in model.history.epoch], model.history.history["loss"])
plt.plot([cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in model.history.epoch], model.history.history["val_loss"])
z = np.polyfit([cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in model.history.epoch], model.history.history["loss"], 2)
p = np.poly1d(z)
plt.plot([cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in model.history.epoch], p([cyclic_rate_schelduler(i) for i in model.history.epoch]))
plt.legend(["loss vs lr", "val_loss vs lr", "2nd degree fit"])
plt.show()
对数据加载器进行基准测试
# Benchmark your dataloader
import time
def benchmark(dataset, num_epochs=1, num_iter=100):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for epoch_num in range(num_epochs):
for iter_num, sample in enumerate(dataset):
if iter_num > 100:
print("break")
break
pass # Performing a training step
tf.print("Dataloader time per iter:", (time.perf_counter() - start_time) / (num_epochs * iter_num) )
benchmark(train_dataset)